目录
一、数据结构
1、hchan
2、环形队列
3、等待队列
4、类型信息
5、锁
6、sudog
二、初始化channel
三、发送数据
四、接收数据
五、关闭
channel是golang语言goroutine间的通信方式。
一、数据结构1、hchan
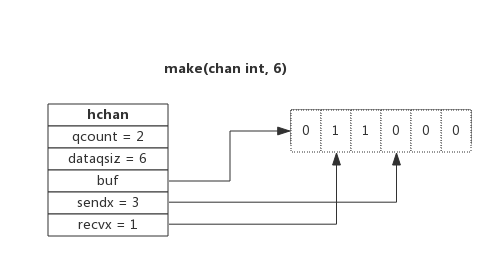
type hchan struct {qcount uint // 目前队列中的数据数量total data in the queuedataqsiz uint // 队列的容量size of the circular queuebuf unsafe.Pointer // 队列points to an array of dataqsiz elementselemsize uint16 //数据的大小closed uint32elemtype *_type // 数据类型element typesendx uint // 发送的Index send indexrecvx uint // 接收的Index receive indexrecvq waitq // 接收的等待G list of recv waiterssendq waitq // 发送的等待G list of send waiters// lock protects all fields in hchan, as well as several// fields in sudogs blocked on this channel.//// Do not change another G's status while holding this lock// (in particular, do not ready a G), as this can deadlock// with stack shrinking.lock mutex}2、环形队列
数据缓冲队列,数据结构是一个链表,但是通过sendx 和 recvx ,实现了环形队列结构
3、等待队列
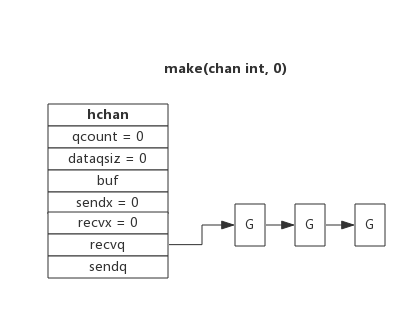
hchan中有两个等待队列:发送的等待队列(sendq)和接收的等待队列(recvq ),存放的是一系列的G
-
因读阻塞的goroutine会被向channel写入数据的goroutine唤醒;
-
因写阻塞的goroutine会被从channel读数据的goroutine唤醒;
4、类型信息
一个channel中,只能存放同一种数据类型的数据,因为我们在发送或者接收的时候,是通过指针来操作数据的,我们通过数据类型可以结算内存地址
-
elemtype代表类型,用于数据传递过程中的赋值;
-
elemsize代表类型大小,用于在buf中定位元素位置。
5、锁
发送和接收的全过程是加锁的,用以保证goroutine安全
6、sudog
等待的G队列,都会包装成sudog的数据结构