微信搜索【脑子进煎鱼了】关注这一只爆肝煎鱼。本文 GitHub github.com/eddycjy/blog 已收录,有我的系列文章、资料和开源 Go 图书。
最新版本的 PProf 分析,推荐阅读:Golang 大杀器之性能剖析 PProf
前言
写了几吨代码,实现了几百个接口。功能测试也通过了,终于成功的部署上线了
结果,性能不佳,什么鬼?😭
想做性能分析
PProf
想要进行性能优化,首先瞩目在 Go 自身提供的工具链来作为分析依据,本文将带你学习、使用 Go 后花园,涉及如下:
- runtime/pprof:采集程序(非 Server)的运行数据进行分析
- net/http/pprof:采集 HTTP Server 的运行时数据进行分析
是什么
pprof 是用于可视化和分析性能分析数据的工具
pprof 以 profile.proto 读取分析样本的集合,并生成报告以可视化并帮助分析数据(支持文本和图形报告)
profile.proto 是一个 Protocol Buffer v3 的描述文件,它描述了一组 callstack 和 symbolization 信息, 作用是表示统计分析的一组采样的调用栈,是很常见的 stacktrace 配置文件格式
支持什么使用模式
- Report generation:报告生成
- Interactive terminal use:交互式终端使用
- Web interface:Web 界面
可以做什么
- CPU Profiling:CPU 分析,按照一定的频率采集所监听的应用程序 CPU(含寄存器)的使用情况,可确定应用程序在主动消耗 CPU 周期时花费时间的位置
- Memory Profiling:内存分析,在应用程序进行堆分配时记录堆栈跟踪,用于监视当前和历史内存使用情况,以及检查内存泄漏
- Block Profiling:阻塞分析,记录 goroutine 阻塞等待同步(包括定时器通道)的位置
- Mutex Profiling:互斥锁分析,报告互斥锁的竞争情况
一个简单的例子
我们将编写一个简单且有点问题的例子,用于基本的程序初步分析
编写 demo 文件
(1)demo.go,文件内容:
package main
import (
"log"
"net/http"
_ "net/http/pprof"
"github.com/EDDYCJY/go-pprof-example/data"
)
func main() {
go func() {
for {
log.Println(data.Add("https://github.com/EDDYCJY"))
}
}()
http.ListenAndServe("0.0.0.0:6060", nil)
}(2)data/d.go,文件内容:
package data
var datas []string
func Add(str string) string {
data := []byte(str)
sData := string(data)
datas = append(datas, sData)
return sData
}
运行这个文件,你的 HTTP 服务会多出 /debug/pprof 的 endpoint 可用于观察应用程序的情况
分析
一、通过 Web 界面
http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof//debug/pprof/
profiles:
0 block
5 goroutine
3 heap
0 mutex
9 threadcreate
full goroutine stack dump这个页面中有许多子页面,咱们继续深究下去,看看可以得到什么?
$HOST/debug/pprof/profile$HOST/debug/pprof/block$HOST/debug/pprof/goroutine$HOST/debug/pprof/heap$HOST/debug/pprof/mutex$HOST/debug/pprof/threadcreate二、通过交互式终端使用
$ go tool pprof http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/profile\?seconds\=60
Fetching profile over HTTP from http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/profile?seconds=60
Saved profile in /Users/eddycjy/pprof/pprof.samples.cpu.007.pb.gz
Type: cpu
Duration: 1mins, Total samples = 26.55s (44.15%)
Entering interactive mode (type "help" for commands, "o" for options)
(pprof) pprof help(pprof) top10
Showing nodes accounting for 25.92s, 97.63% of 26.55s total
Dropped 85 nodes (cum <= 0.13s)
Showing top 10 nodes out of 21
flat flat% sum% cum cum%
23.28s 87.68% 87.68% 23.29s 87.72% syscall.Syscall
0.77s 2.90% 90.58% 0.77s 2.90% runtime.memmove
0.58s 2.18% 92.77% 0.58s 2.18% runtime.freedefer
0.53s 2.00% 94.76% 1.42s 5.35% runtime.scanobject
0.36s 1.36% 96.12% 0.39s 1.47% runtime.heapBitsForObject
0.35s 1.32% 97.44% 0.45s 1.69% runtime.greyobject
0.02s 0.075% 97.51% 24.96s 94.01% main.main.func1
0.01s 0.038% 97.55% 23.91s 90.06% os.(*File).Write
0.01s 0.038% 97.59% 0.19s 0.72% runtime.mallocgc
0.01s 0.038% 97.63% 23.30s 87.76% syscall.Write- flat:给定函数上运行耗时
- flat%:同上的 CPU 运行耗时总比例
- sum%:给定函数累积使用 CPU 总比例
- cum:当前函数加上它之上的调用运行总耗时
- cum%:同上的 CPU 运行耗时总比例
最后一列为函数名称,在大多数的情况下,我们可以通过这五列得出一个应用程序的运行情况,加以优化 🤔
$ go tool pprof http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/heap
Fetching profile over HTTP from http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/heap
Saved profile in /Users/eddycjy/pprof/pprof.alloc_objects.alloc_space.inuse_objects.inuse_space.008.pb.gz
Type: inuse_space
Entering interactive mode (type "help" for commands, "o" for options)
(pprof) top
Showing nodes accounting for 837.48MB, 100% of 837.48MB total
flat flat% sum% cum cum%
837.48MB 100% 100% 837.48MB 100% main.main.func1- -inuse_space:分析应用程序的常驻内存占用情况
- -alloc_objects:分析应用程序的内存临时分配情况
三、PProf 可视化界面
这是令人期待的一小节。在这之前,我们需要简单的编写好测试用例来跑一下
编写测试用例
(1)新建 data/d_test.go,文件内容:
package data
import "testing"
const url = "https://github.com/EDDYCJY"
func TestAdd(t *testing.T) {
s := Add(url)
if s == "" {
t.Errorf("Test.Add error!")
}
}
func BenchmarkAdd(b *testing.B) {
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
Add(url)
}
}(2)执行测试用例
$ go test -bench=. -cpuprofile=cpu.prof
pkg: github.com/EDDYCJY/go-pprof-example/data
BenchmarkAdd-4 10000000 187 ns/op
PASS
ok github.com/EDDYCJY/go-pprof-example/data 2.300s-memprofile 也可以了解一下
启动 PProf 可视化界面
方法一:
$ go tool pprof -http=:8080 cpu.prof方法二:
$ go tool pprof cpu.prof
$ (pprof) webCould not execute dot; may need to install graphviz.graphviz查看 PProf 可视化界面
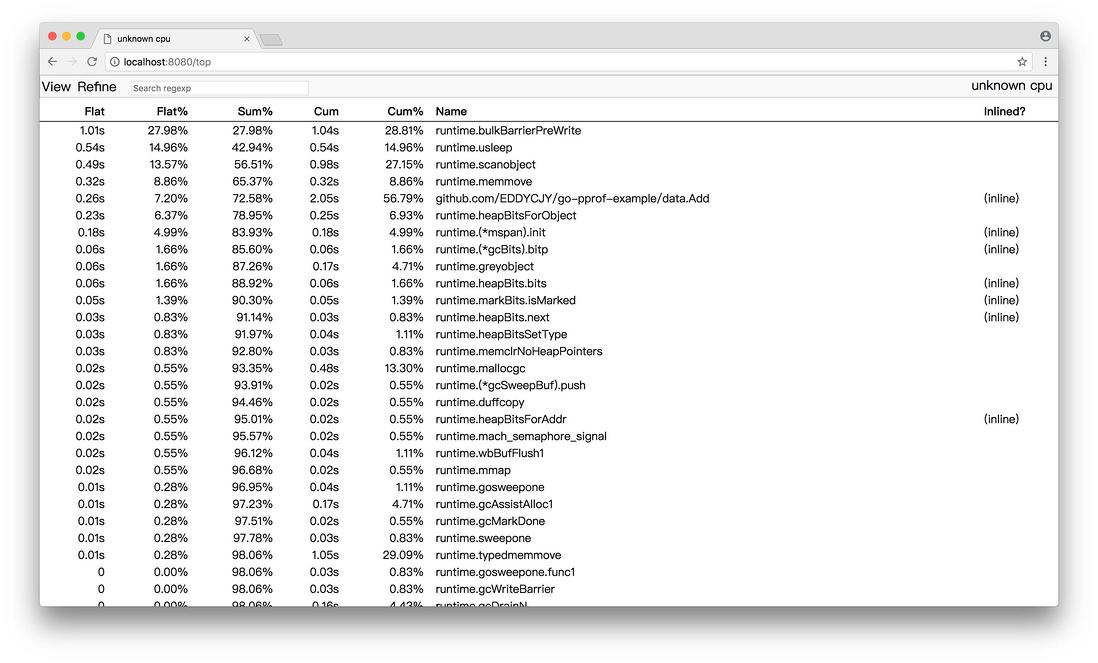
(1)Top
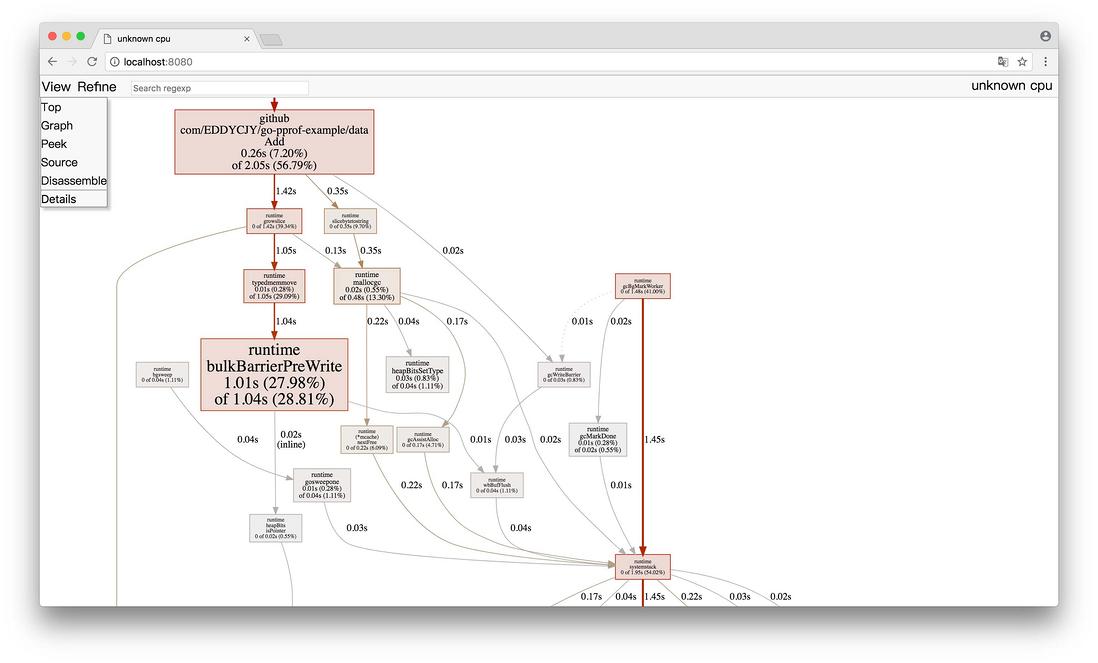
(2)Graph
框越大,线越粗代表它占用的时间越大哦
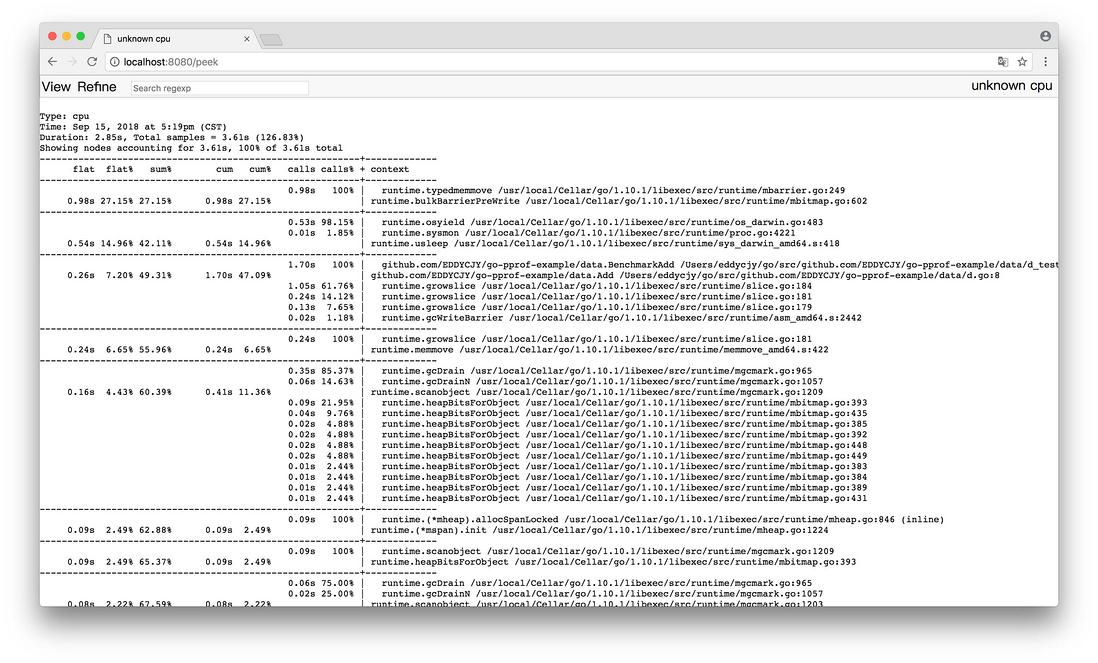
(3)Peek
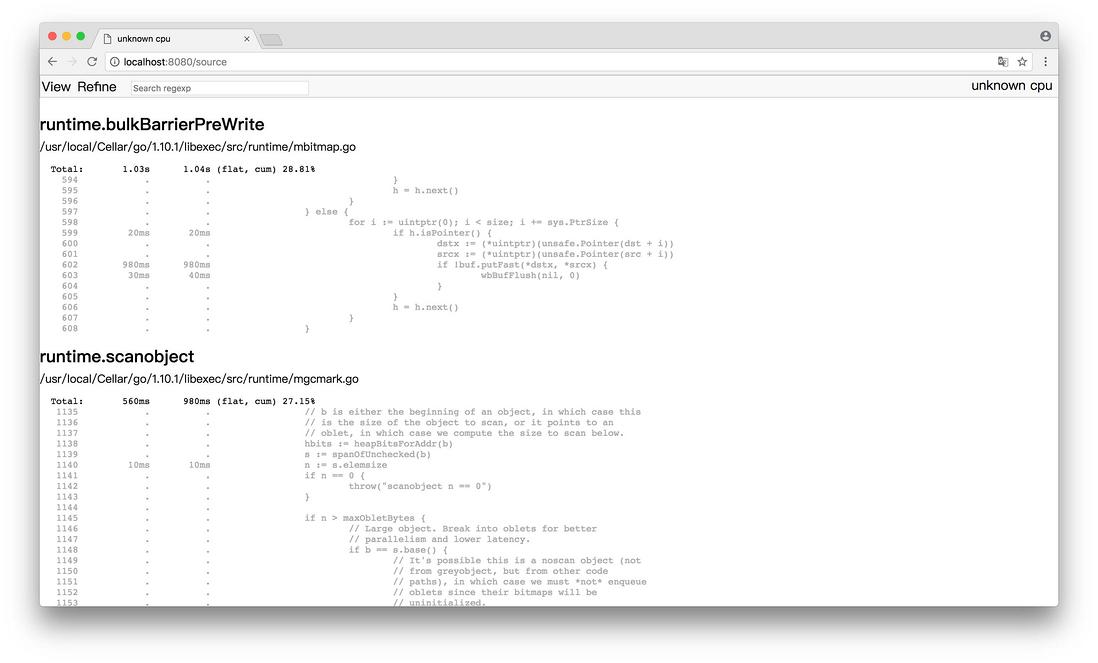
(4)Source
通过 PProf 的可视化界面,我们能够更方便、更直观的看到 Go 应用程序的调用链、使用情况等,并且在 View 菜单栏中,还支持如上多种方式的切换
你想想,在烦恼不知道什么问题的时候,能用这些辅助工具来检测问题,是不是瞬间效率翻倍了呢 👌
四、PProf 火焰图
另一种可视化数据的方法是火焰图,需手动安装原生 PProf 工具:
(1) 安装 PProf
$ go get -u github.com/google/pprof(2) 启动 PProf 可视化界面:
$ pprof -http=:8080 cpu.prof(3) 查看 PProf 可视化界面
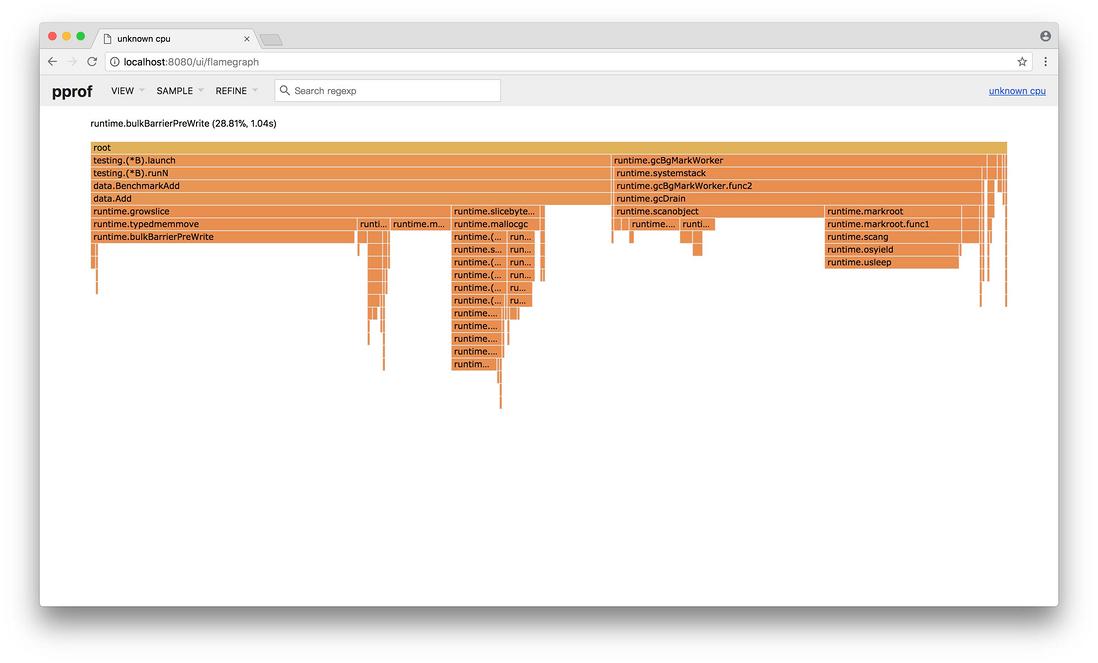
打开 PProf 的可视化界面时,你会明显发现比官方工具链的 PProf 精致一些,并且多了 Flame Graph(火焰图)
它就是本次的目标之一,它的最大优点是动态的。调用顺序由上到下(A -> B -> C -> D),每一块代表一个函数,越大代表占用 CPU 的时间更长。同时它也支持点击块深入进行分析!
总结
在本章节,粗略地介绍了 Go 的性能利器 PProf。在特定的场景中,PProf 给定位、剖析问题带了极大的帮助
希望本文对你有所帮助,另外建议能够自己实际操作一遍,最好是可以深入琢磨一下,内含大量的用法、知识点 🤓
思考题
你很优秀的看到了最后,那么有两道简单的思考题,希望拓展你的思路
(1)flat 一定大于 cum 吗,为什么?什么场景下 cum 会比 flat 大?
(2)本章节的 demo 代码,有什么性能问题?怎么解决它?
来,晒出你的想法!😆