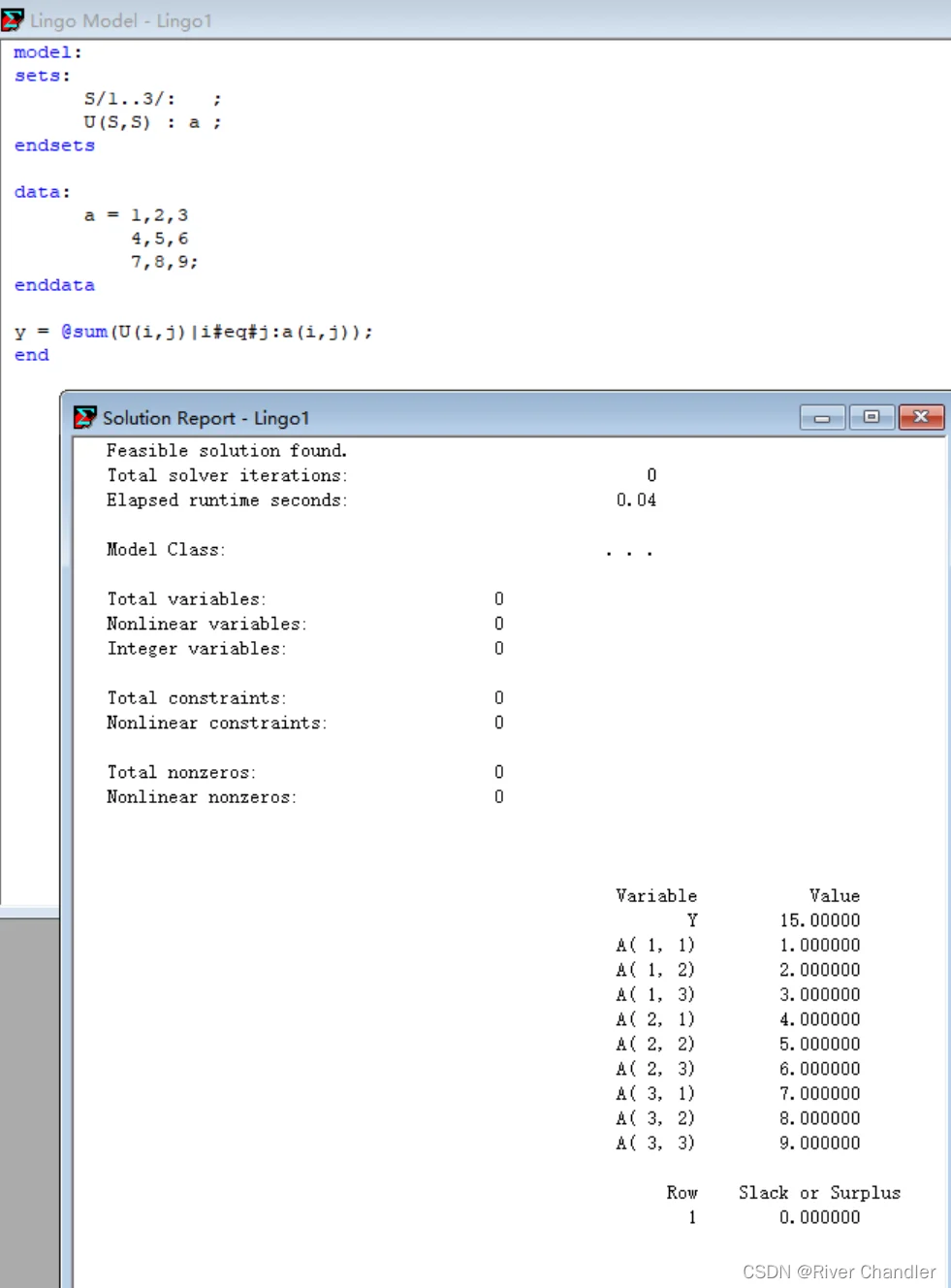
关系运算符
- Lingo 仅识别 "=",">=","<="三种运算符
算术运算符
- 就是 + - 啥的
逻辑运算符
#eq# !相等;
#ne# !不相等;
#gt#
#ge#
#lt#
#le#
#not#
#and#
#or#例
初等函数
@sin(x);
@cos(x);
@tan(x);
@log(x) ! x的自然对数值,其他应当使用换底公式;
@exp(x);边界函数
@bin(x) !x为0或者1;
@gin(x) !x为整数;
@free(x) !x为任意实数;
@bnd(v,x,u) !x的取值区间
!lingo 默认变量为非负实数集合函数
@for
@sum
@prod
@max
@min
@in
@size分支结构设计
例子
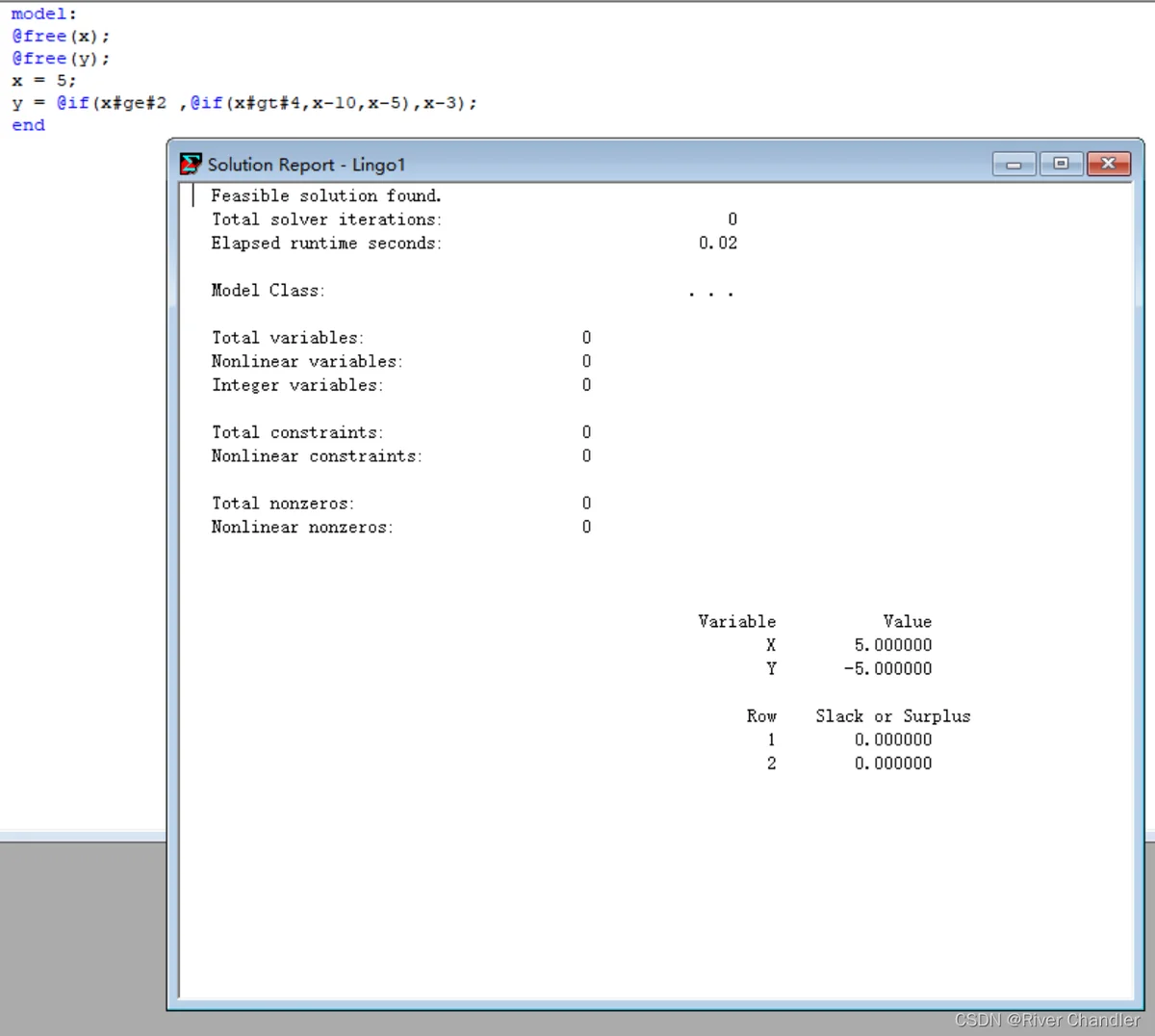
例
max = x1 + 2*x2 + x3;
x1 > x2;
x1 + x2 <= 5;
x1 + x3 >= 2;
@bin(x3);
@gin(x2);
@bnd(2,x1,10);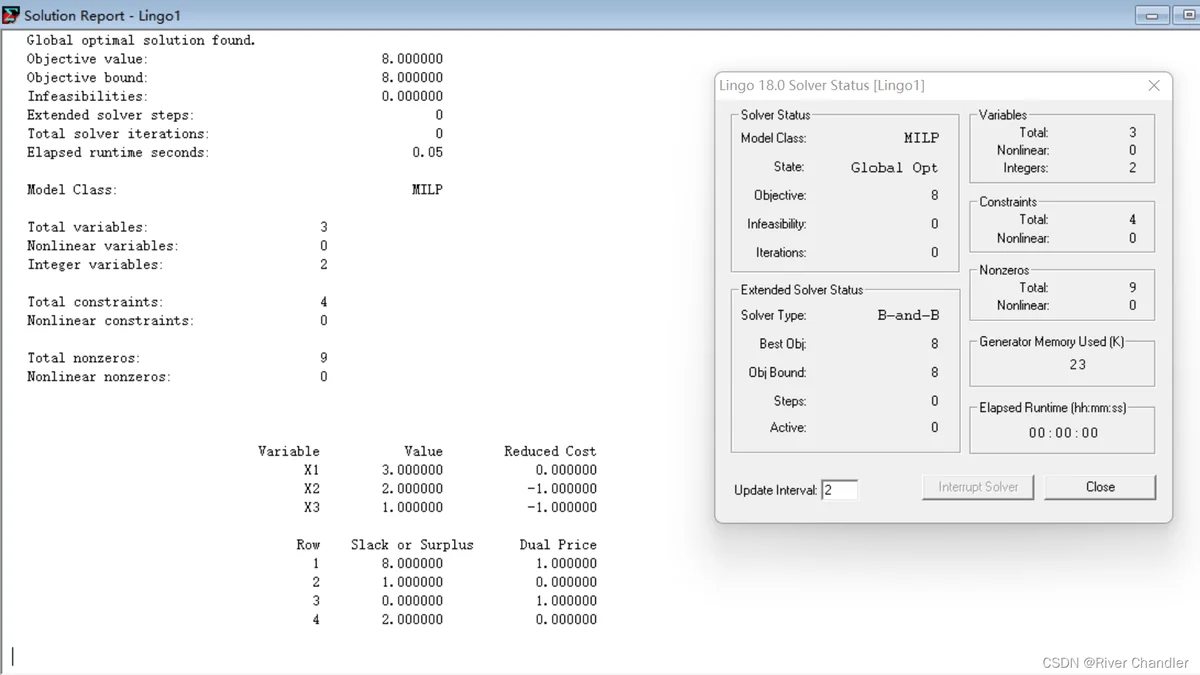
例
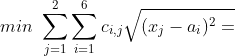
s.t.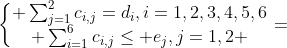
sets:
s/1..6/: a,b,d;
T/1..2/: e,x,y;
U(S,T): c;
endsets
data:
a = 1.25 8.75 0.5 5.75 3 7.25;
b = 1.25 0.75 4.75 5 6.5 7.25;
d = 3 5 4 7 6 11;
x = 5 2;
y = 1 7;
e = 20 20;
enddata
min = @sum(T(j):@sum(S(i):
c(i,j)*@sqrt((x(j)-a(i))^2+(y(j)-b(i))^2)));
@for(S(i):
@sum(T(j):c(i,j))=d(i));
@for(T(j):
@sum(S(i):c(i,j))<=e(j));
实战--最短路径问题
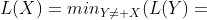
model:
sets:
cities/S,A1,A2,A3,B1,B2,C1,C2,T/:L;
roads(cities,cities)/
S,A1 S,A2 S,A3
A1,B1 A1,B2 A2,B1 A2,B2 A3,B1 A3,B2
B1,C1 B1,C2 B2,C1 B2,C2
C1,T C2,T/:D;
endsets
data:
D = 6,3,3
6 5 8 6 7 4
6 7 8 9
5 6;
L = 0, , , , , , , , ;
enddata
@for(cities(i)|i#GT#@index(S):
L(i)=@min(roads(j,i):L(j)+D(j,i)););
end Variable Value
L( S) 0.000000
L( A1) 6.000000
L( A2) 3.000000
L( A3) 3.000000
L( B1) 10.00000
L( B2) 7.000000
L( C1) 15.00000
L( C2) 16.00000
L( T) 20.00000打开全局求解器
- Solver -> Options -> Global Solver -> tick "Use Global Solver" -> apply -> OK
非线性求解应该设置初值
例
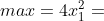
s.t.
model:
init:
x1 = 0.0;
x2 = 0.0;
x3 = 0.0;
endinit
max = 4*x1^2 + x2*@sin(@sqrt(x3));
x1^3 + x3^3 <= 3;
x1^5 - x2^2 >= 0;
x2^2 - x3^2 >= 0;
end 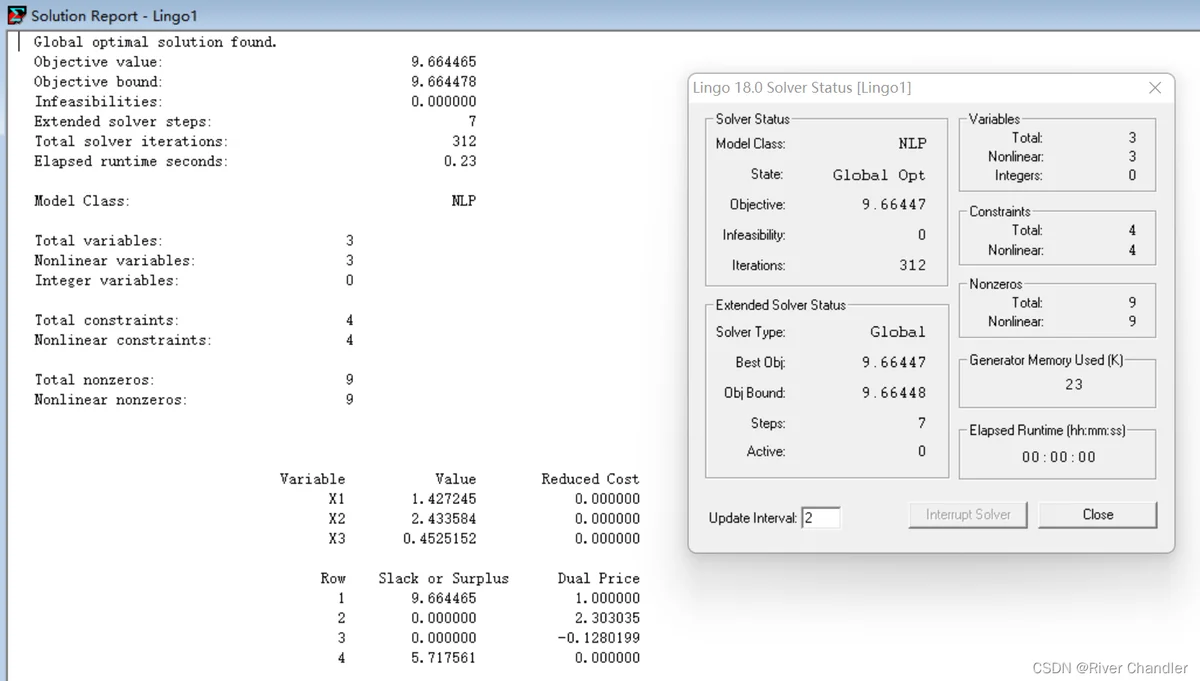
- 早期Lingo版本不支持积分运算
- 现在Lingo-18的版本,支持了,但又没完全支持,你不能指望Lingo有着C++的速度做着Mathematical的事
- Lingo积分只有一个命令,看上去就不像是能支持多元函数的
@INTEGRAL(y1,x,0,5,y);-
Lingo积分的使用就有点鸡肋了,很复杂
MODEL:
PROCEDURE y1:
y = 4*x^3;
ENDPROCEDURE
CALC:
PROB = @INTEGRAL(y1,x,0,5,y);
ENDCALC
END@INTEGRAL 函数在实际问题中的表现
MODEL:
sets:
U/1..3/:a,b;
endsets
data:
a = 1,2,3;
enddata
PROCEDURE y1:
y = b(2)*x^3;
ENDPROCEDURE
PROCEDURE y2:
y = b(1)*x^2;
ENDPROCEDURE
CALC:
PROB1 = @INTEGRAL(y1,x,0,5,y);
PROB2 = @INTEGRAL(y2,x,b(3),5,y);
ENDCALC
min = (PROB2-PROB1-(PROB2-b(3))^2)^b(1);
@bnd(2,b(3),4);
@bnd(1,b(2),4);
@bnd(3,b(1),7);
END解的报告
Local optimal solution found.
Objective value: -0.1582482E+11
Infeasibilities: 0.000000
Extended solver steps: 1
Best multistart solution found at step: 1
Total solver iterations: 4
Elapsed runtime seconds: 0.11
Model Class: NLP
Total variables: 4
Nonlinear variables: 2
Integer variables: 0
Total constraints: 1
Nonlinear constraints: 1
Total nonzeros: 2
Nonlinear nonzeros: 2
Variable Value Reduced Cost
Y 1.234568 0.000000
X 1.234568 0.000000
PROB1 192.9012 0.000000
PROB2 50.66597 0.000000
A( 1) 1.000000 0.000000
A( 2) 2.000000 0.000000
A( 3) 3.000000 0.000000
B( 1) 3.000000 0.000000
B( 2) 1.234568 0.000000
B( 3) 2.000000 0.1840500E+10
Row Slack or Surplus Dual Price
1 -0.1582482E+11 -1.000000
-
别的不说,就运算速度而言,0.11s
-
绝对完爆其他计算软件与程序啊!!!!
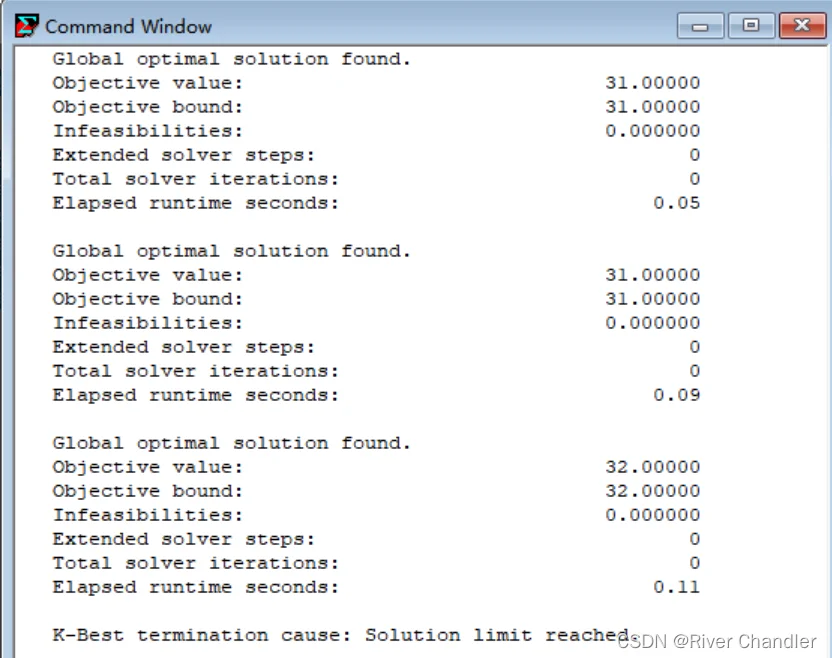
- Lingo 一般只会给出一个解,但对于整数规划来说,很可能会产生多个最优解
- 打开最优解控制器
- Solver >>> Integer Solver >>> K-Bset Solutions >>> Number
- 例:
model:
sets:
variables/1..10/:s,cost;
endsets
data:
cost=5 8 10 6 9 5 7 6 10 8;
enddata
min=@sum(variables(i):s(i)*cost(i));
(s(1)+s(7)-2)*(s(9)-1)=0;
s(3)*s(5)+s(4)*s(5)=0;
@sum(variables(i)|i#ge#5#and#i#le#8:s(i))<=2;
@sum(variables:s)=5;
@for(variables:@bin(s));
end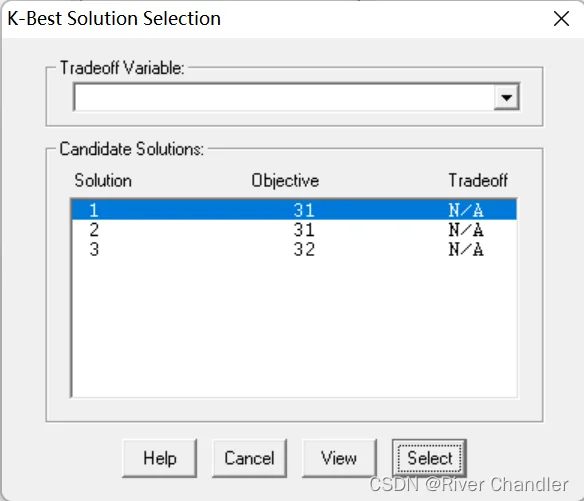
- 我先在这里问候一下SB的某川大学的大学物理实验课!评价SX!评价完。
lingo数据文件
- 读取函数@file(fname);
- 写入函数@text(fname);
这个以后再说吧。反正小规模问题也遇不上,再说了,数据在excel里,你不是还得输入一边吗。当然不是。- 读取函数是一行一行得读取的,至于一行一行的读取,那必然就需要你多次写入
- 希望这个时候你已经很好得理解了set语言了
- 很好,现在我们基本完成了我们所要初步掌握的做的全部操作
输出函数
- 输出函数@TEXT(["filename"])
示范样例
Model:
sets:
myset/@file(myfile.ldt)/:@file(myfile.ldt);
endsets
min = @sum(myset(i):ordered(i)*cost(i));
@for(myset(i):ordered(i)>need(i);
ordered(i)<supply(i));
data:
cost = @file(myfile.ldt);
need = @file(myfile.ldt);
supply = @file(myfile.ldt);
@text("example.txt")=ordered;
enddata
end-
其中myfile.lgt文件中的内容是
Seattle,Detroit,Chicago,Denver~
COST,NEED,SUPPLY,ORDERED~
12,28,15,20~
1600,1800,1200,1000~
1700,1900,1300,1100-
这玩意它长这个样子

Lingo与excel的交互
- 这个就稍微复杂一点儿了。
- 需要宏的知识并在还需要再学习几个lingo的函数
- 很好,那就这样吧。
Solver Status
- Model Class
| LP | 线性模型 |
| QP | 二次模型 |
| ILP | 整数线性模型 |
| IQP | 整数二次模型 |
| PILP | 纯整数线性模型 |
| PIQP | 纯整数二次模型 |
| NLP | 非线性模型 |
| 或者还有其他的。。一些怪怪的模型 |
- State
| Global Optimum | 全局最优 |
| Local Optimum | 局部最优 |
| Feasible | 可行的 |
| Infeasible | 不可行的 |
| Unbounded | 无界的 |
| Interrupted | |
| Undetermined |
- Objective
- max 或者 min 的值
- Infeasibility
- Interations
- 迭代次数
- 其他还有很多,但是我想也不是特别重要。。。
Solution Report
Local optimal solution found.
Objective value: 37.00000
Objective bound: 37.00000
Infeasibilities: 0.000000
Extended solver steps: 3
Total solver iterations: 71
Elapsed runtime seconds: 0.18
Model Class: MIQP
Total variables: 3
Nonlinear variables: 2
Integer variables: 2
Total constraints: 2
Nonlinear constraints: 2
Total nonzeros: 6
Nonlinear nonzeros: 2
Variable Value Reduced Cost
X1 1.000000 -1.000000
X2 4.000000 -9.000001
X3 9.000000 -4.000000
Row Slack or Surplus Dual Price
1 37.00000 1.000000
2 14.00000 0.000000
- 重点是
- Objective value
- Variable列
Help
- Register
- 非正版用户请忽略
- Help topics
- 有全部的帮助文档
- Global optimal solution found.
- 全局最优解找到.
- Objective value
- 最优目标值
-
Infeasibilities
-
指矛盾约束的个数
-
-
Total solver iterations
-
用单纯行法进行了两次迭代
-
-
Model Class
-
Total variables
-
Nonlinear variables
-
Integer variables
-
Total constraints
-
Nonlinear constraints
-
Total nonzeros
-
Nonlinear nonzeros
| Variable | Value | Reduced Cost | Row Slack or Surplus Dual Price |
| 变量 | 最优解中各变量的值 | 某个变量在解中的数值 增加一个单位, 目标函数值必须付出的代价 | 松弛变量,过剩变量 |
