前言
http servernet/httpnet/httpHTTP ServerHTTP 服务处理流程
ClientServer典型的 HTTP 服务的处理流程如下图所示:
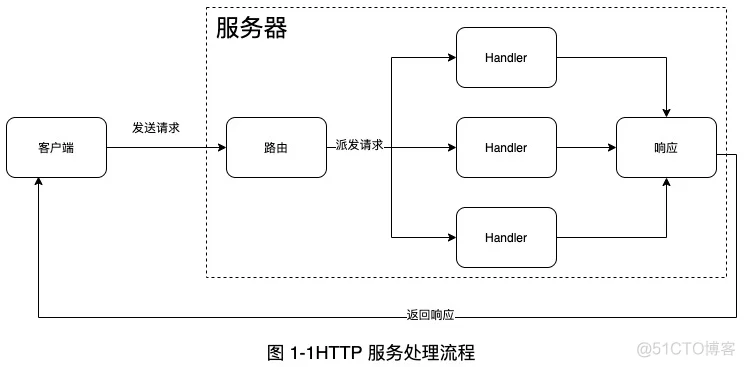
routerMultiplexehandlerhttp server"Hello World"http serverpackage main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func HelloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello World")
}
func main () {
http.HandleFunc("/", HelloHandler)
http.ListenAndServe(":8000", nil)
}
localhost:8000Hello Worldhttp.HandleFunc/HelloHandlerhttp.ListenAndServehandlerhttp.ListenAndServe(":8000", nil) 
我们再看一下另外一种常见的实现方式:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
type HelloHandlerStruct struct {
content string
}
func (handler *HelloHandlerStruct) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, handler.content)
}
func main() {
http.Handle("/", &HelloHandlerStruct{content: "Hello World"})
http.ListenAndServe(":8000", nil)
}
http.HandleFunchttp.Handlehttp.Handlerhttphttp路由注册
http.HandleFunchttp.Handlehttp.HandleFuncfunc(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Requests)http.Handlehttp.Handlerhttp.HandleFunchttp.Handlefunc HandleFunc(pattern string, handler func(ResponseWriter, *Request)) {
DefaultServeMux.HandleFunc(pattern, handler)
}
// HandleFunc registers the handler function for the given pattern.
func (mux *ServeMux) HandleFunc(pattern string, handler func(ResponseWriter, *Request)) {
if handler == nil {
panic("http: nil handler")
}
mux.Handle(pattern, HandlerFunc(handler))
}
func Handle(pattern string, handler Handler) {
DefaultServeMux.Handle(pattern, handler)
}DefaultServeMuxHandleServeMuxHandlerHandler
http.Handlernet/httptype Handler interface {
ServeHTTP(ResponseWriter, *Request)
}HandlerServeHTTPServeHTTPHandlerhttpHandlerHandlerServeHTTPRequestResponseWriterHandleFunc*ServeMux.HandleFuncfunc (mux *ServeMux) HandleFunc(pattern string, handler func(ResponseWriter, *Request)) {
if handler == nil {
panic("http: nil handler")
}
mux.Handle(pattern, HandlerFunc(handler))
}注意一下这行代码:
mux.Handle(pattern, HandlerFunc(handler))
HandlerFunchandlerhttp.HandlerFunchttp.HandleFunchttp.HandlerFuncHandlerFunctype HandlerFunc func(ResponseWriter, *Request)
// ServeHTTP calls f(w, r).
func (f HandlerFunc) ServeHTTP(w ResponseWriter, r *Request) {
f(w, r)
}
HandlerFuncfunc(ResponseWriter, *Request)ServeHTTPServeHTTPHandlerfunc(ResponseWriter, *Request)HandlerServeHTTPServeMux (服务复用器)
http.HandleFunchttp.HandleServerMuxHandleServeMuxtype ServeMux struct {
mu sync.RWMutex
m map[string]muxEntry
es []muxEntry // slice of entries sorted from longest to shortest.
hosts bool // whether any patterns contain hostnames
}
type muxEntry struct {
h Handler
pattern string
}ServeMuxmmapkeyvaluemuxEntrymuxEntryhandlermmapessliceServeMuxServeHTTPfunc (mux *ServeMux) ServeHTTP(w ResponseWriter, r *Request) {
if r.RequestURI == "*" {
if r.ProtoAtLeast(1, 1) {
w.Header().Set("Connection", "close")
}
w.WriteHeader(StatusBadRequest)
return
}
h, _ := mux.Handler(r)
h.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}ServeMuxHandlerServeMuxServeHTTPrequestresponseHandlerrequestreponse注册路由
HandlerServeMuxDefaultServeMux.Handle(pattern, handler)
DefaultServeMuxServeMuxServeMuxDefaultServeMuxServeMuxHandlefunc (mux *ServeMux) Handle(pattern string, handler Handler) {
mux.mu.Lock()
defer mux.mu.Unlock()
if pattern == "" {
panic("http: invalid pattern")
}
if handler == nil {
panic("http: nil handler")
}
// 路由已经注册过处理器函数,直接panic
if _, exist := mux.m[pattern]; exist {
panic("http: multiple registrations for " + pattern)
}
if mux.m == nil {
mux.m = make(map[string]muxEntry)
}
// 用路由的pattern和处理函数创建 muxEntry 对象
e := muxEntry{h: handler, pattern: pattern}
// 向ServeMux的m 字段增加新的路由匹配规则
mux.m[pattern] = e
if pattern[len(pattern)-1] == '/' {
// 如果路由patterm以'/'结尾,则将对应的muxEntry对象加入到[]muxEntry中,路由长的位于切片的前面
mux.es = appendSorted(mux.es, e)
}
if pattern[0] != '/' {
mux.hosts = true
}
}HandleServeMuxmap[string]muxEntry'/'muxEntry[]muxEntry自定义 ServeMux
http.NewServeMux()ServeMuxDefaultServeMuxHello Worldhttp serverServeMuxListenAndServe()/welcomeHandleHandleFuncpackage main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
type WelcomeHandlerStruct struct {
}
func HelloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello World")
}
func (*WelcomeHandlerStruct) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Welcome")
}
func main () {
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/", HelloHandler)
mux.Handle("/welcome", &WelcomeHandlerStruct{})
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
}
ServeMuxServeHTTPmuxHandlerListenAndServe()ServeMuxServerServeMuxDefaultServeMuxmux启动服务
http.ListenAndServefunc ListenAndServe(addr string, handler Handler) error {
server := &Server{Addr: addr, Handler: handler}
return server.ListenAndServe()
}
func (srv *Server) ListenAndServe() error {
if srv.shuttingDown() {
return ErrServerClosed
}
addr := srv.Addr
if addr == "" {
addr = ":http"
}
ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", addr)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return srv.Serve(tcpKeepAliveListener{ln.(*net.TCPListener)})
}ServerhandlerhandlerServeMuxServerListenAndServe()Server(服务器对象)
Servertype Server struct {
Addr string // TCP address to listen on, ":http" if empty
Handler Handler // handler to invoke, http.DefaultServeMux if nil
TLSConfig *tls.Config
ReadTimeout time.Duration
ReadHeaderTimeout time.Duration
WriteTimeout time.Duration
IdleTimeout time.Duration
MaxHeaderBytes int
TLSNextProto map[string]func(*Server, *tls.Conn, Handler)
ConnState func(net.Conn, ConnState)
ErrorLog *log.Logger
disableKeepAlives int32 // accessed atomically.
inShutdown int32
nextProtoOnce sync.Once
nextProtoErr error
mu sync.Mutex
listeners map[*net.Listener]struct{}
activeConn map[*conn]struct{}// 活跃连接
doneChan chan struct{}
onShutdown []func()
}ServerListenAndServeAddrListenServegoroutinegoroutineHandlerfunc (srv *Server) Serve(l net.Listener) error {
......
baseCtx := context.Background() // base is always background, per Issue 16220
ctx := context.WithValue(baseCtx, ServerContextKey, srv)
for {
rw, e := l.Accept()// 接收 listener 过来的网络连接请求
......
c := srv.newConn(rw)
c.setState(c.rwc, StateNew) // 将连接放在 Server.activeConn这个 map 中
go c.serve(ctx)// 创建协程处理请求
}
}ServeListenerAccept()ServernewConn()StateNewgoroutine处理连接
goroutineconnserve()func (c *conn) serve(ctx context.Context) {
...
for {
w, err := c.readRequest(ctx)
if c.r.remain != c.server.initialReadLimitSize() {
// If we read any bytes off the wire, we're active.
c.setState(c.rwc, StateActive)
}
...
serverHandler{c.server}.ServeHTTP(w, w.req)
w.cancelCtx()
if c.hijacked() {
return
}
w.finishRequest()
if !w.shouldReuseConnection() {
if w.requestBodyLimitHit || w.closedRequestBodyEarly() {
c.closeWriteAndWait()
}
return
}
c.setState(c.rwc, StateIdle)
c.curReq.Store((*response)(nil))
...
}
}serve()readRequest()serverHandler{c.server}.ServeHTTP(w, w.req)serverHandlerServertype serverHandler struct {
srv *Server
}
func (sh serverHandler) ServeHTTP(rw ResponseWriter, req *Request) {
handler := sh.srv.Handler
if handler == nil {
handler = DefaultServeMux
}
if req.RequestURI == "*" && req.Method == "OPTIONS" {
handler = globalOptionsHandler{}
}
handler.ServeHTTP(rw, req)
}serverHandlerServeHTTP()sh.srv.Handlerhttp.ListenAndServe()HandlerServeMuxHandlernilDefaultServeMuxServeMuxServeHTTP()handlerfunc (mux *ServeMux) ServeHTTP(w ResponseWriter, r *Request) {
if r.RequestURI == "*" {
if r.ProtoAtLeast(1, 1) {
w.Header().Set("Connection", "close")
}
w.WriteHeader(StatusBadRequest)
return
}
h, _ := mux.Handler(r)
h.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
func (mux *ServeMux) Handler(r *Request) (h Handler, pattern string) {
if r.Method == "CONNECT" {
if u, ok := mux.redirectToPathSlash(r.URL.Host, r.URL.Path, r.URL); ok {
return RedirectHandler(u.String(), StatusMovedPermanently), u.Path
}
return mux.handler(r.Host, r.URL.Path)
}
// All other requests have any port stripped and path cleaned
// before passing to mux.handler.
host := stripHostPort(r.Host)
path := cleanPath(r.URL.Path)
// If the given path is /tree and its handler is not registered,
// redirect for /tree/.
if u, ok := mux.redirectToPathSlash(host, path, r.URL); ok {
return RedirectHandler(u.String(), StatusMovedPermanently), u.Path
}
if path != r.URL.Path {
_, pattern = mux.handler(host, path)
url := *r.URL
url.Path = path
return RedirectHandler(url.String(), StatusMovedPermanently), pattern
}
return mux.handler(host, r.URL.Path)
}
// handler is the main implementation of Handler.
// The path is known to be in canonical form, except for CONNECT methods.
func (mux *ServeMux) handler(host, path string) (h Handler, pattern string) {
mux.mu.RLock()
defer mux.mu.RUnlock()
// Host-specific pattern takes precedence over generic ones
if mux.hosts {
h, pattern = mux.match(host + path)
}
if h == nil {
h, pattern = mux.match(path)
}
if h == nil {
h, pattern
