目录
一、基本介绍
timetime.Timepackage main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
// 查看当前时间
now := time.Now()
// 直接使用时. 输出的是当前的时间. 时区. 毫秒数
fmt.Printf("now type = %T && now = %v",now,now)
}
输出:
now type = time.Time && now = 2021-12-04 14:26:56.096042 +0800 CST m=+0.002252801
2)查看各个时间显示信息
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
now := time.Now()
fmt.Printf("年 = %v\n",now.Year())
// 因为月份输出的是英文. 所以我们可以使用 int 进行转义
fmt.Printf("月 = %v\n",int(now.Month()))
fmt.Printf("日 = %v\n",now.Day())
fmt.Printf("时 = %v\n",now.Hour())
fmt.Printf("分 = %v\n",now.Minute())
fmt.Printf("秒 = %v\n",now.Second())
}
1.格式化日期时间
PrintfSprintfpackage main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
now := time.Now()
fmt.Printf("当前年月日: %d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d\n",now.Year(),now.Month(),now.Day(),now.Hour(),now.Minute(),now.Second())
dateStr := fmt.Sprintf("当前年月日: %d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d\n",now.Year(),now.Month(),now.Day(),now.Hour(),now.Minute(),now.Second())
fmt.Printf("dateStr = %v",dateStr)
}
time.Format()package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
now := time.Now()
// 查看当前年月份和时间
fmt.Printf(now.Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05"))
fmt.Println()
// 查看当前前年月份
fmt.Printf(now.Format("2006-01-02"))
fmt.Println()
// 查看当前时间
fmt.Println(now.Format("15:04:05"))
fmt.Println()
}
2006/01/02 15:04:052.时间的常量
conse (
Nanosecond = 1ns (纳秒)
Microsecond = 1000 * Nanosecond = 1 (微秒)
Millisecond = 1000 * Microsecond = 1 (毫秒)
Second = 1000 * Millisecond = 1 (秒)
Minute = 60 * Second = 1 (分钟)
Hour = 60 * Minute = 1 (小时)
)
100 * time.MillisecondSleeppackage main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
// 每隔 0.1 秒就打印一个数字. 打印到 100 时就退出
i := 0
for {
i++
fmt.Println(i)
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 100)
// 当条件满足时. 便退出循环
if i == 100 {
break
}
}
}
timepackage main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
now := time.Now()
fmt.Printf("Unix 的时间戳 = %v && Unixnano 的时间戳 = %v",now.Unix(),now.UnixNano())
}
输出:
Unix 的时间戳 = 1638604549 && Unixnano 的时间戳 = 1638604549410002500
1970 年 1 月 1 日二、使用介绍
test()package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"strconv"
)
func test() {
str := ""
for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ {
// strconv.Itoa 的作用就是将整数转换成字符串
str += "Hello" + strconv.Itoa(i)
}
}
func main() {
// 在执行 test() 前. 先获取到当前的 Unix 时间戳
start := time.Now().Unix()
test()
end := time.Now().Unix()
fmt.Printf("执行 test() 耗时时间为 %v 秒",end - start) // 用结束后的时间减去执行前的时间
}
1.内置函数
在 Go 中,开发者为了编程方便,提供了一些函数,这些函数可以直接使用,我们称为 Go 的内置函数。
lenstringarrayslicemapchannelnewintfloat32structmakechanneldmapslicebuiltinnewpackage main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
num := 100
fmt.Printf("num 的类型 = %T && num 的值 = %v && num 的内存地址 = %v\n",num,num,&num)
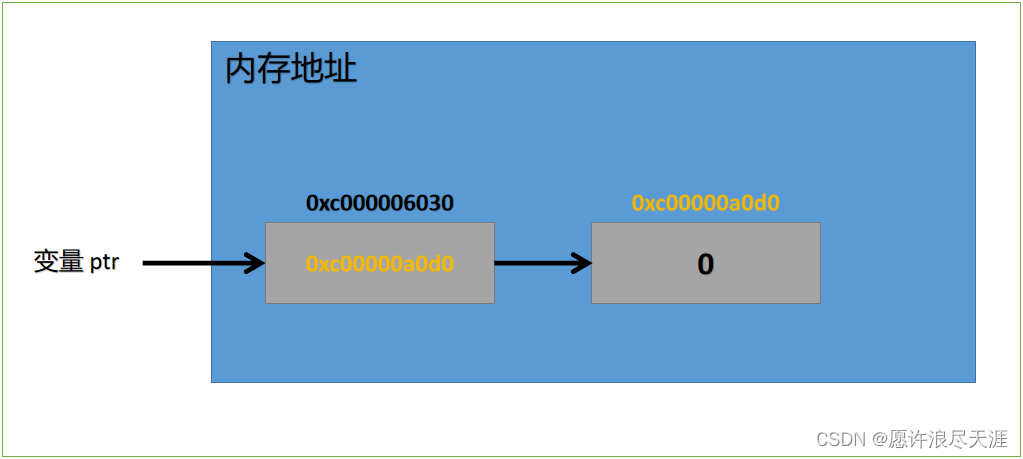
ptr := new(int) // *int (指针类型)
*ptr = 100
fmt.Printf("ptr 的类型 = %T && ptr 的值 = %v && ptr 的内存地址 = %v && ptr 这个指针指向的值为 = %v",ptr,ptr,&ptr,*ptr)
}
new输出:
num 的类型 = int && num 的值 = 100 && num 的内存地址 = 0xc00000a098
ptr 的类型 = *int && ptr 的值 = 0xc00000a0d0 && ptr 的内存地址 = 0xc000006030 && ptr 这个指针指向的值为 = 100
您可能感兴趣的文章:
