1. 什么是pprof?为什么需要使用pprof?
1.1 什么是pprof?
- 用来做性能分析的工具
1.2 pprof可以从哪些角度来进行分析
- CPU Profiling:CPU 分析,按照一定的频率采集所监听的应用程序 CPU(含寄存器)的使用情况,可确定应用程序在主动消耗 CPU 周期时花费时间的位置
- Memory Profiling:内存分析,在应用程序进行堆分配时记录堆栈跟踪,用于监视当前和历史内存使用情况,以及检查内存泄漏
- Block Profiling:阻塞分析,记录 goroutine 阻塞等待同步(包括定时器通道)的位置
- Mutex Profiling:互斥锁分析,报告互斥锁的竞争情况
2. pprof 怎么使用?
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
_ "github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql"
"net/http"
netpprof "net/http/pprof"
"os"
"runtime/pprof"
"time"
)
func main() {
//pprofSingerProgram() // 分析单个程序示例
//pprofHttp() // 分析http服务示例
pprofDiyHttp() // 分析自定义http服务示例
}
func pprofSingerProgram() {
f, _ := os.Create("./test.pprof")
pprof.StartCPUProfile(f)
defer pprof.StopCPUProfile()
for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ {
LocalTz()
DoSomething([]byte(`{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}`))
}
}
func pprofHttp() {
go func() {
for {
LocalTz()
DoSomething([]byte(`{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}`))
}
}()
time.Sleep(1)
fmt.Println("start api server...")
panic(http.ListenAndServe(":8081", nil))
}
func pprofDiyHttp() {
var httpSvc *http.Server
httpAddr := ":8081"
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/", netpprof.Index)
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/cmdline", netpprof.Cmdline)
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/profile", netpprof.Profile)
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/symbol", netpprof.Symbol)
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/trace", netpprof.Trace)
httpSvc = &http.Server{
Addr: httpAddr,
Handler: mux,
}
if err := httpSvc.ListenAndServe(); err != nil && err != http.ErrServerClosed {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
func DoSomething(s []byte) {
var m map[string]interface{}
err := json.Unmarshal(s, &m)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
s1 := make([]string, 0)
s2 := ""
for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
s1 = append(s1, string(s))
s2 += string(s)
}
}
func LocalTz() *time.Location {
tz, _ := time.LoadLocation("Asia/Shanghai")
return tz
}
2.1 在普通的程序中使用
- 以上代码示例:pprofSingerProgram
2.2 在http server 中使用
- 以上代码示例:pprofHttp
- mac 安装 graphviz
- brew install graphviz
- 如果遇到报错,可以换成中科大的源,然后执行一下brew update
2.3 在自己定义的http server中 使用
- 需要自己注册路由
2.3 获取各类数据的地址
- 获取所有的数据:http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/,以下列出其他的相关数据查看,如果你在对应的访问路径上新增 ?debug=1 的话,就可以直接在浏览器访问。否则就是直接下载文件
- allocs:查看过去所有内存分配的样本,访问路径为 $HOST/debug/pprof/allocs。
- block:查看导致阻塞同步的堆栈跟踪,访问路径为 $HOST/debug/pprof/block。
- cmdline: 当前程序的命令行的完整调用路径。
- goroutine:查看当前所有运行的 goroutines 堆栈跟踪,访问路径为 $HOST/debug/pprof/goroutine。
- heap:查看活动对象的内存分配情况, 访问路径为 $HOST/debug/pprof/heap。
- mutex:查看导致互斥锁的竞争持有者的堆栈跟踪,访问路径为 $HOST/debug/pprof/mutex。
- profile: 默认进行 30s 的 CPU Profiling,得到一个分析用的 profile 文件,访问路径为 $HOST/debug/pprof/profile。
- threadcreate:查看创建新 OS 线程的堆栈跟踪,访问路径为 $HOST/debug/pprof/threadcreate。
2.4 获取火焰图:
- go tool pprof -http=:803 http://localhost:802/debug/pprof/profile -seconds 10
- -http=803: 监听在某个端口以供提供网页端查看
- -seconds 10 : 收集最近十秒的信息
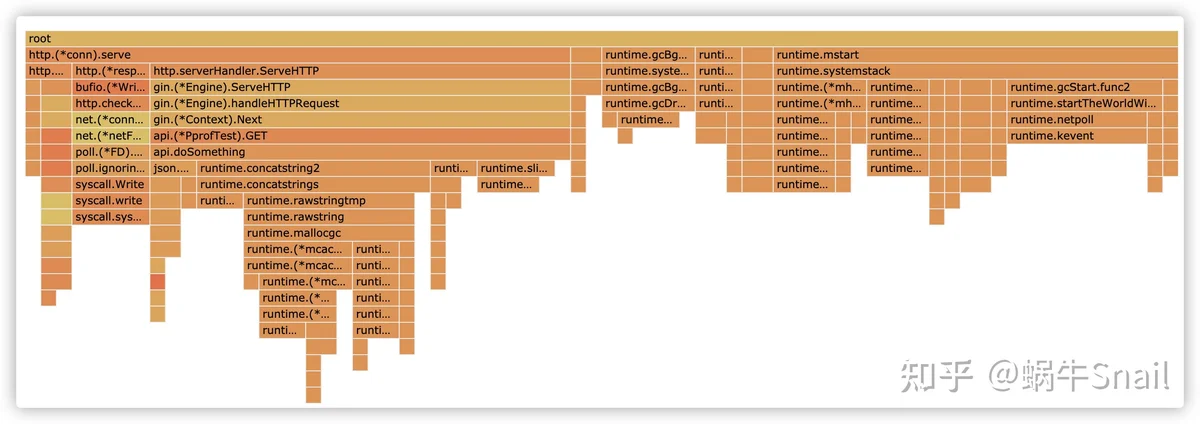
3. 火焰图怎么看?
- 如下图,第一个是root,表示所有的函数的起点
- 一行的数据中的各个函数是平行的,也就是说行元素之间
- 一列的数据中的各个函数相当于上一行的子函数,向上负责的,也就是说列之间存在父子关系
- 同时存在一列函数分为多个函数,长度代表他们的耗时
4. 参考链接
