append扩容机制
在《切片传递的隐藏危机》一文,小菜刀有简单地提及到切片扩容的问题。在读者讨论群,有人举了以下例子,并想得到一个合理的回答。
1package main
2
3func main() {
4 s := []int{1,2}
5 s = append(s, 3,4,5)
6 println(cap(s))
7}
8
9// output: 6
appendappendbuiltinbuiltin.go 1// The append built-in function appends elements to the end of a slice. If
2// it has sufficient capacity, the destination is resliced to accommodate the
3// new elements. If it does not, a new underlying array will be allocated.
4// Append returns the updated slice. It is therefore necessary to store the
5// result of append, often in the variable holding the slice itself:
6// slice = append(slice, elem1, elem2)
7// slice = append(slice, anotherSlice...)
8// As a special case, it is legal to append a string to a byte slice, like this:
9// slice = append([]byte("hello "), "world"...)
10func append(slice []Type, elems ...Type) []Type
11
append 会追加一个或多个数据至 slice 中,这些数据会存储至 slice 的底层数组。其中,底层数组长度是固定的,如果数组的剩余空间足以容纳追加的数据,则可以正常地将数据存入该数组。一旦追加数据后总长度超过原数组长度,原数组就无法满足存储追加数据的要求。此时会怎么处理呢?
同时我们发现,该文件中仅仅定义了函数签名,并没有包含函数实现的任何代码。这里我们不免好奇,append究竟是如何实现的呢?
编译过程
为了回答上述问题,我们不妨从编译入手。Go编译可分为四个阶段:词法与语法分析、类型检查与抽象语法树(AST)转换、中间代码生成和生成最后的机器码。
src/cmd/compile/internal/gc/typecheck.go1func typecheck1(n *Node, top int) (res *Node) {
2 ...
3 switch n.Op {
4 case OAPPEND:
5 ...
6}
src/cmd/compile/internal/gc/walk.go 1func walkexpr(n *Node, init *Nodes) *Node {
2 ...
3 case OAPPEND:
4 // x = append(...)
5 r := n.Right
6 if r.Type.Elem().NotInHeap() {
7 yyerror("%v can't be allocated in Go; it is incomplete (or unallocatable)", r.Type.Elem())
8 }
9 switch {
10 case isAppendOfMake(r):
11 // x = append(y, make([]T, y)...)
12 r = extendslice(r, init)
13 case r.IsDDD():
14 r = appendslice(r, init) // also works for append(slice, string).
15 default:
16 r = walkappend(r, init, n)
17 }
18 ...
19}
src/cmd/compile/internal/gc/ssa.go1// append converts an OAPPEND node to SSA.
2// If inplace is false, it converts the OAPPEND expression n to an ssa.Value,
3// adds it to s, and returns the Value.
4// If inplace is true, it writes the result of the OAPPEND expression n
5// back to the slice being appended to, and returns nil.
6// inplace MUST be set to false if the slice can be SSA'd.
7func (s *state) append(n *Node, inplace bool) *ssa.Value {
8 ...
9}
state.appendinplacestate.appendappend(s, e1, e2, e3) 1 // If inplace is false, process as expression "append(s, e1, e2, e3)":
2 ptr, len, cap := s
3 newlen := len + 3
4 if newlen > cap {
5 ptr, len, cap = growslice(s, newlen)
6 newlen = len + 3 // recalculate to avoid a spill
7 }
8 // with write barriers, if needed:
9 *(ptr+len) = e1
10 *(ptr+len+1) = e2
11 *(ptr+len+2) = e3
12 return makeslice(ptr, newlen, cap)
slice = append(slice, 1, 2, 3) 1 // If inplace is true, process as statement "s = append(s, e1, e2, e3)":
2
3 a := &s
4 ptr, len, cap := s
5 newlen := len + 3
6 if uint(newlen) > uint(cap) {
7 newptr, len, newcap = growslice(ptr, len, cap, newlen)
8 vardef(a) // if necessary, advise liveness we are writing a new a
9 *a.cap = newcap // write before ptr to avoid a spill
10 *a.ptr = newptr // with write barrier
11 }
12 newlen = len + 3 // recalculate to avoid a spill
13 *a.len = newlen
14 // with write barriers, if needed:
15 *(ptr+len) = e1
16 *(ptr+len+1) = e2
17 *(ptr+len+2) = e3
inpalceruntime.growsliceslice=append(slice,1)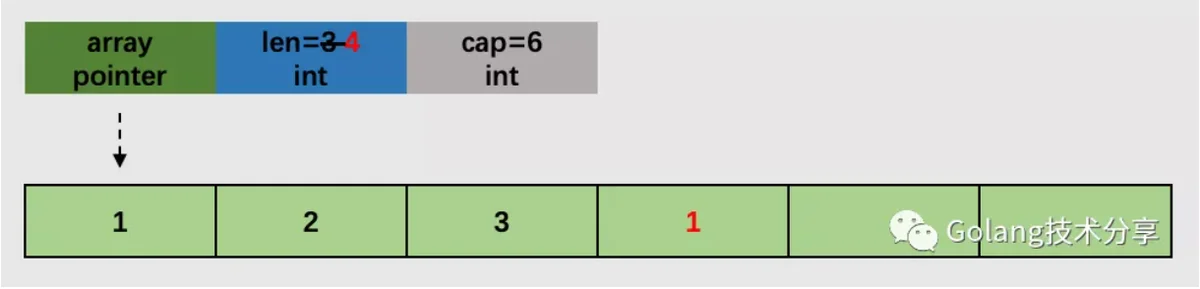
情况1,切片的底层数组还有可容纳追加元素的空间。
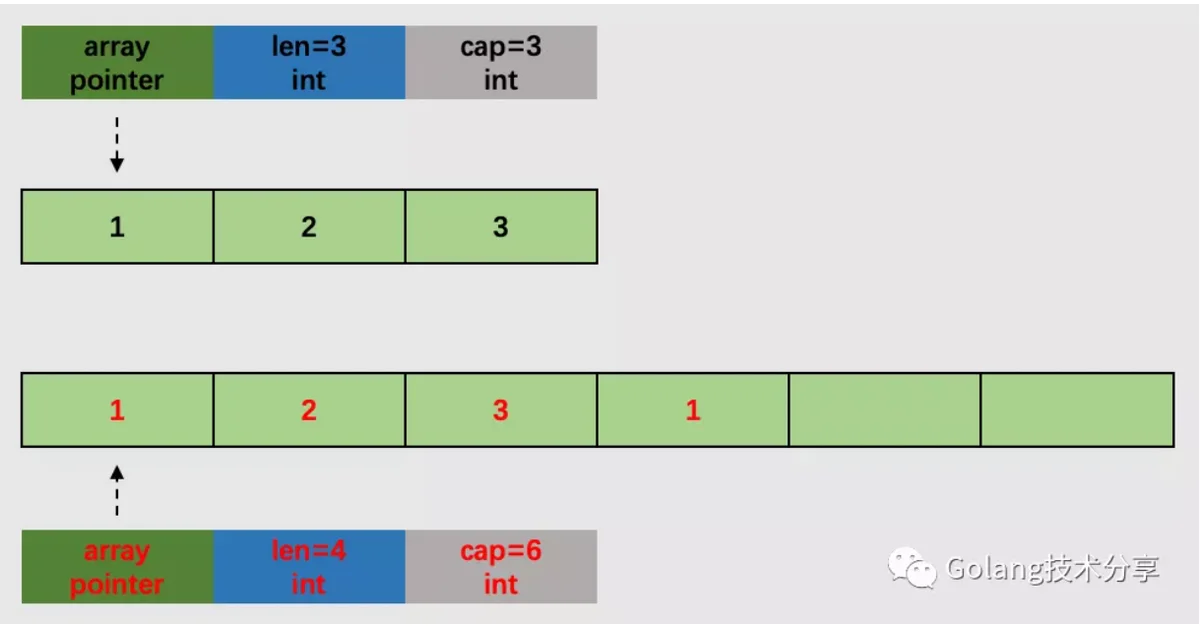
情况2,切片的底层数组已无可容纳追加元素的空间,需调用扩容函数,进行扩容。
扩容函数
growslicecapgrowslice- 初步确定切片容量
1func growslice(et *_type, old slice, cap int) slice {
2 ...
3 newcap := old.cap
4 doublecap := newcap + newcap
5 if cap > doublecap {
6 newcap = cap
7 } else {
8 if old.len < 1024 {
9 newcap = doublecap
10 } else {
11 // Check 0 < newcap to detect overflow
12 // and prevent an infinite loop.
13 for 0 < newcap && newcap < cap {
14 newcap += newcap / 4
15 }
16 // Set newcap to the requested cap when
17 // the newcap calculation overflowed.
18 if newcap <= 0 {
19 newcap = cap
20 }
21 }
22 }
23 ...
24}
capdoublecapnewcap- 计算容量所需内存大小
1 var overflow bool
2 var lenmem, newlenmem, capmem uintptr
3
4 switch {
5 case et.size == 1:
6 lenmem = uintptr(old.len)
7 newlenmem = uintptr(cap)
8 capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap))
9 overflow = uintptr(newcap) > maxAlloc
10 newcap = int(capmem)
11 case et.size == sys.PtrSize:
12 lenmem = uintptr(old.len) * sys.PtrSize
13 newlenmem = uintptr(cap) * sys.PtrSize
14 capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap) * sys.PtrSize)
15 overflow = uintptr(newcap) > maxAlloc/sys.PtrSize
16 newcap = int(capmem / sys.PtrSize)
17 case isPowerOfTwo(et.size):
18 var shift uintptr
19 if sys.PtrSize == 8 {
20 // Mask shift for better code generation.
21 shift = uintptr(sys.Ctz64(uint64(et.size))) & 63
22 } else {
23 shift = uintptr(sys.Ctz32(uint32(et.size))) & 31
24 }
25 lenmem = uintptr(old.len) << shift
26 newlenmem = uintptr(cap) << shift
27 capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap) << shift)
28 overflow = uintptr(newcap) > (maxAlloc >> shift)
29 newcap = int(capmem >> shift)
30 default:
31 lenmem = uintptr(old.len) * et.size
32 newlenmem = uintptr(cap) * et.size
33 capmem, overflow = math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(newcap))
34 capmem = roundupsize(capmem)
35 newcap = int(capmem / et.size)
36 }
在该环节,通过判断切片元素的字节大小是否为1,系统指针大小(32位为4,64位为8)或2的倍数,进入相应所需内存大小的计算逻辑。
roundupsizesizemallocgc 1func roundupsize(size uintptr) uintptr {
2 if size < _MaxSmallSize {
3 if size <= smallSizeMax-8 {
4 return uintptr(class_to_size[size_to_class8[divRoundUp(size, smallSizeDiv)]])
5 } else {
6 return uintptr(class_to_size[size_to_class128[divRoundUp(size-smallSizeMax, largeSizeDiv)]])
7 }
8 }
9
10 // Go的内存管理虚拟地址页大小为 8k(_PageSize)
11 // 当size的大小即将溢出时,就不采用向上取整的做法,直接用当前期望size值。
12 if size+_PageSize < size {
13 return size
14 }
15 return alignUp(size, _PageSize)
16}
<_MaxSmallSizedivRoundUpclass_to_sizesize_to_class8size_to_class1281// _NumSizeClasses = 67 代表67种特定大小的对象类型
2var class_to_size = [_NumSizeClasses]uint16{0, 8, 16, 32, 48, 64, 80, 96, 112,...}
alignUpsize_PageSize- 内存分配
1 if overflow || capmem > maxAlloc {
2 panic(errorString("growslice: cap out of range"))
3 }
4
5 var p unsafe.Pointer
6 if et.ptrdata == 0 {
7 p = mallocgc(capmem, nil, false)
8 memclrNoHeapPointers(add(p, newlenmem), capmem-newlenmem)
9 } else {
10 p = mallocgc(capmem, et, true)
11 if lenmem > 0 && writeBarrier.enabled {
12 bulkBarrierPreWriteSrcOnly(uintptr(p), uintptr(old.array), lenmem-et.size+et.ptrdata)
13 }
14 }
15 memmove(p, old.array, lenmem)
16
17 return slice{p, old.len, newcap}
panicmallocgccapmemmemclrNoHeapPointersbulkBarrierPreWriteSrcOnlymemmovepgrowslicelen =3cap=3slice=append(slice,1)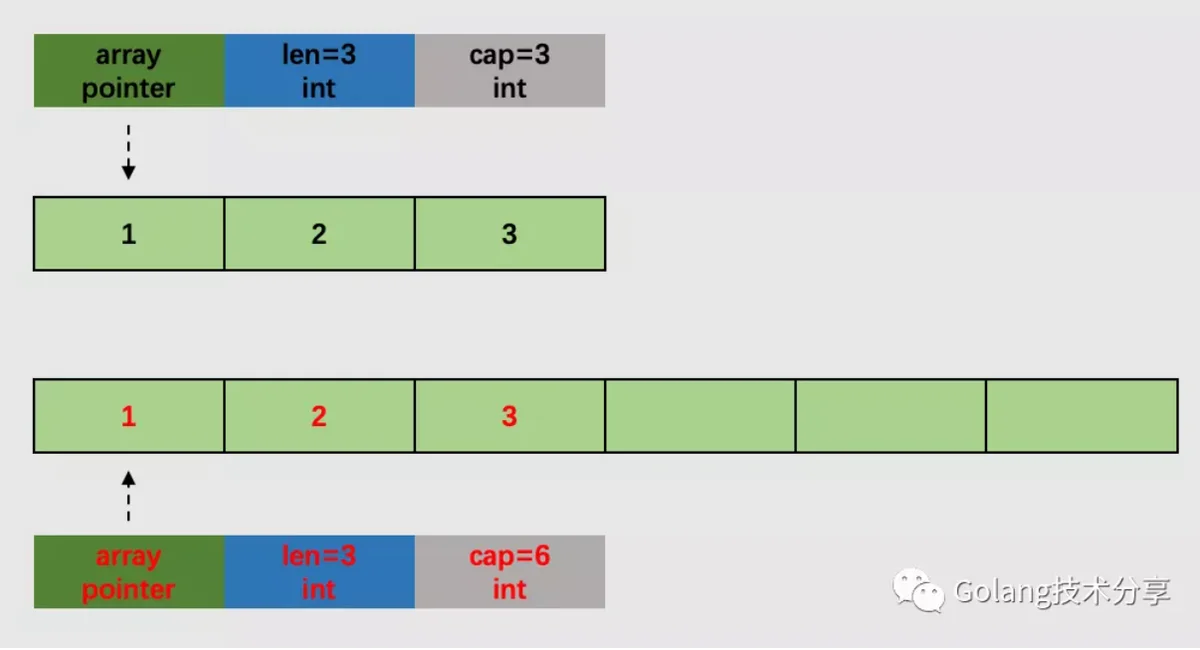
growslicelen总结
这里回到文章开头中的例子
1package main
2
3func main() {
4 s := []int{1,2}
5 s = append(s, 3,4,5)
6 println(cap(s))
7}
sappendgrowslicecapdoublecapdoublecapcapnewcap=5intsys.PtrSizeroundupsizecapmemnewcapappend在扩容的容量确定上,相对比较复杂,它与CPU位数、元素大小、是否包含指针、追加个数等都有关系。当我们看完扩容源码逻辑后,发现去纠结它的扩容确切值并没什么必要。
在实际使用中,如果能够确定切片的容量范围,比较合适的做法是:切片初始化时就分配足够的容量空间,在append追加操作时,就不用再考虑扩容带来的性能损耗问题。
1func BenchmarkAppendFixCap(b *testing.B) {
2 for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
3 a := make([]int, 0, 1000)
4 for i := 0; i < 1000; i++ {
5 a = append(a, i)
6 }
7 }
8}
9
10func BenchmarkAppend(b *testing.B) {
11 for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
12 a := make([]int, 0)
13 for i := 0; i < 1000; i++ {
14 a = append(a, i)
15 }
16 }
17}
它们的压测结果如下,孰优孰劣,一目了然。
1 $ go test -bench=. -benchmem
2
3BenchmarkAppendFixCap-8 1953373 617 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
4BenchmarkAppend-8 426882 2832 ns/op 16376 B/op 11 allocs/op
