golang中函数是一等公民
Server端建立http服务
import "net/http"
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", IndexHandler)
http.ListenAndServe(":8088",nil)
}
func IndexHandler(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
writer.Write([]byte("hello world"))
}http.HandleFunc构建路由
func HandleFunc(pattern string, handler func(ResponseWriter, *Request)) {
DefaultServeMux.HandleFunc(pattern, handler)
}func (mux *ServeMux) HandleFunc(pattern string, handler func(ResponseWriter, *Request)) {
if handler == nil {
panic("http: nil handler")
}
mux.Handle(pattern, HandlerFunc(handler))
}func (mux *ServeMux) Handle(pattern string, handler Handler) {
mux.mu.Lock()
defer mux.mu.Unlock()
if pattern == "" {
panic("http: invalid pattern")
}
if handler == nil {
panic("http: nil handler")
}
if _, exist := mux.m[pattern]; exist {
panic("http: multiple registrations for " + pattern)
}
if mux.m == nil {
mux.m = make(map[string]muxEntry)
}
e := muxEntry{h: handler, pattern: pattern}
mux.m[pattern] = e
if pattern[len(pattern)-1] == '/' {
mux.es = appendSorted(mux.es, e)
}
if pattern[0] != '/' {
mux.hosts = true
}
}Handle()会将路由URL和处理器方法注册到DefaultServeMux中,ServeMux结构如下:
type ServeMux struct {
mu sync.RWMutex
m map[string]muxEntry
es []muxEntry // slice of entries sorted from longest to shortest.
hosts bool // whether any patterns contain hostnames
}
type muxEntry struct {
h Handler
pattern string
}
// NewServeMux allocates and returns a new ServeMux.
func NewServeMux() *ServeMux { return new(ServeMux) }
// DefaultServeMux is the default ServeMux used by Serve.
var DefaultServeMux = &defaultServeMux
var defaultServeMux ServeMuxhttp.ListenAndServe(":8088",nil)监听请求
func (srv *Server) ListenAndServe() error {
if srv.shuttingDown() {
return ErrServerClosed
}
addr := srv.Addr
if addr == "" {
addr = ":http"
}
ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", addr)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return srv.Serve(ln)
}由net.Listen("tcp", addr)构建出tcp服务,监听设置端口,再由srv.Serve(ln)获取并处理请求。
在func (srv *Server) Serve(l net.Listener) 中由rw, err := l.Accept()接受请求,在单独的携程中处理请求 go c.serve(connCtx)
在func (c *conn) serve(ctx context.Context)中,由 w, err := c.readRequest(ctx) 读出请求内容,在serverHandler{c.server}.ServeHTTP(w, w.req) 中得到处理器,并由处理器处理请求
client端
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net"
"net/http"
"time"
)
func main() {
//连接池
transport := &http.Transport{
DialContext: (&net.Dialer{
Timeout: 30 * time.Second, //连接超时时间
KeepAlive: 30 * time.Second, //长链接超时时间
}).DialContext,
MaxIdleConns: 100, //最大空闲连接数
IdleConnTimeout: 90 * time.Second, //空闲超时时间
TLSHandshakeTimeout: 10 * time.Second, //tls握手超时时间
ExpectContinueTimeout: 1 * time.Second, //100-continue状态码超时时间
}
client := &http.Client{
Timeout: 30 * time.Second,
Transport: transport,
}
resp, err := client.Get("127.0.0.1:8088")
if err!=nil{
panic(err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
all, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err!=nil{
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println(all)
}
会在 func (c *Client) do(req *Request) 中调用 c.send(req, deadline)
func (c *Client) send(req *Request, deadline time.Time) (resp *Response, didTimeout func() bool, err error) {
if c.Jar != nil {
for _, cookie := range c.Jar.Cookies(req.URL) {
req.AddCookie(cookie)
}
}
resp, didTimeout, err = send(req, c.transport(), deadline)
if err != nil {
return nil, didTimeout, err
}
if c.Jar != nil {
if rc := resp.Cookies(); len(rc) > 0 {
c.Jar.SetCookies(req.URL, rc)
}
}
return resp, nil, nil
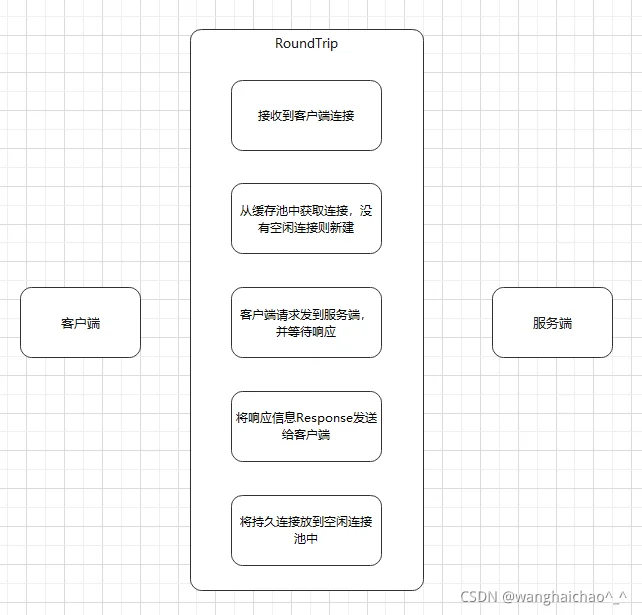
}在send方法中由 RoundTripper.RoundTrip(req) 发起请求,并得到response
Transport
Transport结构体主要属性
type Transport struct {
idleMu sync.Mutex //
closeIdle bool //用户是否已请求关闭所有空闲连接
idleConn map[connectMethodKey][]*persistConn//保存从connect到persistConn的映射
}type connectMethodKey struct {
proxy string, //代理url,浏览器透明代理
scheme string, //协议 http https
addr string // 代理base的url,下游服务base地址
onlyH1 bool // 是否http1.1
}func (t *Transport) RoundTrip(req *Request) (*Response, error) {
return t.roundTrip(req)
}func (t *Transport) roundTrip(req *Request) (*Response, error)中
pconn, err := t.getConn(treq, cm) 获取持久化连接
persistConn结构体
type persistConn struct {
br *bufio.Reader // from conn
bw *bufio.Writer // to conn
reqch chan requestAndChan //read by readLoop
writech chan writeRequest //read by writeLoop
}t.getConn流程:
1.trace.GotConn(pc.gotIdleConnTrace(pc.idleAt)) 尝试获取空闲的连接
2.获取不到 t.queueForDial(w) --> go t.dialConnFor(w) 开启一个协程新建一个连接
3.select case 监听事件:监听连接是否重建成功,如果连接创建成功则返回该新建的连接,其他则返回空
最终调用getConn获得的连接的roundTrip方法
pconn.roundTrip(treq) --> pc.writech <- writeRequest{req, writeErrCh, continueCh}
Transport RoundTrip基本流程