是什么?用一句话来定义它:一个基于golang协程、支持水平扩容的分布式高性能工作流框架。
它具有以下特点:
DAGfastflowfastflowPrometheusfastflow为什么要开发 Fastflow
组内有很多项目都涉及复杂的任务流场景,比如离线任务,集群上下架,容器迁移等,这些场景都有几个共同的特点:
1、流程耗时且步骤复杂,比如创建一个 k8s 集群,需要几十步操作,其中包含脚本执行、接口调用等,且相互存在依赖关系。
2、任务量巨大,比如容器平台每天都会有几十万的离线任务需要调度执行、再比如我们管理数百个K8S集群,几乎每天会有集群需要上下节点、迁移容器等。
我们尝试过各种解法:
进程进程Concept
工作流模型
fastflow 的工作流模型基于 ,下图是一个简单的 DAG 示意图:
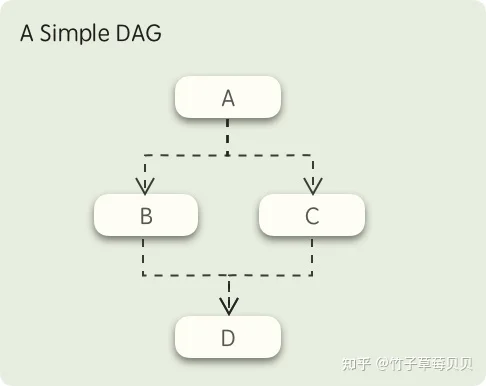
在这个图中,首先 A 节点所定义的任务会被执行,当 A 执行完毕后,B、C两个节点所定义的任务将同时被触发,而只有 B、C 两个节点都执行成功后,最后的 D 节点才会被触发,这就是 fastflow 的工作流模型。
工作流的要素
fastflow 执行任务的过程会涉及到几个概念:Dag, Task, Action, DagInstance
Dag
Task编程yaml一个编程式定义的DAG
dag := &entity.Dag{
BaseInfo: entity.BaseInfo{
ID: "test-dag",
},
Name: "test",
Tasks: []entity.Task{
{ID: "task1", ActionName: "PrintAction"},
{ID: "task2", ActionName: "PrintAction", DependOn: []string{"task1"}},
{ID: "task3", ActionName: "PrintAction", DependOn: []string{"task2"}},
},
}对应的yaml如下:
id: "test-dag"
name: "test"
tasks:
- id: "task1"
actionName: "PrintAction"
- id: ["task2"]
actionName: "PrintAction"
dependOn: ["task1"]
- id: "task3"
actionName: "PrintAction"
dependOn: ["task2"]同时 Dag 可以定义这个工作流所需要的参数,以便于在各个 Task 去消费它:
id: "test-dag"
name: "test"
vars:
fileName:
desc: "the file name"
defaultValue: "file.txt"
filePath:
desc: "the file path"
defaultValue: "/tmp/"
tasks:
- id: "task1"
actionName: "PrintAction"
params:
writeName: "{{fileName}}"
writePath: "{{filePath}}"Task
Actionid: "test-dag"
name: "test"
vars:
fileName:
desc: "the file name"
defaultValue: "file.txt"
tasks:
- id: "task1"
actionName: "PrintAction"
preCheck:
- act: skip #you can set "skip" or "block"
conditions:
- source: vars # source could be "vars" or "share-data"
key: "fileName"
op: "in"
values: ["warn.txt", "error.txt"]
Task 的状态有以下几个:
RunAction
Action 是工作流的核心,定义了该节点将执行什么操作,fastflow携带了一些开箱即用的Action,但是一般你都需要根据具体的业务场景自行编写,它有几个关键属性:
RequiredRequiredOptionalOptionalOptional自行开发的 Action 在使用前都必须先注册到 fastflow,如下所示:
type PrintParams struct {
Key string
Value string
}
type PrintAction struct {
}
// Name define the unique action identity, it will be used by Task
func (a *PrintAction) Name() string {
return "PrintAction"
}
func (a *PrintAction) Run(ctx run.ExecuteContext, params interface{}) error {
cinput := params.(*ActionParam)
fmt.Println("action start: ", time.Now())
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("params: key[%s] value[%s]", cinput.Key, cinput.Value))
return nil
}
func (a *PrintAction) ParameterNew() interface{} {
return &PrintParams{}
}
func main() {
...
// Register action
fastflow.RegisterAction([]run.Action{
&PrintAction{},
})
...
}DagInstance
DagInstance实例类型与Module
首先 fastflow 是一个分布式的框架,意味着你可以部署多个实例来分担负载,而实例被分为两类角色:
协程模块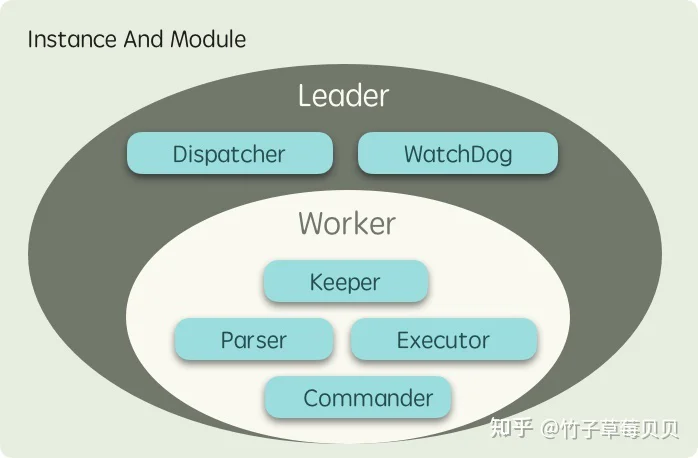
仲裁者从上面的图看,Leader 实例会比 Worker 实例多运行一些模块用于执行中仲裁者相关的任务,模块之间的协作关系如下图所示:
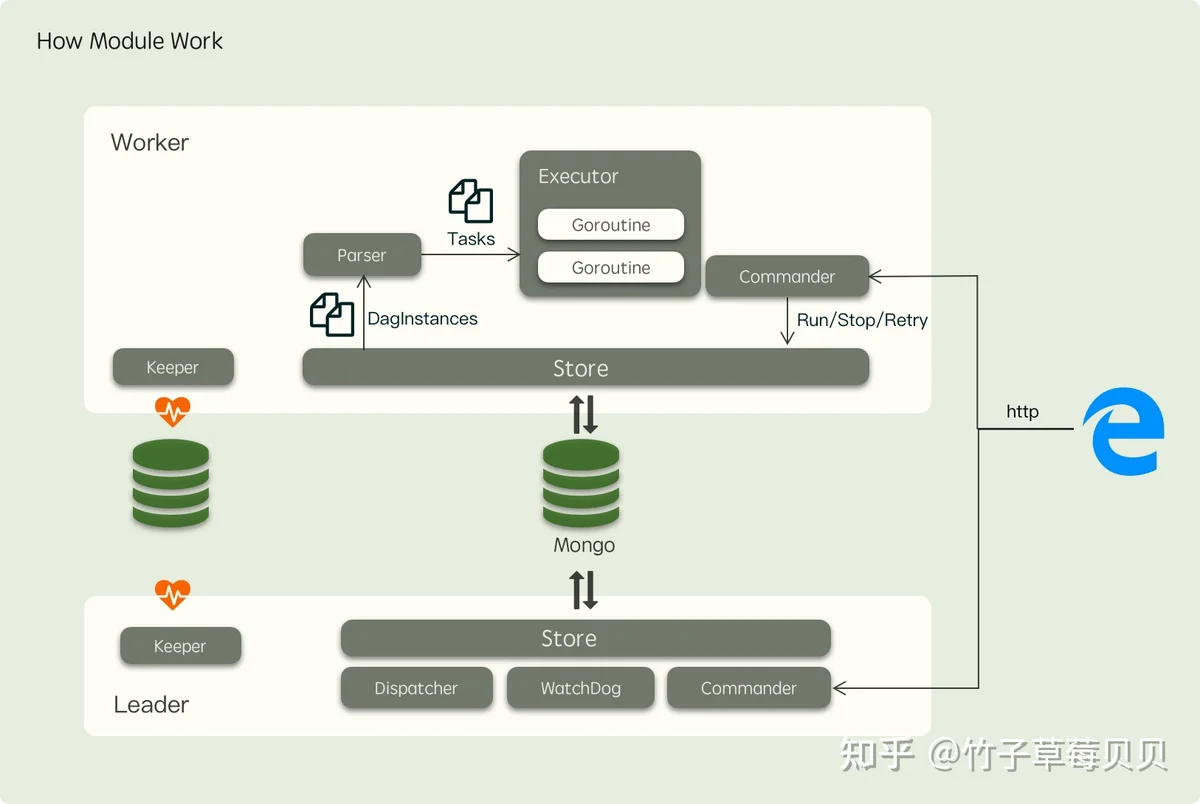
其中各个模块的职责如下:
每个节点都会运行分布式锁EtcdZookeepperMongo每个节点都会运行MongoMysqlMongoWorker 节点运行Executor每个节点都会运行Worker 节点运行Leader节点才会运行Leader节点才会运行Tips
以上模块的分布机制仅仅只是 fastflow 的默认实现,你也可以自行决定实例运行的模块,比如在 Leader 上不再运行 Worker 的实例,让其专注于任务调度。
GetStart
examples准备一个Mongo实例
如果已经你已经有了可测试的实例,可以直接替换为你的实例,如果没有的话,可以使用Docker容器在本地跑一个,指令如下:
docker run -d --name fastflow-mongo --network host mongo运行 fastflow
运行以下示例
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/shiningrush/fastflow"
mongoKeeper "github.com/shiningrush/fastflow/keeper/mongo"
"github.com/shiningrush/fastflow/pkg/entity/run"
"github.com/shiningrush/fastflow/pkg/mod"
mongoStore "github.com/shiningrush/fastflow/store/mongo"
)
type PrintAction struct {
}
// Name define the unique action identity, it will be used by Task
func (a *PrintAction) Name() string {
return "PrintAction"
}
func (a *PrintAction) Run(ctx run.ExecuteContext, params interface{}) error {
fmt.Println("action start: ", time.Now())
return nil
}
func main() {
// Register action
fastflow.RegisterAction([]run.Action{
&PrintAction{},
})
// init keeper, it used to e
keeper := mongoKeeper.NewKeeper(&mongoKeeper.KeeperOption{
Key: "worker-1",
// if your mongo does not set user/pwd, youshould remove it
ConnStr: "mongodb://root:pwd@127.0.0.1:27017/fastflow?authSource=admin",
Database: "mongo-demo",
Prefix: "test",
})
if err := keeper.Init(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(fmt.Errorf("init keeper failed: %w", err))
}
// init store
st := mongoStore.NewStore(&mongoStore.StoreOption{
// if your mongo does not set user/pwd, youshould remove it
ConnStr: "mongodb://root:pwd@127.0.0.1:27017/fastflow?authSource=admin",
Database: "mongo-demo",
Prefix: "test",
})
if err := st.Init(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(fmt.Errorf("init store failed: %w", err))
}
go createDagAndInstance()
// start fastflow
if err := fastflow.Start(&fastflow.InitialOption{
Keeper: keeper,
Store: st,
// use yaml to define dag
ReadDagFromDir: "./",
}); err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("init fastflow failed: %s", err))
}
}
func createDagAndInstance() {
// wait fast start completed
time.Sleep(time.Second)
// run some dag instance
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
_, err := mod.GetCommander().RunDag("test-dag", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second * 10)
}
}
test-dag.yamlid: "test-dag"
name: "test"
tasks:
- id: "task1"
actionName: "PrintAction"
- id: "task2"
actionName: "PrintAction"
dependOn: ["task1"]
- id: "task3"
actionName: "PrintAction"
dependOn: ["task2"]
Basic
Task与Task之间的通信
goroutinecontextfunc (a *UpAction) Run(ctx run.ExecuteContext, params interface{}) error {
ctx.WithValue("key", "value")
return nil
}
func (a *DownAction) Run(ctx run.ExecuteContext, params interface{}) error {
val := ctx.Context().Value("key")
return nil
}
但是注意这样做有个弊端:当节点重启时,如果任务尚未执行完毕,那么这部分内容会丢失。
Storefunc (a *UpAction) Run(ctx run.ExecuteContext, params interface{}) error {
ctx.ShareData().Set("key", "value")
return nil
}
func (a *DownAction) Run(ctx run.ExecuteContext, params interface{}) error {
val := ctx.ShareData().Get("key")
return nil
}
任务日志
Storefunc (a *Action) Run(ctx run.ExecuteContext, params interface{}) error {
ctx.Trace("some message")
return nil
}
使用Dag变量
上面的文章中提到,我们可以在 Dag 中定义一些变量,在创建工作流时可以对这些变量进行赋值,比如以下的Dag,定义了一个名为 `fileName 的变量
id: "test-dag"
name: "test"
vars:
fileName:
desc: "the file name"
defaultValue: "file.txt"
Commandermod.GetCommander().RunDag("test-id", map[string]string{
"fileName": "demo.txt",
})
demo.txt- 带参数的Action
id: "test-dag"
name: "test"
vars:
fileName:
desc: "the file name"
defaultValue: "file.txt"
tasks:
- id: "task1"
action: "PrintAction"
params:
# using {{var}} to consume dag's variable
fileName: "{{fileName}}"
PrintAction.go:
type PrintParams struct {
FileName string `json:"fileName"`
}
type PrintAction struct {
}
// Name define the unique action identity, it will be used by Task
func (a *PrintAction) Name() string {
return "PrintAction"
}
func (a *PrintAction) Run(ctx run.ExecuteContext, params interface{}) error {
cinput := params.(*ActionParam)
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("params: file[%s]", cinput.FileName, cinput.Value))
return nil
}
func (a *PrintAction) ParameterNew() interface{} {
return &PrintParams{}
}
2.编程式读取
fastflow 也提供了相关函数来获取 Dag 变量
func (a *Action) Run(ctx run.ExecuteContext, params interface{}) error {
// get variable by name
ctx.GetVar("fileName")
// iterate variables
ctx.IterateVars(func(key, val string) (stop bool) {
...
})
return nil
}
分布式锁
Keeper...
mod.GetKeeper().NewMutex("mutex key").Lock(ctx.Context(),
mod.LockTTL(time.Second),
mod.Reentrant("worker-key1"))
...
其中:
LockTTL30sReentrant