maphashmapmap的内存模型
我的go源码版本是:go1.17.2
Go_SDK\go1.17.2\src\runtime\map.go首先我们来看一下map最重要的两个结构:
hmap:
// A header for a Go map.
type hmap struct {
// Note: the format of the hmap is also encoded in cmd/compile/internal/reflectdata/reflect.go.
// Make sure this stays in sync with the compiler's definition.
count int // # live cells == size of map. Must be first (used by len() builtin)
flags uint8
B uint8 // log_2 of # of buckets (can hold up to loadFactor * 2^B items)
noverflow uint16 // approximate number of overflow buckets; see incrnoverflow for details
hash0 uint32 // hash seed
buckets unsafe.Pointer // array of 2^B Buckets. may be nil if count==0.
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // previous bucket array of half the size, non-nil only when growing
nevacuate uintptr // progress counter for evacuation (buckets less than this have been evacuated)
extra *mapextra // optional fields
}
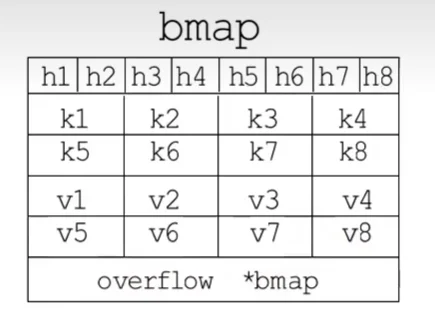
bmap:(bucket桶)
// A bucket for a Go map.
type bmap struct {
// tophash generally contains the top byte of the hash value
// for each key in this bucket. If tophash[0] < minTopHash,
// tophash[0] is a bucket evacuation state instead.
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8
// Followed by bucketCnt keys and then bucketCnt elems.
// NOTE: packing all the keys together and then all the elems together makes the
// code a bit more complicated than alternating key/elem/key/elem/... but it allows
// us to eliminate padding which would be needed for, e.g., map[int64]int8.
// Followed by an overflow pointer.
}
实际上在golang runtime时,编译器会动态为bmap创建一个新结构:
type bmap struct {
topbits [8]uint8
keys [8]keytype
values [8]valuetype
pad uintptr
overflow uintptr
}
hmap(a header for a go map)bmap(a bucket for a Go mapbuckethmap:
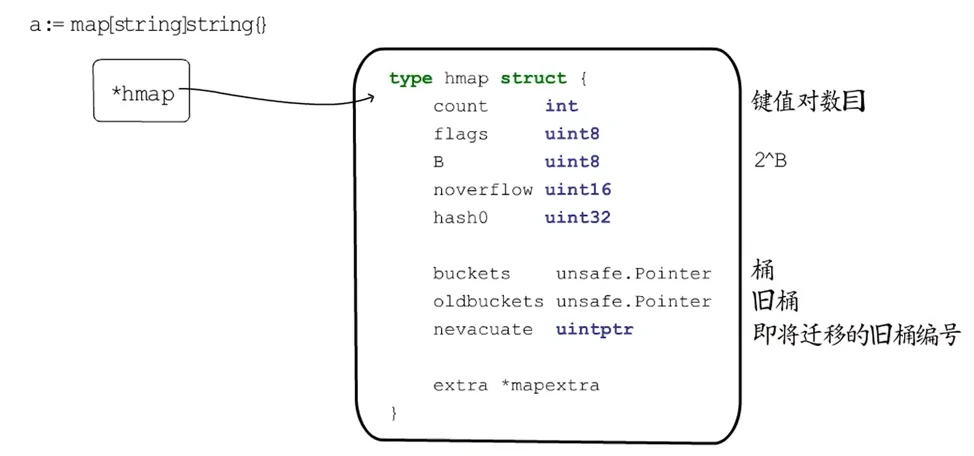
- count:键值对数目。
- flags:状态标志。
- B:当前桶个数的二次幂。
- noverflow:溢出桶的个数。
- hash0:哈希种子。
- buckets:哈希桶的地址。
- old buckets:旧桶的地址,用于扩容。
- nevacuate:即将迁移的旧桶编号,可以作为搬迁进度,小于nevacuate的已经搬迁。
- overflow:溢出桶的信息。
bucket:
其中键值对被保存在溢出桶中,溢出桶的结构是这样的:
“高位哈希值”数组存储的是通过哈希函数计算后的key再经取模后的高八位,而储存键值对的数组一共可以储存8个键值对,其中key都存在数组的前面,而value都存在后面。最后一个字段是一个指向溢出桶的指针。
hmapbucket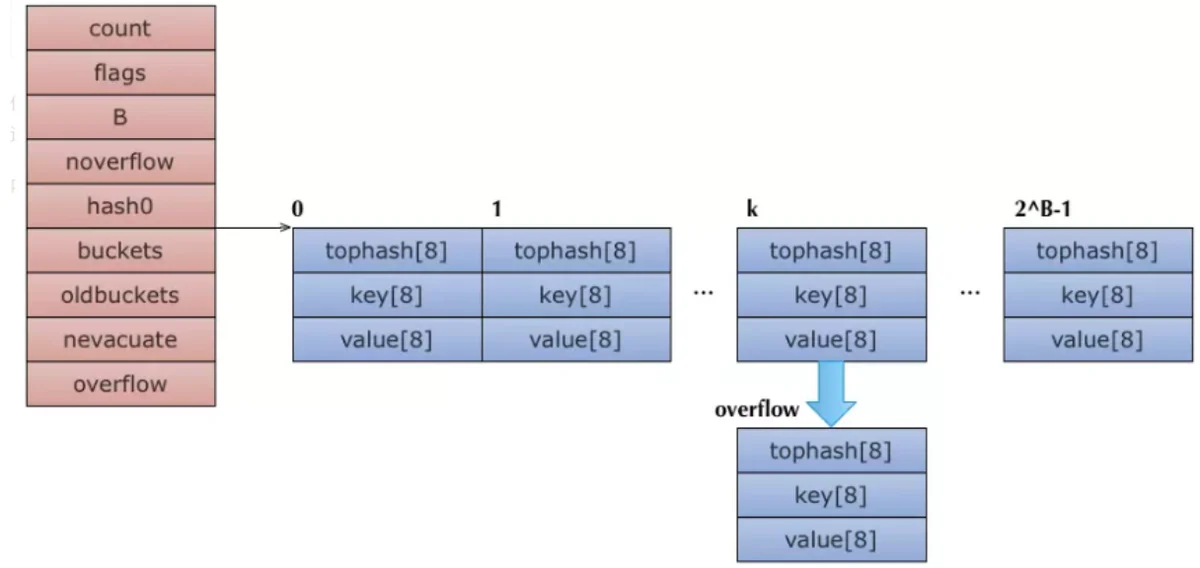
对key求哈希
mapGolang把求得的值按照用途一分为二:高位和低位。
hmapmapmap的扩容
渐进式扩容
桶(Bucket)oldbucketsnevacuate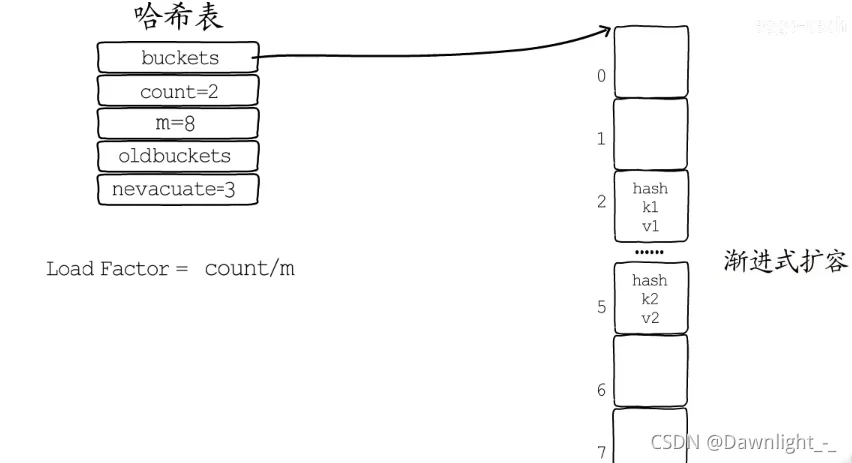
扩容规则
bmap结构体的最后一个字段是一个bmap型指针,指向一个溢出桶。溢出桶的内存布局与常规桶相同,是为了减少扩容次数而引入的。
当一个桶存满了,还有可用的溢出桶时,就会在后面链一个溢出桶,继续往这里面存。
2 ^ 42 ^ (B - 4)2 ^ Bextramapextranextoverflowoverflowslicenoverfloweroldoverflower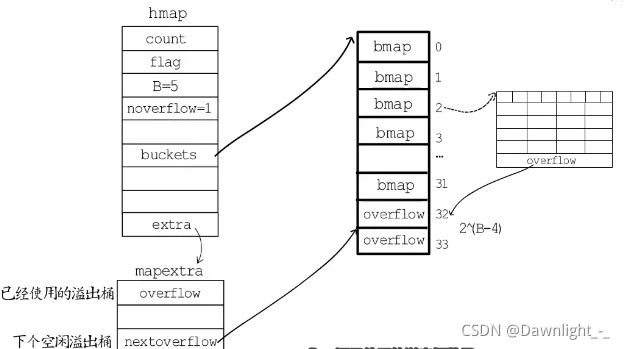
翻倍扩容
负载因子
负载因子count / (2 ^ B) > 6.5hmap.B++bucketsoldbucketsnevacuate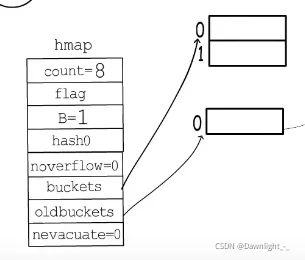
等量扩容
等量扩容那么用多少溢出桶算多了呢?
2 ^ 152 ^ 152 ^ 15所谓等量扩容,就是创建和旧桶数目一样多的新桶。然后把原来的键值对迁移到新桶中,但是既然是等量,那来回迁移的又有什么用呢?
什么情况下,桶的负载因子没有超过上限值,却偏偏使用了很多溢出桶呢?自然是有很多键值对被删除的情况。同样数目的键值对,迁移到新桶中,能够排列的更加紧凑,从而减少溢出桶的使用。这就是等量扩容的意义所在。
