今天学习下Golang中多模块的基础知识,学习多模块的运行原理,使用多模块的方式,可以让开发者的代码在其他多个模块中构建、运行。提高代码的复用,从而提高开发效率。
在今天的学习中,将在工作工作空间中创建两个模块,然后进行模块之间的引用,并运行程序结果。
前提条件
基本要求
- Go 1.18 及更高版本
- 合适的编译工具 - text编辑器也满足要求
- 命令终端 - Linux、Mac系统shell, Windows系统的Cmd、PowerShell
本地环境
- Go 版本信息
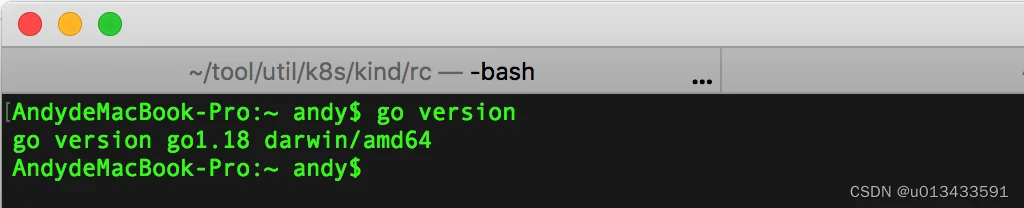
- 系统信息 - MacOS
- 编辑工具 - Sublime Text
代码开发
创建模块
$ mkdir workspace
$ cd workspace
$ mkdir hello
$ cd hello
$ go mod init example.com/hello
go: creating new go.mod: module example.com/hello
$ go get golang.org/x/example
package main
import (
"fmt"
"golang.org/x/example/stringutil"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(stringutil.Reverse("Hello"))
}
$ go run example.com/hello
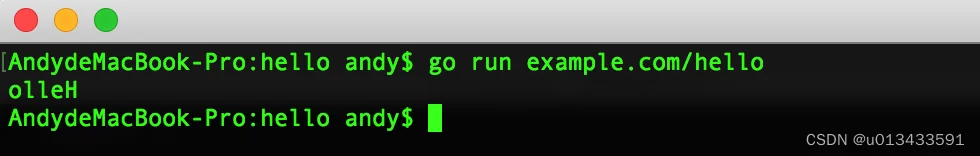
创建工作空间
在这一步中,创建go.workwe
$ go work init ./hello
$ go run example.com/hello
Go命令将工作空间中的所有模块作为主模块。这允许我们引用模块内的包,甚至模块外的包。在模块或工作区外运行go run命令将导致错误,因为go命令不知道要使用哪些模块。
接下来,我们将向工作区添加golang.org/x/example模块的本地副本。然后,我们将向stringtil包添加一个新函数,我们可以使用它来代替Reverse。
修改源码
在这一步中,我们将下载包含golang.org/x/example模块的Git repo副本,将其添加到工作区,然其中添加一个新函数,然后将从hello程序中使用该函数。
$ git clone https://go.googlesource.com/example
Cloning into 'example'...
remote: Total 165 (delta 27), reused 165 (delta 27)
Receiving objects: 100% (165/165), 434.18 KiB | 1022.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (27/27), done.
go work use ./example
package stringutil
import "unicode"
// ToUpper uppercases all the runes in its argument string.
func ToUpper(s string) string {
r := []rune(s)
for i := range r {
r[i] = unicode.ToUpper(r[i])
}
return string(r)
}
func main() {
fmt.Println(stringutil.ToUpper("Hello"))
fmt.Println(stringutil.Reverse("Hello"))
}
go run example.com/hello
至此,我们学会了拉取github上的原代码,并学会了如何新增函数,如何调用。
