在阅读此文前,需要先了解一下三色标记法以及混合写屏障这些概念。
源文件 版本 1.16.2。
基本知识在介绍GC之前,我们需要认识有些与GC相关的基本信息,如GC的状态、模式、统计信息等。
三种状态
共有三种状态
const ( _GCoff = iota // GC not running; sweeping in background, write barrier disabled _GCmark // GC marking roots and workbufs: allocate black, write barrier ENABLED _GCmarktermination // GC mark termination: allocate black, P's help GC, write barrier ENABLED )
_GCoff_GCmark_GCmarktermination三种模式
支持三种模式:
const (
gcBackgroundMode gcMode = iota // concurrent GC and sweep
gcForceMode // stop-the-world GC now, concurrent sweep
gcForceBlockMode // stop-the-world GC now and STW sweep (forced by user)
)
gcBackgroundModegcForceModegcForceBlockMode针对每种模式,在标记阶段会采用不同的标记策略,详细见
全局变量
gcControllerworkgcControllerworkgcphase_GCoff_GCmark_GCmarkterminationworldsemamSTWgcsemagcBlackenEnabledgcpercent100runtime.gcBgMarkWorkerPool *gcBgMarkWorkerNodegcBgMarkWorker()runtime.gcBgMarkWorkerCountgcBgMarkWorkergcBgMarkStartWorkers()memstats.gc_trigger下面主要介绍下 gcController 和 work 这两个数据结构
gcController
数据结构
var gcController gcControllerState
type gcControllerState struct {
scanWork int64
bgScanCredit int64
assistTime int64
dedicatedMarkTime int64
fractionalMarkTime int64
idleMarkTime int64
markStartTime int64
assistWorkPerByte uint64
assistBytesPerWork uint64
dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded int64
fractionalUtilizationGoal float64
_ cpu.CacheLinePad
}
gcController字段介绍
scanWorkbgScanCreditassistTimededicatedMarkTimefractionalMarkTimeidleMarkTimemarkStartTimeassistWorkPerByteassistBytesPerWorkassistWorkPerBytededicatedMarkWorkersNeededfractionalUtilizationGoaldedicatedMarkWorkersNeededfractionalUtilizationGoalwork
数据结构
var work struct {
full lfstack // lock-free list of full blocks workbuf
empty lfstack // lock-free list of empty blocks workbuf
pad0 cpu.CacheLinePad // prevents false-sharing between full/empty and nproc/nwait
wbufSpans struct {
lock mutex
// free is a list of spans dedicated to workbufs, but
// that don't currently contain any workbufs.
free mSpanList
// busy is a list of all spans containing workbufs on
// one of the workbuf lists.
busy mSpanList
}
// Restore 64-bit alignment on 32-bit.
_ uint32
// 周期内已标记的字节大小,包含多种对象,见源码注释。由于标记过程中存在竞争,所以这个数字不是太准确,但也很接近
bytesMarked uint64
markrootNext uint32 // next markroot job
markrootJobs uint32 // number of markroot jobs
nproc uint32
tstart int64
nwait uint32
// 统计变量,在 gcMarkRootPrepare() 函数中使用
nFlushCacheRoots int
nDataRoots, nBSSRoots, nSpanRoots, nStackRoots int
startSema uint32
// 保护从mark 到 mark termination 的转换
markDoneSema uint32
bgMarkReady note // signal background mark worker has started
bgMarkDone uint32 // cas to 1 when at a background mark completion point
// GC的工作模式,上面已介绍过
mode gcMode
// 当前GC是否为用户强制执行调用
userForced bool
// 从程序开始时,到gc的时间,只有当debug.gctrace>0有效
totaltime int64
// 在gc开始时,值为 memstats.heap_live
initialHeapLive uint64
// 由于没有足够的信用来窃取或工作来完成而被阻止的协助队列
assistQueue struct {
lock mutex
q gQueue
}
// gc 从 mark terminaton 转为 sweep时,要唤醒的goroutines
sweepWaiters struct {
lock mutex
list gList
}
// 已完成的gc次数
cycles uint32
// 周期内的统计信息
stwprocs, maxprocs int32
tSweepTerm, tMark, tMarkTerm, tEnd int64 // nanotime() of phase start
pauseNS int64 // total STW time this cycle
pauseStart int64 // nanotime() of last STW
// debug.gctrace 使用
heap0, heap1, heap2, heapGoal uint64
}
work提供全局工作队列缓存,并记录栈、数据段等需要扫描的root节点的相关信息;还会记录当前是第几个GC cycle,当前GC cycle已经标记了多少字节,已经STW了多长时间,以及控制GC向下一阶段过度的信息等等。
GC流程runtime.GC()func GC() {
// 从work全局变量里读取当前已GC的次数
n := atomic.Load(&work.cycles)
// 确保第n次GC "清扫终止"、"标记阶段" 和 ”标记终止“,如果已标记完成会立即返回
gcWaitOnMark(n)
// 触发第n+1次GC,其逻辑中的首要工作就是对上一轮n次GC的清扫终止操作,即第一阶段
// 也就是说gcStart() 包含前两个阶段
gcStart(gcTrigger{kind: gcTriggerCycle, n: n + 1})
// Wait for mark termination N+1 to complete.
// 第三阶段:同上
gcWaitOnMark(n + 1)
// 第四阶段:清扫
for atomic.Load(&work.cycles) == n+1 && sweepone() != ^uintptr(0) {
sweep.nbgsweep++
Gosched()
}
for atomic.Load(&work.cycles) == n+1 && atomic.Load(&mheap_.sweepers) != 0 {
Gosched()
}
mp := acquirem()
cycle := atomic.Load(&work.cycles)
if cycle == n+1 || (gcphase == _GCmark && cycle == n+2) {
mProf_PostSweep()
}
releasem(mp)
}
gcWaitOnMark()清扫终止标记标记终止gcStart()gcWaitOnWait()清扫终止标记标记终止sweepone()Gosched()mProf_PostSweep()这里调用的函数为 gcWaitOnMark()
// gcWaitOnMark blocks until GC finishes the Nth mark phase. If GC has
// already completed this mark phase, it returns immediately.
func gcWaitOnMark(n uint32) {
for {
// Disable phase transitions.
lock(&work.sweepWaiters.lock)
nMarks := atomic.Load(&work.cycles)
if gcphase != _GCmark {
// We've already completed this cycle's mark.
nMarks++
}
// 标记完成,直接返回
if nMarks > n {
// We're done.
unlock(&work.sweepWaiters.lock)
return
}
// Wait until sweep termination, mark, and mark
// termination of cycle N complete.
work.sweepWaiters.list.push(getg())
goparkunlock(&work.sweepWaiters.lock, waitReasonWaitForGCCycle, traceEvGoBlock, 1)
}
}
清扫终止“标记标记终止gcStart()func gcStart(trigger gcTrigger) {
// 判断当前G是否可抢占, 不可抢占时不触发GC
mp := acquirem()
if gp := getg(); gp == mp.g0 || mp.locks > 1 || mp.preemptoff != "" {
releasem(mp)
return
}
releasem(mp)
mp = nil
// 并发清除上一轮未清除的span【GC第一阶段:GC 清理终止】
for trigger.test() && sweepone() != ^uintptr(0) {
sweep.nbgsweep++
}
// 加锁,重新检查是否满足触发GC的条件,不满足的话,解锁并直接返回
semacquire(&work.startSema)
if !trigger.test() {
semrelease(&work.startSema)
return
}
// 记录是否为用户强制GC(是否由用户调用 runtime.GC 函数触发)
work.userForced = trigger.kind == gcTriggerCycle
// 如果为 debug.gcstoptheword 调试模式下,则相应的升级为GC模式(共三种模式)
mode := gcBackgroundMode
if debug.gcstoptheworld == 1 {
mode = gcForceMode // 只在清扫阶段支持并发
} else if debug.gcstoptheworld == 2 {
mode = gcForceBlockMode // GC全程需要STW
}
// Ok, we're doing it! Stop everybody else
// 加锁,两个全局锁
semacquire(&gcsema) // 持有此锁的m将拥有stop the world 的权限,直到当前gc完成。同时有防止GOMAXPROCES并发修改
semacquire(&worldsema) // 持有此锁的m将拥有stop the world的权限
if trace.enabled {
traceGCStart()
}
// Check that all Ps have finished deferred mcache flushes.
for _, p := range allp {
if fg := atomic.Load(&p.mcache.flushGen); fg != mheap_.sweepgen {
println("runtime: p", p.id, "flushGen", fg, "!= sweepgen", mheap_.sweepgen)
throw("p mcache not flushed")
}
}
// 启用后台 标记工作 线程
gcBgMarkStartWorkers()
// 在系统栈上运行gcResetMarkState()函数,实现在标记(concurrent或STW)之前重置全局状态,并重置所有Gs的栈扫描状态。
systemstack(gcResetMarkState)
// 初始化cpu数量及其它参数值
work.stwprocs, work.maxprocs = gomaxprocs, gomaxprocs
if work.stwprocs > ncpu {
// This is used to compute CPU time of the STW phases,
// so it can't be more than ncpu, even if GOMAXPROCS is.
work.stwprocs = ncpu
}
work.heap0 = atomic.Load64(&memstats.heap_live) // 首次堆大小
work.pauseNS = 0 // stw 的累计时间
work.mode = mode // 模式
// GC开始时间
now := nanotime()
work.tSweepTerm = now
work.pauseStart = now
if trace.enabled {
traceGCSTWStart(1)
}
// 停止所有运行中的G, 并禁止它们运行
systemstack(stopTheWorldWithSema)
// !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
// 从现在开始,世界已停止(STW)...
// !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
// 在开始并发扫描之前,在系统栈上调用finishsweep_m()函数,确定已完成上一轮的清扫工作【确保第一阶段“清扫终止”全部完成并结束】
systemstack(func() {
finishsweep_m()
})
// 在开始本轮GC之前,进行清理工作(清理对象有 sync.Pools 、central sudog cache 和 central defer pools)
clearpools()
// GC次数更新+1
work.cycles++
// 本轮gc控制器状态初始化
gcController.startCycle()
// 下次堆触发GC的大小
work.heapGoal = memstats.next_gc
// In STW mode, disable scheduling of user Gs. This may also
// disable scheduling of this goroutine, so it may block as
// soon as we start the world again.
if mode != gcBackgroundMode {
schedEnableUser(false)
}
// 进入并发标记阶段并启用写屏障。修改GC状态为 _GCmark
setGCPhase(_GCmark)
// 做标记准备工作(重置后台标记任务的计数)
gcBgMarkPrepare() // Must happen before assist enable.
// 计算扫描根对象的任务数量
gcMarkRootPrepare()
// 标记所有活跃小对象
gcMarkTinyAllocs()
// 设置gcBlackenEnabled=1,可以辅助助手和标记线程允许置黑对象
// 此时所有的P都启用了写屏障,从而保障了没有白色到黑色的情况(三色标记法中的写屏障保障了GC期间,所有新对象将默认为黑色)
atomic.Store(&gcBlackenEnabled, 1)
// 设置 gc控制器本轮标记开始时间
gcController.markStartTime = now
// In STW mode, we could block the instant systemstack
// returns, so make sure we're not preemptible.
// 在STW模式下获取当前G所在的m,这样就可以防止系统栈返回,以此确保无法抢占
mp = acquirem()
// 在系统栈上并发标记
systemstack(func() {
// 重新启动世界,并更新相关信息
now = startTheWorldWithSema(trace.enabled)
work.pauseNS += now - work.pauseStart // 对gc的时间进行累计
work.tMark = now //
memstats.gcPauseDist.record(now - work.pauseStart)
})
// !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
// 世界已重新启动...
// !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
// 解锁。在stw模式下,要在Gosched()调用前释放worldsema锁,稍候需要重新获取它,若不释放会导致在g转为可运动状态时死锁
semrelease(&worldsema)
releasem(mp)
// 确保在stw模式下,一直处于阻塞状态而不是返回用户代码
if mode != gcBackgroundMode {
Gosched()
}
semrelease(&work.startSema)
}
整个流程
wordstopTheWorldWithSema_GCMark<16K16-32K>32KstartTheWorldWithSema扫描终止gcsemaworldsema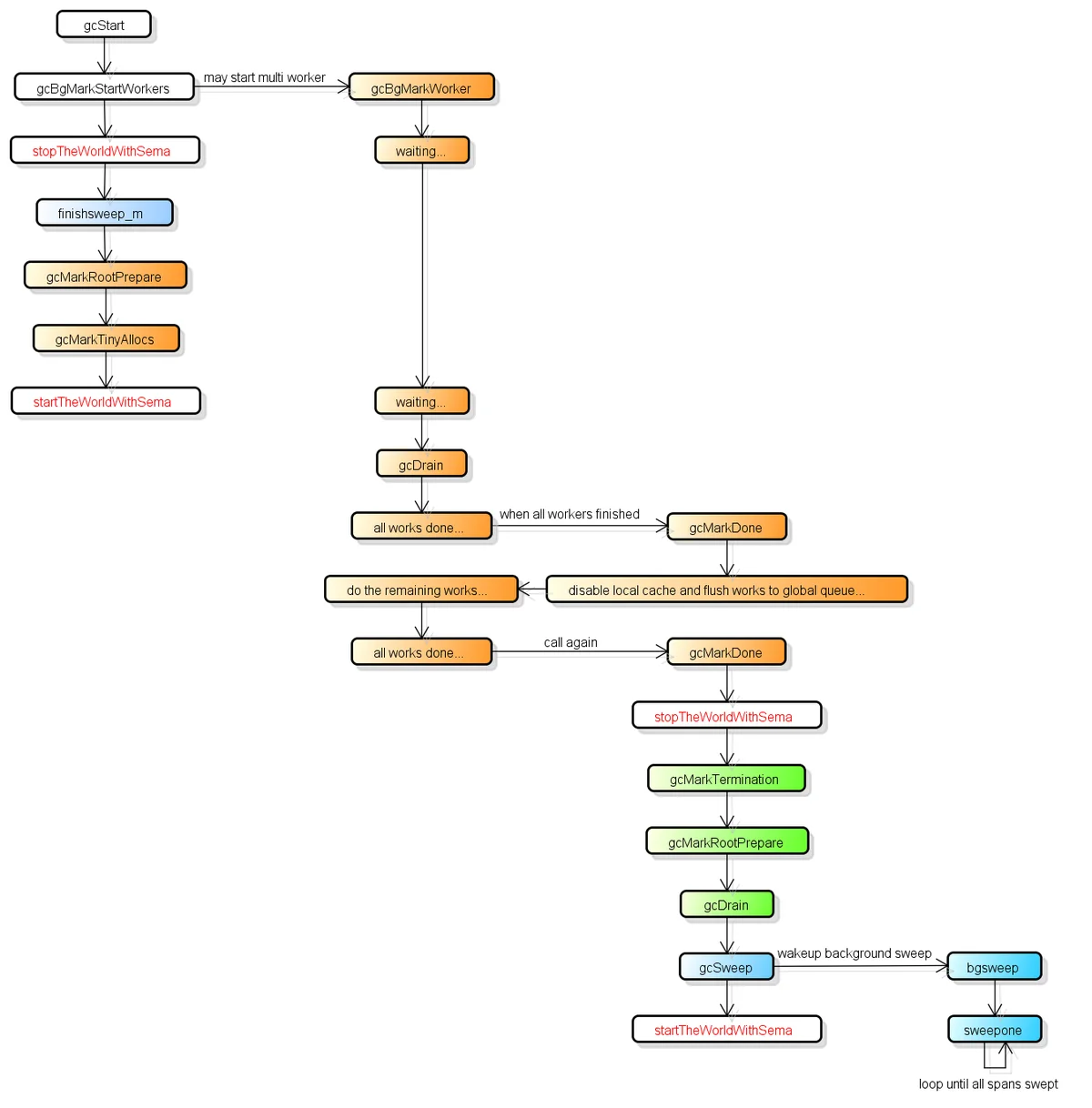
启用后台标记工作线程 gcBgMarkStartWorkers
gcBgMarkWorker goroutinegcController.findRunnableGCWorkerruntime.schedulefunc gcBgMarkStartWorkers() {
// 为每个P启动一个 gcBgMarkWorker() goroutine
for gcBgMarkWorkerCount < gomaxprocs {
go gcBgMarkWorker()
// 启动后等待该任务通知信号量bgMarkReady再继续
notetsleepg(&work.bgMarkReady, -1)
noteclear(&work.bgMarkReady)
// The worker is now guaranteed to be added to the pool before
// its P's next findRunnableGCWorker.
gcBgMarkWorkerCount++
}
}
worldsemaGOMAXPROCSgcBgMarkWorker goroutine// 返回指定P中的后台标记工作线程 g(满足 gcBlackenEnabled!=0 条件)
func (c *gcControllerState) findRunnableGCWorker(_p_ *p) *g {
if gcBlackenEnabled == 0 {
throw("gcControllerState.findRunnable: blackening not enabled")
}
// 检查当前P是否可以执行标记工作
if !gcMarkWorkAvailable(_p_) {
return nil
}
// 从 gcBgMarkWorkerPool 列表中获取一个标记线程 goroutine
node := (*gcBgMarkWorkerNode)(gcBgMarkWorkerPool.pop())
if node == nil {
return nil
}
decIfPositive := func(ptr *int64) bool {
for {
v := atomic.Loadint64(ptr)
if v <= 0 {
return false
}
// TODO: having atomic.Casint64 would be more pleasant.
if atomic.Cas64((*uint64)(unsafe.Pointer(ptr)), uint64(v), uint64(v-1)) {
return true
}
}
}
// GC 模式
if decIfPositive(&c.dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded) {
// 这个P现在专用于标记,直到并发标记阶段结束; gcMarkWorkerDedicatedMode 模式
_p_.gcMarkWorkerMode = gcMarkWorkerDedicatedMode
} else if c.fractionalUtilizationGoal == 0 {
// No need for fractional workers.
gcBgMarkWorkerPool.push(&node.node)
return nil
} else {
// gcMarkWorkerFractionalMode 模式
delta := nanotime() - gcController.markStartTime
if delta > 0 && float64(_p_.gcFractionalMarkTime)/float64(delta) > c.fractionalUtilizationGoal {
// Nope. No need to run a fractional worker.
gcBgMarkWorkerPool.push(&node.node)
return nil
}
_p_.gcMarkWorkerMode = gcMarkWorkerFractionalMode
}
// 从封装过的node中解析出来goroutine并返回
gp := node.gp.ptr()
casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunnable)
if trace.enabled {
traceGoUnpark(gp, 0)
}
return gp
}
gcBgMarkWorkerPoolgcBgMarkWorkergroutinegcBgMarkWorker goroutine并发扫描与标记 gcBgMarkWorker()
重点看下 函数的实现原理。
ggcBgMarkWorkerNodegcMarkDone()func gcBgMarkWorker() {
gp := getg()
// 将当前g封装成 gcBgMarkWorkerNode 数据结构
gp.m.preemptoff = "GC worker init"
node := new(gcBgMarkWorkerNode)
gp.m.preemptoff = ""
// 设置node绑定的 g和m
node.gp.set(gp)
node.m.set(acquirem())
// 通知gcBgMarkStartWorkers可以继续处理
notewakeup(&work.bgMarkReady)
for {
// mark workers 协程进入休眠状态,直到通过 gcController.findRunnableGCWorker() 唤醒
gopark(func(g *g, nodep unsafe.Pointer) bool {
node := (*gcBgMarkWorkerNode)(nodep)
if mp := node.m.ptr(); mp != nil {
releasem(mp)
}
// Release this G to the pool.
gcBgMarkWorkerPool.push(&node.node)
return true
}, unsafe.Pointer(node), waitReasonGCWorkerIdle, traceEvGoBlock, 0)
node.m.set(acquirem())
pp := gp.m.p.ptr() // P can't change with preemption disabled.
......
startTime := nanotime()
pp.gcMarkWorkerStartTime = startTime
decnwait := atomic.Xadd(&work.nwait, -1)
// 系统栈运行
systemstack(func() {
casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gwaiting)
// GC 模式
switch pp.gcMarkWorkerMode {
default:
throw("gcBgMarkWorker: unexpected gcMarkWorkerMode")
case gcMarkWorkerDedicatedMode:
gcDrain(&pp.gcw, gcDrainUntilPreempt|gcDrainFlushBgCredit)
if gp.preempt {
// 将当前P上的所有G加入全局运行队列
lock(&sched.lock)
for {
gp, _ := runqget(pp)
if gp == nil {
break
}
globrunqput(gp)
}
unlock(&sched.lock)
}
gcDrain(&pp.gcw, gcDrainFlushBgCredit)
case gcMarkWorkerFractionalMode:
gcDrain(&pp.gcw, gcDrainFractional|gcDrainUntilPreempt|gcDrainFlushBgCredit)
case gcMarkWorkerIdleMode:
gcDrain(&pp.gcw, gcDrainIdle|gcDrainUntilPreempt|gcDrainFlushBgCredit)
}
casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunning)
})
// Account for time.
duration := nanotime() - startTime
switch pp.gcMarkWorkerMode {
case gcMarkWorkerDedicatedMode:
atomic.Xaddint64(&gcController.dedicatedMarkTime, duration)
atomic.Xaddint64(&gcController.dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded, 1)
case gcMarkWorkerFractionalMode:
atomic.Xaddint64(&gcController.fractionalMarkTime, duration)
atomic.Xaddint64(&pp.gcFractionalMarkTime, duration)
case gcMarkWorkerIdleMode:
atomic.Xaddint64(&gcController.idleMarkTime, duration)
}
// Was this the last worker and did we run out of work?
incnwait := atomic.Xadd(&work.nwait, +1)
pp.gcMarkWorkerMode = gcMarkWorkerNotWorker
// If this worker reached a background mark completion
// point, signal the main GC goroutine.
if incnwait == work.nproc && !gcMarkWorkAvailable(nil) {
releasem(node.m.ptr())
node.m.set(nil)
// 标记完成
gcMarkDone()
}
}
}
gcDrain()gcMarkDone()扫描对象gcDrain()
gcDrain()func gcDrain(gcw *gcWork, flags gcDrainFlags) {
if !writeBarrier.needed {
throw("gcDrain phase incorrect")
}
gp := getg().m.curg
preemptible := flags&gcDrainUntilPreempt != 0
flushBgCredit := flags&gcDrainFlushBgCredit != 0
idle := flags&gcDrainIdle != 0
initScanWork := gcw.scanWork
// checkWork is the scan work before performing the next
// self-preempt check.
checkWork := int64(1<<63 - 1)
var check func() bool
if flags&(gcDrainIdle|gcDrainFractional) != 0 {
checkWork = initScanWork + drainCheckThreshold
if idle {
check = pollWork
} else if flags&gcDrainFractional != 0 {
check = pollFractionalWorkerExit
}
}
// 根扫描标记工作
if work.markrootNext < work.markrootJobs {
// Stop if we're preemptible or if someone wants to STW.
for !(gp.preempt && (preemptible || atomic.Load(&sched.gcwaiting) != 0)) {
job := atomic.Xadd(&work.markrootNext, +1) - 1
if job >= work.markrootJobs {
break
}
// 标记根对象
markroot(gcw, job)
if check != nil && check() {
goto done
}
}
}
// 堆扫描标记工作
for !(gp.preempt && (preemptible || atomic.Load(&sched.gcwaiting) != 0)) {
if work.full == 0 {
gcw.balance()
}
b := gcw.tryGetFast()
if b == 0 {
b = gcw.tryGet()
if b == 0 {
// Flush the write barrier buffer; this may create more work.
wbBufFlush(nil, 0)
b = gcw.tryGet()
}
}
if b == 0 {
// Unable to get work.
break
}
// 从b位置开始扫描对象,并在内部调用 greyobject() 函数找到活跃的对象,并将其置为灰色
scanobject(b, gcw)
// Flush background scan work credit to the global
// account if we've accumulated enough locally so
// mutator assists can draw on it.
if gcw.scanWork >= gcCreditSlack {
atomic.Xaddint64(&gcController.scanWork, gcw.scanWork)
if flushBgCredit {
gcFlushBgCredit(gcw.scanWork - initScanWork)
initScanWork = 0
}
checkWork -= gcw.scanWork
gcw.scanWork = 0
if checkWork <= 0 {
checkWork += drainCheckThreshold
if check != nil && check() {
break
}
}
}
}
done:
// Flush remaining scan work credit.
if gcw.scanWork > 0 {
atomic.Xaddint64(&gcController.scanWork, gcw.scanWork)
if flushBgCredit {
gcFlushBgCredit(gcw.scanWork - initScanWork)
}
gcw.scanWork = 0
}
}
标记根对象
func markroot(gcw *gcWork, i uint32) {
baseFlushCache := uint32(fixedRootCount)
baseData := baseFlushCache + uint32(work.nFlushCacheRoots)
baseBSS := baseData + uint32(work.nDataRoots)
baseSpans := baseBSS + uint32(work.nBSSRoots)
baseStacks := baseSpans + uint32(work.nSpanRoots)
end := baseStacks + uint32(work.nStackRoots)
// Note: if you add a case here, please also update heapdump.go:dumproots.
switch {
case baseFlushCache <= i && i < baseData:
// 释放所有p下的mcache
flushmcache(int(i - baseFlushCache))
case baseData <= i && i < baseBSS:
// 可读写的全局变量(静态区)
for _, datap := range activeModules() {
markrootBlock(datap.data, datap.edata-datap.data, datap.gcdatamask.bytedata, gcw, int(i-baseData))
}
case baseBSS <= i && i < baseSpans:
// 数据段未初始化的全局变量
for _, datap := range activeModules() {
markrootBlock(datap.bss, datap.ebss-datap.bss, datap.gcbssmask.bytedata, gcw, int(i-baseBSS))
}
case i == fixedRootFinalizers:
// 扫描 finalizers 队列
for fb := allfin; fb != nil; fb = fb.alllink {
cnt := uintptr(atomic.Load(&fb.cnt))
scanblock(uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&fb.fin[0])), cnt*unsafe.Sizeof(fb.fin[0]), &finptrmask[0], gcw, nil)
}
case i == fixedRootFreeGStacks:
// Switch to the system stack so we can call stackfree.
systemstack(markrootFreeGStacks)
case baseSpans <= i && i < baseStacks:
// mark mspan.specials
markrootSpans(gcw, int(i-baseSpans))
default:
// 扫描 goroutine stacks
var gp *g
if baseStacks <= i && i < end {
gp = allgs[i-baseStacks]
} else {
throw("markroot: bad index")
}
// remember when we've first observed the G blocked needed only to output in traceback
status := readgstatus(gp) // We are not in a scan state
if (status == _Gwaiting || status == _Gsyscall) && gp.waitsince == 0 {
gp.waitsince = work.tstart
}
// 扫描 stack 必须在系统栈完成,以防扫描自己的stack
systemstack(func() {
userG := getg().m.curg
// 如果当前扫描的是自己所在的stack,则将G的状态修改为_Gwaiting
selfScan := gp == userG && readgstatus(userG) == _Grunning
if selfScan {
casgstatus(userG, _Grunning, _Gwaiting)
userG.waitreason = waitReasonGarbageCollectionScan
}
// 暂停g
stopped := suspendG(gp)
if stopped.dead {
gp.gcscandone = true
return
}
if gp.gcscandone {
throw("g already scanned")
}
// 扫描g
scanstack(gp, gcw)
gp.gcscandone = true
// 恢复g
resumeG(stopped)
// 如果扫描的是自己的stack, 则将当前g 恢复到运行状态
if selfScan {
casgstatus(userG, _Gwaiting, _Grunning)
}
})
}
}
runtime.markroot标记终止 gcMarkDone()
func gcMarkDone() {
semacquire(&work.markDoneSema)
top:
// Re-check transition condition under transition lock.
if !(gcphase == _GCmark && work.nwait == work.nproc && !gcMarkWorkAvailable(nil)) {
semrelease(&work.markDoneSema)
return
}
// forEachP needs worldsema to execute, and we'll need it to
// stop the world later, so acquire worldsema now.
semacquire(&worldsema)
// Flush all local buffers and collect flushedWork flags.
gcMarkDoneFlushed = 0
systemstack(func() {
gp := getg().m.curg
casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gwaiting)
forEachP(func(_p_ *p) {
wbBufFlush1(_p_)
_p_.gcw.dispose()
if _p_.gcw.flushedWork {
atomic.Xadd(&gcMarkDoneFlushed, 1)
_p_.gcw.flushedWork = false
}
})
casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunning)
})
if gcMarkDoneFlushed != 0 {
semrelease(&worldsema)
goto top
}
// There was no global work, no local work, and no Ps
// communicated work since we took markDoneSema. Therefore
// there are no grey objects and no more objects can be
// shaded. Transition to mark termination.
now := nanotime()
work.tMarkTerm = now
work.pauseStart = now
getg().m.preemptoff = "gcing"
if trace.enabled {
traceGCSTWStart(0)
}
systemstack(stopTheWorldWithSema)
// The gcphase is _GCmark, it will transition to _GCmarktermination
// below. The important thing is that the wb remains active until
// all marking is complete. This includes writes made by the GC.
// There is sometimes work left over when we enter mark termination due
// to write barriers performed after the completion barrier above.
// Detect this and resume concurrent mark. This is obviously
// unfortunate.
//
// See issue #27993 for details.
//
// Switch to the system stack to call wbBufFlush1, though in this case
// it doesn't matter because we're non-preemptible anyway.
restart := false
systemstack(func() {
for _, p := range allp {
wbBufFlush1(p)
if !p.gcw.empty() {
restart = true
break
}
}
})
if restart {
getg().m.preemptoff = ""
systemstack(func() {
now := startTheWorldWithSema(true)
work.pauseNS += now - work.pauseStart
memstats.gcPauseDist.record(now - work.pauseStart)
})
semrelease(&worldsema)
goto top
}
// Disable assists and background workers. We must do
// this before waking blocked assists.
atomic.Store(&gcBlackenEnabled, 0)
// Wake all blocked assists. These will run when we
// start the world again.
gcWakeAllAssists()
// Likewise, release the transition lock. Blocked
// workers and assists will run when we start the
// world again.
semrelease(&work.markDoneSema)
// In STW mode, re-enable user goroutines. These will be
// queued to run after we start the world.
schedEnableUser(true)
// endCycle depends on all gcWork cache stats being flushed.
// The termination algorithm above ensured that up to
// allocations since the ragged barrier.
nextTriggerRatio := gcController.endCycle()
// Perform mark termination. This will restart the world.
// 第三阶段:标记终止
gcMarkTermination(nextTriggerRatio)
}
gcMarkTermination()_GCmarkterminationfunc gcMarkTermination(nextTriggerRatio float64) {
// 阶段修改
setGCPhase(_GCmarktermination)
work.heap1 = memstats.heap_live
startTime := nanotime()
mp := acquirem()
mp.preemptoff = "gcing"
_g_ := getg()
_g_.m.traceback = 2
gp := _g_.m.curg
casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gwaiting)
gp.waitreason = waitReasonGarbageCollection
systemstack(func() {
gcMark(startTime)
})
systemstack(func() {
work.heap2 = work.bytesMarked
......
// marking is complete so we can turn the write barrier off
setGCPhase(_GCoff)
gcSweep(work.mode)
})
_g_.m.traceback = 0
casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunning)
// all done
mp.preemptoff = ""
// Record next_gc and heap_inuse for scavenger.
memstats.last_next_gc = memstats.next_gc
memstats.last_heap_inuse = memstats.heap_inuse
// Update GC trigger and pacing for the next cycle.
gcSetTriggerRatio(nextTriggerRatio)
// Update timing memstats
now := nanotime()
sec, nsec, _ := time_now()
unixNow := sec*1e9 + int64(nsec)
work.pauseNS += now - work.pauseStart
work.tEnd = now
memstats.gcPauseDist.record(now - work.pauseStart)
atomic.Store64(&memstats.last_gc_unix, uint64(unixNow)) // must be Unix time to make sense to user
atomic.Store64(&memstats.last_gc_nanotime, uint64(now)) // monotonic time for us
memstats.pause_ns[memstats.numgc%uint32(len(memstats.pause_ns))] = uint64(work.pauseNS)
memstats.pause_end[memstats.numgc%uint32(len(memstats.pause_end))] = uint64(unixNow)
memstats.pause_total_ns += uint64(work.pauseNS)
// Update work.totaltime.
sweepTermCpu := int64(work.stwprocs) * (work.tMark - work.tSweepTerm)
markCpu := gcController.assistTime + gcController.dedicatedMarkTime + gcController.fractionalMarkTime
markTermCpu := int64(work.stwprocs) * (work.tEnd - work.tMarkTerm)
cycleCpu := sweepTermCpu + markCpu + markTermCpu
work.totaltime += cycleCpu
// Compute overall GC CPU utilization.
totalCpu := sched.totaltime + (now-sched.procresizetime)*int64(gomaxprocs)
memstats.gc_cpu_fraction = float64(work.totaltime) / float64(totalCpu)
// Reset sweep state.
sweep.nbgsweep = 0
sweep.npausesweep = 0
if work.userForced {
memstats.numforcedgc++
}
// Bump GC cycle count and wake goroutines waiting on sweep.
lock(&work.sweepWaiters.lock)
memstats.numgc++
injectglist(&work.sweepWaiters.list)
unlock(&work.sweepWaiters.lock)
mProf_NextCycle()
systemstack(func() { startTheWorldWithSema(true) })
// Flush the heap profile so we can start a new cycle next GC.
mProf_Flush()
// Prepare workbufs for freeing by the sweeper. We do this
// asynchronously because it can take non-trivial time.
prepareFreeWorkbufs()
// Free stack spans. This must be done between GC cycles.
systemstack(freeStackSpans)
systemstack(func() {
forEachP(func(_p_ *p) {
_p_.mcache.prepareForSweep()
})
})
......
semrelease(&worldsema)
semrelease(&gcsema)
// Careful: another GC cycle may start now.
releasem(mp)
mp = nil
// now that gc is done, kick off finalizer thread if needed
if !concurrentSweep {
// give the queued finalizers, if any, a chance to run
Gosched()
}
}
重置全局状态和栈扫描状态 gcResetMarkState()
//go:systemstack
func gcResetMarkState() {
// 并发阶段调用,要确保所有G不会被修改,所以加 allglock 锁
// 将所有g都gc字段初始化
lock(&allglock)
for _, gp := range allgs {
gp.gcscandone = false // set to true in gcphasework
gp.gcAssistBytes = 0
}
unlock(&allglock)
// Clear page marks. This is just 1MB per 64GB of heap, so the
// time here is pretty trivial.
// 页标记置0
lock(&mheap_.lock)
arenas := mheap_.allArenas
unlock(&mheap_.lock)
for _, ai := range arenas {
ha := mheap_.arenas[ai.l1()][ai.l2()]
for i := range ha.pageMarks {
ha.pageMarks[i] = 0
}
}
// 标记字节大小初始化为0, 初始化堆大小为当前堆的大小
work.bytesMarked = 0
work.initialHeapLive = atomic.Load64(&memstats.heap_live)
}
heapArea.pageMarks0heapArea.pageMarks[i]spansmheap.heapArena确保上一轮的清扫终止工作 finishsweep_m()
spansfunc finishsweep_m() {
assertWorldStopped()
// 必须在标记开始前完成清扫, 清扫所有未扫描的spans。
// 循环调用 seeepone() 函数完成所有堆 span,返回值为 ^uintptr(0) 时表示清扫完成
for sweepone() != ^uintptr(0) {
sweep.npausesweep++
}
// 重置 mheap_.central 中的 spans 状态
sg := mheap_.sweepgen
for i := range mheap_.central {
c := &mheap_.central[i].mcentral
c.partialUnswept(sg).reset()
c.fullUnswept(sg).reset()
}
// Sweeping is done, so if the scavenger isn't already awake
wakeScavenger()
nextMarkBitArenaEpoch()
}
清除pools对象 clearpools()
清除的对象有三类,需加锁处理
sync.Poolscentral sudog cache sched.sudogcachecentral defer poolsched.deferpool可以看到,其中清理的对象有两类都在调度器结构体中。
func clearpools() {
// 清除 sync.Pools
if poolcleanup != nil {
poolcleanup()
}
// 清除 central sudog cache.
lock(&sched.sudoglock)
var sg, sgnext *sudog
for sg = sched.sudogcache; sg != nil; sg = sgnext {
sgnext = sg.next
sg.next = nil
}
sched.sudogcache = nil
unlock(&sched.sudoglock)
// 清除 central defer pools.
lock(&sched.deferlock)
for i := range sched.deferpool {
// disconnect cached list before dropping it on the floor,
// so that a dangling ref to one entry does not pin all of them.
var d, dlink *_defer
for d = sched.deferpool[i]; d != nil; d = dlink {
dlink = d.link
d.link = nil
}
sched.deferpool[i] = nil
}
unlock(&sched.deferlock)
}
新一轮GC控制器的初始化 gcController.startCycle()
当准备好了GC准备工作后,会调用 正式开始新一轮的GC。
// startCycle resets the GC controller's state and computes estimates
// for a new GC cycle. The caller must hold worldsema and the world
// must be stopped.
func (c *gcControllerState) startCycle() {
// 新一轮GC 重置状态
c.scanWork = 0
c.bgScanCredit = 0
c.assistTime = 0
c.dedicatedMarkTime = 0
c.fractionalMarkTime = 0
c.idleMarkTime = 0
// 下次gc触发的条件做准备(gcTriggerHeap)
if memstats.next_gc < memstats.heap_live+1024*1024 {
memstats.next_gc = memstats.heap_live + 1024*1024
}
// gcBackgroundUtilization 默认值为 0.25
// c.dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded = float64(cpu数量 * 0.25 + 0.5)
totalUtilizationGoal := float64(gomaxprocs) * gcBackgroundUtilization
c.dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded = totalUtilizationGoal + 0.5
utilError := float64(c.dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded)/totalUtilizationGoal - 1
const maxUtilError = 0.3
if utilError < -maxUtilError || utilError > maxUtilError {
// Rounding put us more than 30% off our goal. With
// gcBackgroundUtilization of 25%, this happens for
// GOMAXPROCS<=3 or GOMAXPROCS=6. Enable fractional
// workers to compensate.
if float64(c.dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded) > totalUtilizationGoal {
// Too many dedicated workers.
c.dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded--
}
c.fractionalUtilizationGoal = (totalUtilizationGoal - float64(c.dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded)) / float64(gomaxprocs)
} else {
c.fractionalUtilizationGoal = 0
}
// In STW mode, we just want dedicated workers.
if debug.gcstoptheworld > 0 {
c.dedicatedMarkWorkersNeeded = int64(gomaxprocs)
c.fractionalUtilizationGoal = 0
}
// 清除所有P上的gc相关值
for _, p := range allp {
p.gcAssistTime = 0
p.gcFractionalMarkTime = 0
}
// Compute initial values for controls that are updated
// throughout the cycle.
c.revise()
......
}
dedicatedMarkWorkersNeededfractionalUtilizationGoal修改GC状态为 _GCMark
写屏障func setGCPhase(x uint32) {
atomic.Store(&gcphase, x)
writeBarrier.needed = gcphase == _GCmark || gcphase == _GCmarktermination
writeBarrier.enabled = writeBarrier.needed || writeBarrier.cgo
}
做标记准备工作 gcBgMarkPrepare()
初始化后台标记线程有状态
// gcBgMarkPrepare sets up state for background marking.
// Mutator assists must not yet be enabled.
func gcBgMarkPrepare() {
work.nproc = ^uint32(0)
work.nwait = ^uint32(0)
}
扫描根对象并加入队 gcMarkRootPrepare()
统计根对象信息,并记录到 work 全局变量相关字段。
func gcMarkRootPrepare() {
assertWorldStopped()
// 初始化各种类型根对象
work.nFlushCacheRoots = 0
// 统计data 和 bss 段块的数量
nBlocks := func(bytes uintptr) int {
return int(divRoundUp(bytes, rootBlockBytes))
}
work.nDataRoots = 0
work.nBSSRoots = 0
// Scan globals.
for _, datap := range activeModules() {
nDataRoots := nBlocks(datap.edata - datap.data)
if nDataRoots > work.nDataRoots {
work.nDataRoots = nDataRoots
}
}
for _, datap := range activeModules() {
nBSSRoots := nBlocks(datap.ebss - datap.bss)
if nBSSRoots > work.nBSSRoots {
work.nBSSRoots = nBSSRoots
}
}
// Scan span roots for finalizer specials.
mheap_.markArenas = mheap_.allArenas[:len(mheap_.allArenas):len(mheap_.allArenas)]
work.nSpanRoots = len(mheap_.markArenas) * (pagesPerArena / pagesPerSpanRoot)
// 扫描 stacks,在此期间可能会有新的goroutine创建,可以直接忽略掉它,交给写屏障处理
work.nStackRoots = int(atomic.Loaduintptr(&allglen))
work.markrootNext = 0
work.markrootJobs = uint32(fixedRootCount + work.nFlushCacheRoots + work.nDataRoots + work.nBSSRoots + work.nSpanRoots + work.nStackRoots)
}
work.nDataRootswork.nBssRootsstackgcMarkTinyAllocs()p.mcache.tinygreyobject()// gcMarkTinyAllocs greys all active tiny alloc blocks.
func gcMarkTinyAllocs() {
assertWorldStopped()
for _, p := range allp {
c := p.mcache
if c == nil || c.tiny == 0 {
continue
}
_, span, objIndex := findObject(c.tiny, 0, 0)
gcw := &p.gcw
// 置灰
greyobject(c.tiny, 0, 0, span, gcw, objIndex)
}
}
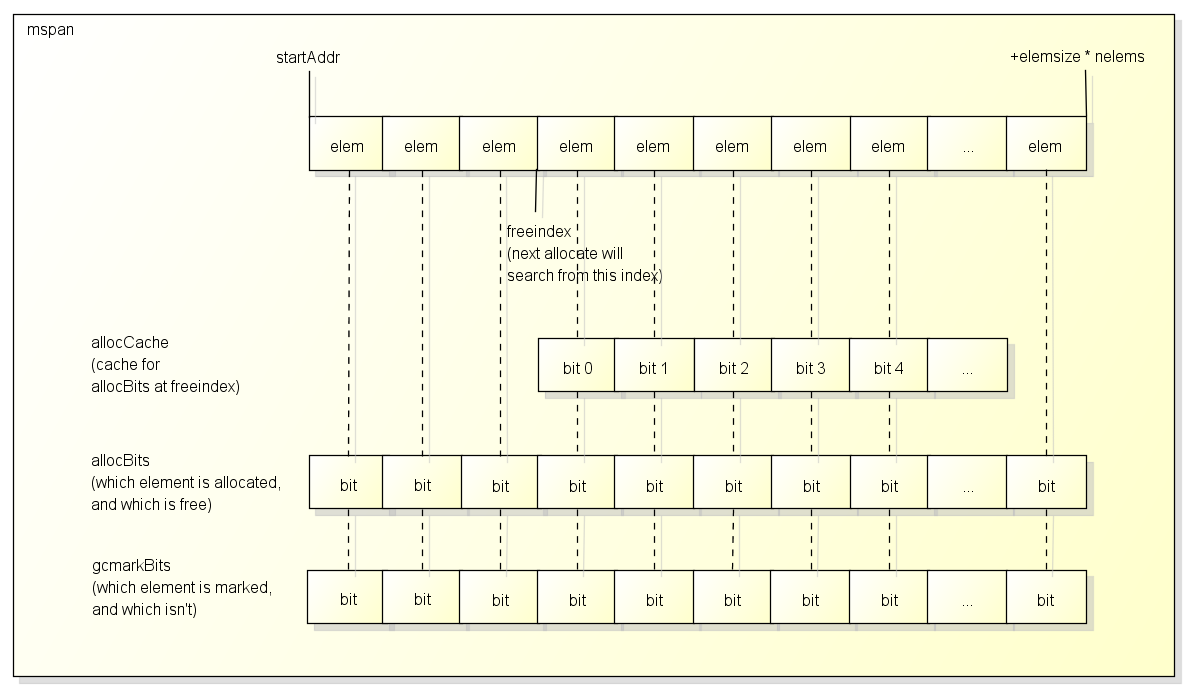
greyobject 函数
func greyobject(obj, base, off uintptr, span *mspan, gcw *gcWork, objIndex uintptr) {
// 标记位,它可以提供访问heap中对象的mark bit 信息
mbits := span.markBitsForIndex(objIndex)
// 如果使用 checkmark位 代替了标准的 mark bits方法
if useCheckmark {
if setCheckmark(obj, base, off, mbits) {
return
}
} else {
......
// 已标记过,直接返回
if mbits.isMarked() {
return
}
// 设置标记状态
mbits.setMarked()
// 标记span
arena, pageIdx, pageMask := pageIndexOf(span.base())
if arena.pageMarks[pageIdx]&pageMask == 0 {
atomic.Or8(&arena.pageMarks[pageIdx], pageMask)
}
// 如果span为 noscan 类型,则更新gcw.bytesMarked 大小
if span.spanclass.noscan() {
gcw.bytesMarked += uint64(span.elemsize)
return
}
}
// 加入 gcWork 缓存中或全局队列中
if !gcw.putFast(obj) {
gcw.put(obj)
}
}
每个span的都有一个对应的bit位,用来表示当前span的标记状态,所以标记的时候,除了对标记位进行标记,还要对其span的地方进行标记。
总结本文主要是对GC的调用流程进行了大概的描述,但实现中有太多的细节并未提到。如果想要对GC这块内容有深刻的理解,则需要更深入的了解每段代码才可以,本文仅作为学习参考。
参考资料