目录
0. 简介
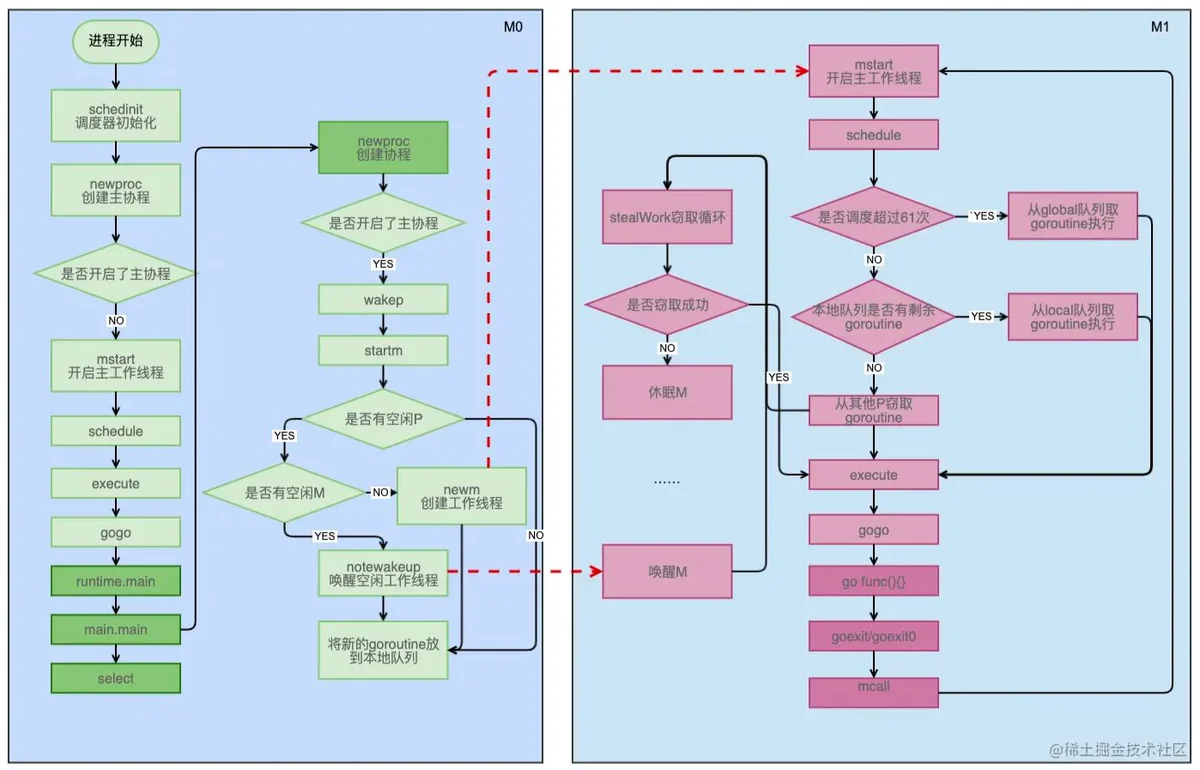
goroutine1. 协程调度发生的时机
goroutine| 情形 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| go func(){} | 使用go关键字创建一个新的goroutine,调度器会考虑调度 |
| GC | 由于GC也需要在系统线程M上执行,且其中需要所有的goroutine都停止运行,所以也会发生调度 |
| 系统调用 | 发生系统的调用时,会阻塞M,所以它会被调度走,同时新的goroutine也会被调度上来 |
| 同步内存访问 | mutex、channel等操作会使得goroutine阻塞,因此会被调度走,等条件满足后,还会被调度上来继续运行 |
2. 创建协程时的调度
gofunc newproc(fn *funcval) {
gp := getg()
pc := getcallerpc()
systemstack(func() {
newg := newproc1(fn, gp, pc)
_p_ := getg().m.p.ptr()
runqput(_p_, newg, true)
if mainStarted {
wakep()
}
})
}
goGoruntime.newprocmain goroutineruntime.mainmainStartedtrueruntime.wakepfunc wakep() {
if atomic.Load(&sched.npidle) == 0 {
return
}
// be conservative about spinning threads
if atomic.Load(&sched.nmspinning) != 0 || !atomic.Cas(&sched.nmspinning, 0, 1) {
return
}
startm(nil, true)
}
wakepspinningstartmfunc startm(_p_ *p, spinning bool) {
// Disable preemption.
//
// Every owned P must have an owner that will eventually stop it in the
// event of a GC stop request. startm takes transient ownership of a P
// (either from argument or pidleget below) and transfers ownership to
// a started M, which will be responsible for performing the stop.
//
// Preemption must be disabled during this transient ownership,
// otherwise the P this is running on may enter GC stop while still
// holding the transient P, leaving that P in limbo and deadlocking the
// STW.
//
// Callers passing a non-nil P must already be in non-preemptible
// context, otherwise such preemption could occur on function entry to
// startm. Callers passing a nil P may be preemptible, so we must
// disable preemption before acquiring a P from pidleget below.
mp := acquirem() // 保证在此期间不会发生栈扩展
lock(&sched.lock)
if _p_ == nil { // 没有指定p,那么需要从空闲队列中取一个p
_p_ = pidleget()
if _p_ == nil {// 如果没有空闲的p,直接返回
unlock(&sched.lock)
if spinning {
// The caller incremented nmspinning, but there are no idle Ps,
// so it's okay to just undo the increment and give up.
if int32(atomic.Xadd(&sched.nmspinning, -1)) < 0 {
throw("startm: negative nmspinning")
}
}
releasem(mp)
return
}
}
nmp := mget() // 如果有空闲的p,那么取出一个空闲的m
if nmp == nil {// 如果没有空闲的m,那么调用newm创建一个,然后返回
// No M is available, we must drop sched.lock and call newm.
// However, we already own a P to assign to the M.
//
// Once sched.lock is released, another G (e.g., in a syscall),
// could find no idle P while checkdead finds a runnable G but
// no running M's because this new M hasn't started yet, thus
// throwing in an apparent deadlock.
//
// Avoid this situation by pre-allocating the ID for the new M,
// thus marking it as 'running' before we drop sched.lock. This
// new M will eventually run the scheduler to execute any
// queued G's.
id := mReserveID()
unlock(&sched.lock)
var fn func()
if spinning {
// The caller incremented nmspinning, so set m.spinning in the new M.
fn = mspinning
}
newm(fn, _p_, id)
// Ownership transfer of _p_ committed by start in newm.
// Preemption is now safe.
releasem(mp)
return
}
unlock(&sched.lock)
if nmp.spinning {
throw("startm: m is spinning")
}
if nmp.nextp != 0 {
throw("startm: m has p")
}
if spinning && !runqempty(_p_) {
throw("startm: p has runnable gs")
}
// The caller incremented nmspinning, so set m.spinning in the new M.
nmp.spinning = spinning
nmp.nextp.set(_p_)
notewakeup(&nmp.park) // 如果有空闲的m,则唤醒这个m
// Ownership transfer of _p_ committed by wakeup. Preemption is now
// safe.
releasem(mp)
}
startmwakepgoroutinegoroutinegoroutinegoroutinegoroutinefindrunnablefunc findrunnable() (gp *g, inheritTime bool) {
_g_ := getg()
top:
_p_ := _g_.m.p.ptr()
...
// local runq
// 再从本地队列找找
if gp, inheritTime := runqget(_p_); gp != nil {
return gp, inheritTime
}
// global runq
// 再看看全局队列
if sched.runqsize != 0 {
lock(&sched.lock)
gp := globrunqget(_p_, 0)
unlock(&sched.lock)
if gp != nil {
return gp, false
}
}
...
// Spinning Ms: steal work from other Ps.
//
// Limit the number of spinning Ms to half the number of busy Ps.
// This is necessary to prevent excessive CPU consumption when
// GOMAXPROCS>>1 but the program parallelism is low.
procs := uint32(gomaxprocs)
if _g_.m.spinning || 2*atomic.Load(&sched.nmspinning) < procs-atomic.Load(&sched.npidle) {
if !_g_.m.spinning {
_g_.m.spinning = true
atomic.Xadd(&sched.nmspinning, 1)
}
gp, inheritTime, tnow, w, newWork := stealWork(now) // 调用stealWork盗取goroutine
now = tnow
if gp != nil {
// Successfully stole.
return gp, inheritTime
}
if newWork {
// There may be new timer or GC work; restart to
// discover.
goto top
}
if w != 0 && (pollUntil == 0 || w < pollUntil) {
// Earlier timer to wait for.
pollUntil = w
}
}
...
// return P and block
// 上面的窃取没有成功,那么解除m和p的绑定,摒弃娥江p放到空闲队列,然后去休眠
lock(&sched.lock)
if sched.gcwaiting != 0 || _p_.runSafePointFn != 0 {
unlock(&sched.lock)
goto top
}
if sched.runqsize != 0 {
gp := globrunqget(_p_, 0)
unlock(&sched.lock)
return gp, false
}
if releasep() != _p_ {
throw("findrunnable: wrong p")
}
pidleput(_p_)
unlock(&sched.lock)
...
_g_.m.spinning = false // m即将睡眠,状态不再是spinning
if int32(atomic.Xadd(&sched.nmspinning, -1)) < 0 {
throw("findrunnable: negative nmspinning")
}
...
stopm() // 休眠
goto top
}
goroutinewakepstartmstealWorkstopmfunc stopm() {
_g_ := getg()
if _g_.m.locks != 0 {
throw("stopm holding locks")
}
if _g_.m.p != 0 {
throw("stopm holding p")
}
if _g_.m.spinning {
throw("stopm spinning")
}
lock(&sched.lock)
mput(_g_.m) // 把m放到sched.midle空闲队列
unlock(&sched.lock)
mPark()
acquirep(_g_.m.nextp.ptr()) // 绑定这个m和其下一个p,这里没有看懂为啥这么操作
_g_.m.nextp = 0
}
func mPark() {
gp := getg()
notesleep(&gp.m.park) // 进入睡眠状态
noteclear(&gp.m.park)
}
stopmnotesleepnotego runtimenotesleepnotewakeup小结
goroutinewakep非main goroutinemstartmstartstartmschedulegoroutinegoroutinegoroutine如果是去唤醒工作协程,唤醒后会在休眠的地方开始,重新进行窃取。
窃取到工作协程后,就会去执行,然后就会因为各种原因重新开始调度循环。
3. 主动挂起
Gogoroutinechannelgoroutine3.1 协程挂起
channelv := <- ch v, ok := <- ch
chanrecv1chanrecv2//go:nosplit
func chanrecv1(c *hchan, elem unsafe.Pointer) {
chanrecv(c, elem, true)
}
//go:nosplit
func chanrecv2(c *hchan, elem unsafe.Pointer) (received bool) {
_, received = chanrecv(c, elem, true)
return
}
chanrecvfunc chanrecv(c *hchan, ep unsafe.Pointer, block bool) (selected, received bool) {
...
c.recvq.enqueue(mysg) // 将这个goroutine放到channel的recv的queue中
atomic.Store8(&gp.parkingOnChan, 1)
// 挂起这个goroutine
gopark(chanparkcommit, unsafe.Pointer(&c.lock), waitReasonChanReceive, traceEvGoBlockRecv, 2)
...
}
chanrecvgoroutinechannelrecvqueuegoparkgoroutinefunc gopark(unlockf func(*g, unsafe.Pointer) bool, lock unsafe.Pointer, reason waitReason, traceEv byte, traceskip int) {
if reason != waitReasonSleep {
checkTimeouts() // timeouts may expire while two goroutines keep the scheduler busy
}
mp := acquirem()
gp := mp.curg
status := readgstatus(gp)
if status != _Grunning && status != _Gscanrunning {
throw("gopark: bad g status")
}
mp.waitlock = lock
mp.waitunlockf = unlockf
gp.waitreason = reason
mp.waittraceev = traceEv
mp.waittraceskip = traceskip
releasem(mp)
// can't do anything that might move the G between Ms here.
mcall(park_m)
}
goparkmcallgoroutineg0park_m// park continuation on g0.
func park_m(gp *g) {
_g_ := getg()
if trace.enabled {
traceGoPark(_g_.m.waittraceev, _g_.m.waittraceskip)
}
casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gwaiting)
dropg()
if fn := _g_.m.waitunlockf; fn != nil {
ok := fn(gp, _g_.m.waitlock)
_g_.m.waitunlockf = nil
_g_.m.waitlock = nil
if !ok {
if trace.enabled {
traceGoUnpark(gp, 2)
}
casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunnable)
execute(gp, true) // Schedule it back, never returns.
}
}
schedule()
}
park_mgoroutine_Gwaitinggoroutinechanneldropggmschedulegoroutine3.2 协程唤醒
goroutinechannelfunc chansend(c *hchan, ep unsafe.Pointer, block bool, callerpc uintptr) bool {
...
if sg := c.recvq.dequeue(); sg != nil {
// Found a waiting receiver. We pass the value we want to send
// directly to the receiver, bypassing the channel buffer (if any).
send(c, sg, ep, func() { unlock(&c.lock) }, 3)
return true
}
...
}
func send(c *hchan, sg *sudog, ep unsafe.Pointer, unlockf func(), skip int) {
...
goready(gp, skip+1)
}
channelsendgoreadyfunc goready(gp *g, traceskip int) {
systemstack(func() {
ready(gp, traceskip, true)
})
}
func ready(gp *g, traceskip int, next bool) {
if trace.enabled {
traceGoUnpark(gp, traceskip)
}
status := readgstatus(gp)
// Mark runnable.
_g_ := getg()
mp := acquirem() // disable preemption because it can be holding p in a local var
if status&^_Gscan != _Gwaiting {
dumpgstatus(gp)
throw("bad g->status in ready")
}
// status is Gwaiting or Gscanwaiting, make Grunnable and put on runq
casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunnable)
runqput(_g_.m.p.ptr(), gp, next)
wakep()
releasem(mp)
}
readywakepgoroutinegoroutine到这里,一个被挂起的协程也就被唤醒了。
4. 小结
channel
您可能感兴趣的文章:
