/*
#include <stdio.h>
void say(){
printf("hello world\n");
}
*/
import "C"
func main() {
/*
1.C语言的代码都需要利用单行注册或者多行注释注释起来
2.在C语言代码紧随其后的位置写上import "C"
3.就可以在go代码中通过C.函数名称 方式来访问C语言的函数
注意点:
1,C语言代码的注释和import "C"之间不写能任何其他的内容
2.C语言的代码可以利用多行注释注释起来, 也可以利用单行注释注释起来
*/
C.say()
}
例如,用Go语言调用C语言的贪吃蛇(贪吃蛇代码来自近期我完成的软件工程专业导论的作业代码)可以实现如下。新创建一个文件夹,里面声明属于包main的文件snake.go
package main;
/*
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
static struct termios ori_attr, cur_attr;
static __inline
int tty_reset(void)
{
if (tcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO, TCSANOW, &ori_attr) != 0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
static __inline
int tty_set(void)
{
if ( tcgetattr(STDIN_FILENO, &ori_attr) )
return -1;
memcpy(&cur_attr, &ori_attr, sizeof(cur_attr) );
cur_attr.c_lflag &= ~ICANON;
// cur_attr.c_lflag |= ECHO;
cur_attr.c_lflag &= ~ECHO;
cur_attr.c_cc[VMIN] = 1;
cur_attr.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
if (tcsetattr(STDIN_FILENO, TCSANOW, &cur_attr) != 0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
static __inline
int kbhit(void)
{
fd_set rfds;
struct timeval tv;
int retval;
// Watch stdin (fd 0) to see when it has input.
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_SET(0, &rfds);
// Wait up to five seconds.
tv.tv_sec = 0;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
retval = select(1, &rfds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
// Don't rely on the value of tv now!
if (retval == -1) {
perror("select()");
return 0;
} else if (retval)
return 1;
// FD_ISSET(0, &rfds) will be true.
else
return 0;
return 0;
}
// long long getSystemTime(){
// struct timeb t;
// ftime(&t);
// return 1000ll * t.time + t.millitm;
// }
//将你的 snake 代码放在这里
#define SNAKE_MAX_LENGTH 100 //贪吃蛇的最大长度
#define SNAKE_HEAD 'H' //贪吃蛇头部的字符标记
#define SNAKE_BODY 'X' //贪吃蛇身体的字符标记
#define BLANK_CELL ' ' //地图上空地的字符标记
#define SNAKE_FOOD '$' //地图上食物的字符标记
#define WALL_CELL '*' //地图上墙壁/障碍的字符标记
#define MAP_HEIGHT 12 //地图高度
#define MAP_WIDTH 12 //地图宽度
#define PRINT_COUNT 75000//循环多少次刷新一次地图
#define MOVE_TIME (CLOCKS_PER_SEC*6/10)//移动的时间间隔(毫秒)
#define EXTRA_MOVE (MOVE_TIME/6)//立即(连续)切换方向时获得的速度增益
char gameMap[MAP_HEIGHT + 1][MAP_WIDTH + 1]=//预定义的地图
{"************",
"*XXXXH *",
"* *** *",
"* *",
"* * *",
"* * *",
"* * *",
"* * *",
"* * *",
"* * *",
"* *",
"************"};
char START_DIRECTION = 'D';
int snakeX[SNAKE_MAX_LENGTH] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1};//蛇占据的位置X坐标 从0开始增大表示蛇头到蛇尾
int snakeY[SNAKE_MAX_LENGTH] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};//蛇占据的位置Y坐标 从0开始增大表示蛇头到蛇尾
int snake_length = 5;//蛇的长度
int headX = 1;//蛇头X坐标
int headY = 5;//蛇头Y坐标
int eat, score = 0;//eat表示蛇是否吃到了食物 score表示当前游戏得分
void printMap(){//输出游戏界面
printf("\033[2J");//清空屏幕
printf("\033[1;1H");
printf("pressed `q` to quit!\n");
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < MAP_HEIGHT; ++i){//逐行输出地图
for(j = 0; j < MAP_WIDTH; ++j){//每一行逐个字符输出地图
if (gameMap[i][j] == SNAKE_HEAD || gameMap[i][j] == SNAKE_BODY)
printf("\033[42;34m%c\033[0m", gameMap[i][j]);
else if (gameMap[i][j] == SNAKE_FOOD)
printf("\033[43;31m%c\033[0m", gameMap[i][j]);
else
putchar(gameMap[i][j]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
printf("Score: %d\n", score);//输出分数
}
void get_move(char ch, int *dx, int *dy){//根据ch字符获得X,Y坐标对应的方向增量
switch (ch){
case 'w': case 'W'://向上
*dx = -1;
*dy = 0;
break;
case 'a': case 'A'://向左
*dx = 0;
*dy = -1;
break;
case 's': case 'S'://向下
*dx = 1;
*dy = 0;
break;
case 'd': case 'D'://向右
*dx = 0;
*dy = 1;
break;
default://其他方向无效
*dx = 0;
*dy = 0;
break;
}
}
void updateGameMap(){//更新游戏地图
if (!eat)//没有增长蛇的身体
gameMap[snakeX[snake_length - 1]][snakeY[snake_length - 1]] = BLANK_CELL;//蛇身体最后一个格子要变为空格(因为离开了格子且蛇没有增长) 否则不用变为空格
gameMap[snakeX[0]][snakeY[0]] = SNAKE_BODY;//之前的蛇头所在格子变为蛇的身体所在格子
gameMap[headX][headY] = SNAKE_HEAD;//新移动到的格子字符变为蛇头标记
}
void updateSnake(){//更新蛇身体占据位置的数组
if (eat)//吃到了 增加身体长度
++snake_length;
int i;
for(i = snake_length - 1; i; --i){//每一个位置的坐标更新为移动之前的蛇身体上一个位置坐标
snakeX[i] = snakeX[i - 1];
snakeY[i] = snakeY[i - 1];
}
snakeX[0] = headX;//蛇头坐标更新为新移动到的格子坐标
snakeY[0] = headY;
}
void snakeMoveTo(const int dx, const int dy){//蛇移动到相邻的(dx, dy)坐标
headX = dx;//更新头部坐标
headY = dy;
updateGameMap(); //更新地图
updateSnake();//更新蛇身体占据位置的坐标
}
void putFood(){//放置食物
int x, y;
while (1){
x = rand() % MAP_HEIGHT;//随机选择一个X
y = rand() % MAP_WIDTH;//随机选择一个Y
if (gameMap[x][y] == BLANK_CELL){//是空地
gameMap[x][y] = SNAKE_FOOD;//变成食物
break;//成功放置 退出
}
}
}
char str[50];//读入的用户输入缓冲区
int snake(){
//设置终端进入非缓冲状态
int tty_set_flag;
tty_set_flag = tty_set();
int dx, dy, nx, ny, newdx, newdy;
get_move(START_DIRECTION, &dx, &dy);//获得X坐标,Y坐标增量
//将你的 snake 代码放在这里
srand(time(NULL));//随机种子初始化
putFood();//放置一个食物
int count = 0;
// long long lasTime = getSystemTime(), nowTime;
clock_t lasTime = clock(), nowTime;
printMap();//输出地图
while(1) {
++count;
if (count == PRINT_COUNT){
printMap();//输出地图
count = 0;
}
if(kbhit()) {
const int key = getchar();
// printf("%c pressed\n", key);
if(key == 'q')
break;
get_move(key, &newdx, &newdy);//获得X坐标,Y坐标增量
if ((newdx || newdy) && !(newdx == -dx && newdy == -dy)){//如果方向不是蛇上一次移动的反方向 且为有效的移动方向 则更新方向
dx = newdx;
dy = newdy;
lasTime -= EXTRA_MOVE;
}
}else{
// fprintf(stderr, "<no key detected>\n");
}
nowTime = clock();//getSystemTime();
if (nowTime >= lasTime + MOVE_TIME){
nx = dx + headX;//更新按当前步走之后到达的位置坐标
ny = dy + headY;
if (gameMap[nx][ny] == WALL_CELL || gameMap[nx][ny] == SNAKE_BODY)//为墙壁 或者 蛇的身体 游戏结束
break;
eat = 0;//先标记为没有吃到
if (gameMap[nx][ny] == SNAKE_FOOD){//是食物
if (snake_length < SNAKE_MAX_LENGTH)//如果没有超过蛇允许的最大长度
eat = 1;//蛇变长
++score;//分数增加
}
snakeMoveTo(nx, ny);//移动
if (eat)//吃掉了食物
putFood();//需要重新放置食物
lasTime = nowTime;
}
}
printf("Game Over!!!\n");//输出失败信息
//恢复终端设置
if(tty_set_flag == 0)
tty_reset();
return 0;
}
*/
import "C"
func main() {
C.snake()
}
运行结果如下:


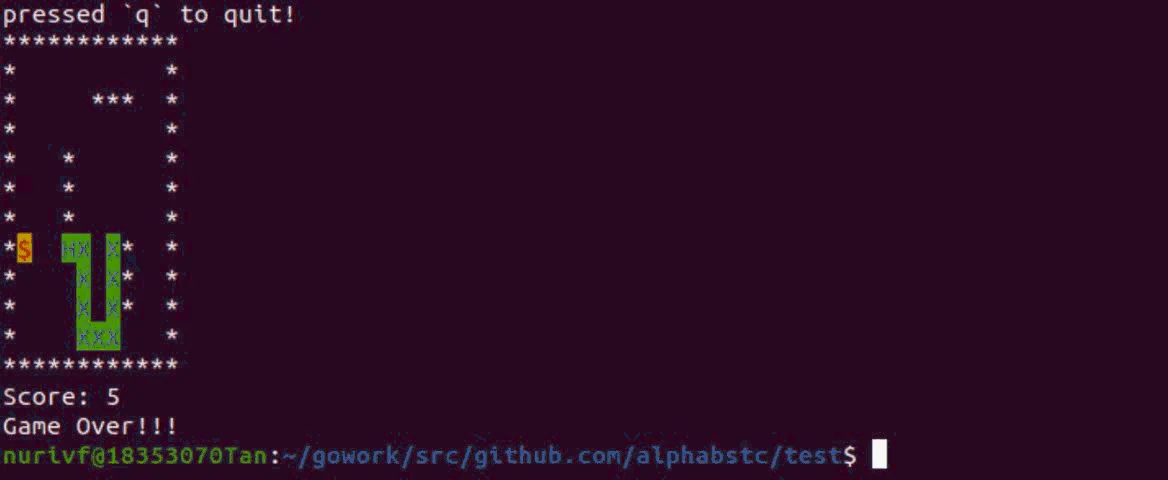
可以看到,对于复杂的C语言代码(包含很多函数,全局变量,以及许多引用的头文件与宏定义,条件编译等代码与语法特性),Go语言均可以兼容并可以方便地调用内嵌C函数,运行结果也没有出现问题。Go语言对于调用内嵌C函数提供了健壮稳定的支持。
