Golang 中反向代理的实现主要使用了标准库的 net/http/httputil 包。
当读完这篇文章之后,你会学到:
- 如何响应 HTTP 请求
- 如何解析请求体
- 如何通过反向代理将流量转发到另一台服务器
反向代理的概念
反向代理是什么?有个很棒的说法是流量转发。我获取到客户端来的请求,将它发往另一个服务器,从服务器获取到响应再回给原先的客户端。反向的意义简单来说在于这个代理自身决定了何时将流量发往何处。
它们让你可以控制来自客户端的请求和来自服务器的响应,然后我们利用这个特点,可以增加缓存、做一些提高网站的安全性措施等。
正向代理和反向代理的区别
在我们深入了解有关反向代理之前,让我们快速看普通代理(也称为正向代理)和反向代理之间的区别。
在正向代理中,代理代表原始客户端从另一个网站检索数据。 它位于客户端(浏览器)前面,并确保没有后端服务器直接与客户端通信。 所有客户端的请求都通过代理被转发,因此服务器只与这个代理通信(服务器会认为代理是它的客户端)。 在这种情况下,代理可以隐藏真正的客户端。
另一方面,反向代理位于后端服务器的前面,确保没有客户端直接与服务器通信。 所有客户端请求都会通过反向代理发送到服务器,因此客户端始终只与反向代理通信, 而从不会直接与实际服务器通信。 在这种情况下,代理可以隐藏后端服务器。 几个常见的反向代理有 Nginx, HAProxy。
反向代理使用场景
负载均衡(Load balancing): 反向代理可以提供负载均衡解决方案,将传入的流量均匀地分布在不同的服务器之间,以防止单个服务器过载。
防止安全攻击: 由于真正的后端服务器永远不需要暴露公共 IP,所以 DDoS 等攻击只能针对反向代理进行, 这能确保在网络攻击中尽量多的保护你的资源,真正的后端服务器始终是安全的。
缓存: 假设你的实际服务器与用户所在的地区距离比较远,那么你可以在当地部署反向代理,它可以缓存网站内容并为当地用户提供服务。
SSL 加密: 由于与每个客户端的 SSL 通信会耗费大量的计算资源,因此可以使用反向代理处理所有与 SSL 相关的内容, 然后释放你真正服务器上的宝贵资源。
编写一个反向代理的案例
http://localhost:1330proxy_conditionproxy_conditionAhttp://localhost:1331proxy_conditionBhttp://localhost:1332http://localhost:1333http://localhost:1330proxy_condition环境准备
基础工作
main.goPORTA_CONDITION_URLB_CONDITION_URLDEFAULT_CONDITION_URL/注:原文中的这几个变量是写入在系统环境变量中的,后续从系统环境变量中读取。这里为了精简,将其写成了常量的形式。
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"net/http/httputil"
"net/url"
"strings"
)
const PORT = "1330"
const A_CONDITION_URL = "http://localhost:1331"
const B_CONDITION_URL = "http://localhost:1332"
const DEFAULT_CONDITION_URL = "http://localhost:1333"
type requestPayloadStruct struct {
ProxyCondition string `json:"proxy_condition"`
}
// Get the port to listen on
func getListenAddress() string {
return ":" + PORT
}
// Log the env variables required for a reverse proxy
func logSetup() {
a_condtion_url := A_CONDITION_URL
b_condtion_url := B_CONDITION_URL
default_condtion_url := DEFAULT_CONDITION_URL
log.Printf("Server will run on: %s\n", getListenAddress())
log.Printf("Redirecting to A url: %s\n", a_condtion_url)
log.Printf("Redirecting to B url: %s\n", b_condtion_url)
log.Printf("Redirecting to Default url: %s\n", default_condtion_url)
}
// Given a request send it to the appropriate url
func handleRequestAndRedirect(res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// We will get to this...
}
func main() {
// Log setup values
logSetup()
// start server
http.HandleFunc("/", handleRequestAndRedirect)
if err := http.ListenAndServe(getListenAddress(), nil); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
现在你就可以运行代码了。
解析请求体
handleRequestAndRedirectproxy_conditiontype requestPayloadStruct struct {
ProxyCondition string `json:"proxy_condition"`
}
// Get a json decoder for a given requests body
func requestBodyDecoder(request *http.Request) *json.Decoder {
// Read body to buffer
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(request.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error reading body: %v", err)
panic(err)
}
// Because go lang is a pain in the ass if you read the body then any susequent calls
// are unable to read the body again....
request.Body = ioutil.NopCloser(bytes.NewBuffer(body))
return json.NewDecoder(ioutil.NopCloser(bytes.NewBuffer(body)))
}
// Parse the requests body
func parseRequestBody(request *http.Request) requestPayloadStruct {
decoder := requestBodyDecoder(request)
var requestPayload requestPayloadStruct
err := decoder.Decode(&requestPayload)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return requestPayload
}
// Given a request send it to the appropriate url
func handleRequestAndRedirect(res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
requestPayload := parseRequestBody(req)
// ... more to come
}
通过 proxy_condition 判断将流量发往何处
proxy_conditionproxy_conditionAA_CONDITION_URLproxy_conditionBB_CONDITION_URLDEFAULT_CONDITION_URL// Log the typeform payload and redirect url
func logRequestPayload(requestionPayload requestPayloadStruct, proxyUrl string) {
log.Printf("proxy_condition: %s, proxy_url: %s\n", requestionPayload.ProxyCondition, proxyUrl)
}
// Get the url for a given proxy condition
func getProxyUrl(proxyConditionRaw string) string {
proxyCondition := strings.ToUpper(proxyConditionRaw)
a_condtion_url := A_CONDITION_URL
b_condtion_url := B_CONDITION_URL
default_condtion_url := DEFAULT_CONDITION_URL
if proxyCondition == "A" {
return a_condtion_url
}
if proxyCondition == "B" {
return b_condtion_url
}
return default_condtion_url
}
// Given a request send it to the appropriate url
func handleRequestAndRedirect(res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
requestPayload := parseRequestBody(req)
url := getProxyUrl(requestPayload.ProxyCondition)
logRequestPayload(requestPayload, url)
// more still to come...
}
反向代理到 URL
最终我们来到了实际的反向代理部分。在如此多的语言中要编写一个反向代理需要考虑很多东西,写大段的代码。或者至少引入一个复杂的外部库。
然而 Go 的标准库使得创建一个反向代理非常简单以至于你都不敢相信。下面就是你所需要的最关键的一行代码:
httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(url).ServeHTTP(res, req)
注意下面代码中我们做了些许修改来让它能完整地支持 SSL 重定向(虽然不是必须的,只使用上面那一句代码也是可以的)。
// Serve a reverse proxy for a given url
func serveReverseProxy(target string, res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// parse the url
url, _ := url.Parse(target)
// create the reverse proxy
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(url)
// Update the headers to allow for SSL redirection
req.URL.Host = url.Host
req.URL.Scheme = url.Scheme
req.Header.Set("X-Forwarded-Host", req.Header.Get("Host"))
req.Host = url.Host
// Note that ServeHttp is non blocking and uses a go routine under the hood
proxy.ServeHTTP(res, req)
}
// Given a request send it to the appropriate url
func handleRequestAndRedirect(res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
requestPayload := parseRequestBody(req)
url := getProxyUrl(requestPayload.ProxyCondition)
logRequestPayload(requestPayload, url)
serveReverseProxy(url, res, req)
}
完整代码
现在再次给出完整代码:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"net/http/httputil"
"net/url"
"strings"
)
const PORT = "1330"
const A_CONDITION_URL = "http://localhost:1331"
const B_CONDITION_URL = "http://localhost:1332"
const DEFAULT_CONDITION_URL = "http://localhost:1333"
type requestPayloadStruct struct {
ProxyCondition string `json:"proxy_condition"`
}
// Get the port to listen on
func getListenAddress() string {
return ":" + PORT
}
// Log the env variables required for a reverse proxy
func logSetup() {
a_condtion_url := A_CONDITION_URL
b_condtion_url := B_CONDITION_URL
default_condtion_url := DEFAULT_CONDITION_URL
log.Printf("Server will run on: %s\n", getListenAddress())
log.Printf("Redirecting to A url: %s\n", a_condtion_url)
log.Printf("Redirecting to B url: %s\n", b_condtion_url)
log.Printf("Redirecting to Default url: %s\n", default_condtion_url)
}
// Get a json decoder for a given requests body
func requestBodyDecoder(request *http.Request) *json.Decoder {
// Read body to buffer
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(request.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error reading body: %v", err)
panic(err)
}
// Because go lang is a pain in the ass if you read the body then any susequent calls
// are unable to read the body again....
request.Body = ioutil.NopCloser(bytes.NewBuffer(body))
return json.NewDecoder(ioutil.NopCloser(bytes.NewBuffer(body)))
}
// Parse the requests body
func parseRequestBody(request *http.Request) requestPayloadStruct {
decoder := requestBodyDecoder(request)
var requestPayload requestPayloadStruct
err := decoder.Decode(&requestPayload)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return requestPayload
}
// Log the typeform payload and redirect url
func logRequestPayload(requestionPayload requestPayloadStruct, proxyUrl string) {
log.Printf("proxy_condition: %s, proxy_url: %s\n", requestionPayload.ProxyCondition, proxyUrl)
}
// Get the url for a given proxy condition
func getProxyUrl(proxyConditionRaw string) string {
proxyCondition := strings.ToUpper(proxyConditionRaw)
a_condtion_url := A_CONDITION_URL
b_condtion_url := B_CONDITION_URL
default_condtion_url := DEFAULT_CONDITION_URL
if proxyCondition == "A" {
return a_condtion_url
}
if proxyCondition == "B" {
return b_condtion_url
}
return default_condtion_url
}
// Serve a reverse proxy for a given url
func serveReverseProxy(target string, res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// parse the url
url, _ := url.Parse(target)
// create the reverse proxy
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(url)
// Update the headers to allow for SSL redirection
//req.URL.Host = url.Host
//req.URL.Scheme = url.Scheme
//req.Header.Set("X-Forwarded-Host", req.Header.Get("Host"))
//req.Host = url.Host
// Note that ServeHttp is non blocking and uses a go routine under the hood
proxy.ServeHTTP(res, req)
}
// Given a request send it to the appropriate url
func handleRequestAndRedirect(res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
requestPayload := parseRequestBody(req)
url := getProxyUrl(requestPayload.ProxyCondition)
logRequestPayload(requestPayload, url)
serveReverseProxy(url, res, req)
}
func main() {
// Log setup values
logSetup()
// start server
http.HandleFunc("/", handleRequestAndRedirect)
if err := http.ListenAndServe(getListenAddress(), nil); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
全部启动
好了,现在启动我们的反向代理程序让其监听 1330 端口。让其他的 3 个简单的服务分别监听 1331–1333 端口(在各自的终端中)。
# 终端1:运行代码,监听 1330 端口
$ go run main.go
# 终端2:启动一个 http 服务器,监听 1331 端口
$ http-server -p 1331
# 终端3:启动一个 http 服务器,监听 1332 端口
$ http-server -p 1332
# 终端4:启动一个 http 服务器,监听 1333 端口
$ http-server -p 1333
使用 curl 命令进行测试
这些服务都启动之后,我们就可以在另一个终端中像下面这样开始发送带有 JSON 体的请求了:
$ curl --request GET \
--url http://localhost:1330/ \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '{
"proxy_condition": "a"
}'
proxy_condition上述测试代码可以在终端1的输出中看到被转发到的后端服务器的地址:
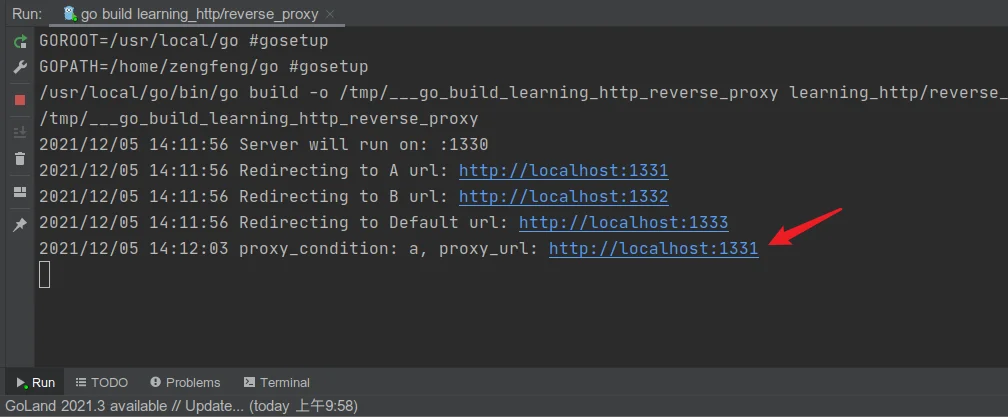
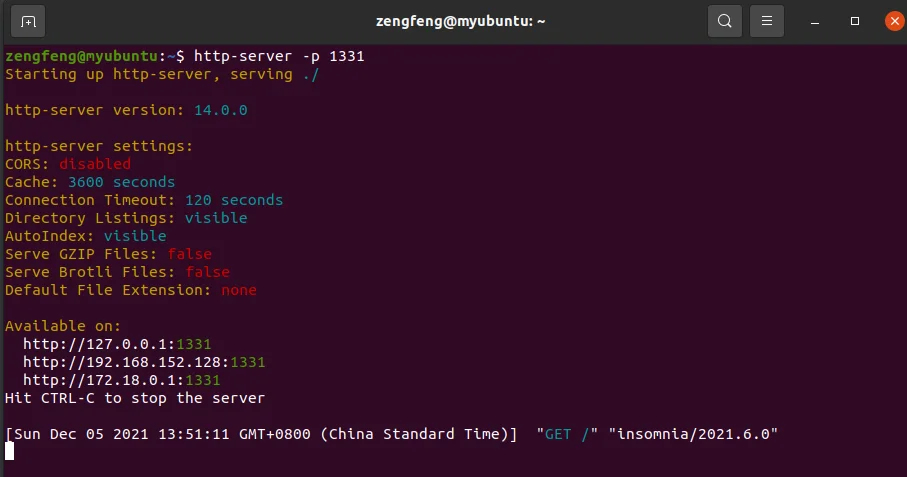
同时,在终端2看到发来的请求的输出:
如果你在找一个好用的 HTTP 请求客户端,我极力推荐 Insomnia。
使用 Insomnia 进行测试
Insomnia 的安装教程可以看这篇:Ubuntu 安装 Insomnia
测试过程如图所示:
proxy_condition使用进阶
修改 Response 信息
httputil 反向代理为我们提供了一种非常简单的机制来修改我们从服务器获得的响应,可以根据你的应用场景来缓存或更改此响应,让我们看看应该如何实现:
// Serve a reverse proxy for a given url
func serveReverseProxy(target string, res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// parse the url
url, _ := url.Parse(target)
// create the reverse proxy
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(url)
// modify the response
proxy.ModifyResponse = modifyResponse
// Note that ServeHttp is non blocking and uses a go routine under the hood
proxy.ServeHTTP(res, req)
}
func modifyResponse(resp *http.Response) error {
resp.Header.Set("X-Proxy", "Magical")
return nil
}
X-ProxyReverseProxy.ServeHTTP() 方法的底层会调用 ReverseProxy对象的 modifyResponse() 方法。
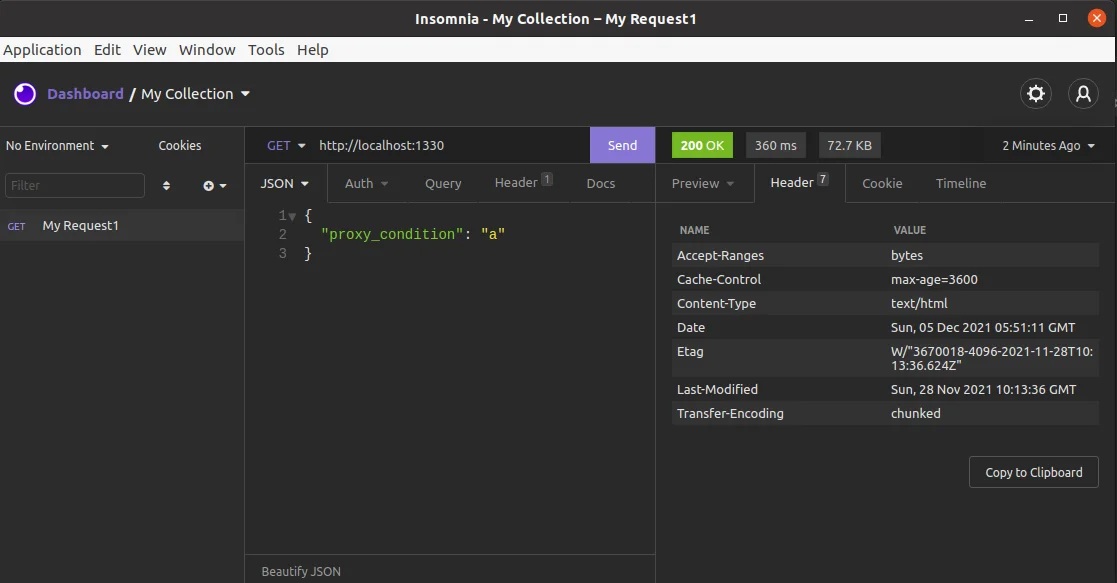
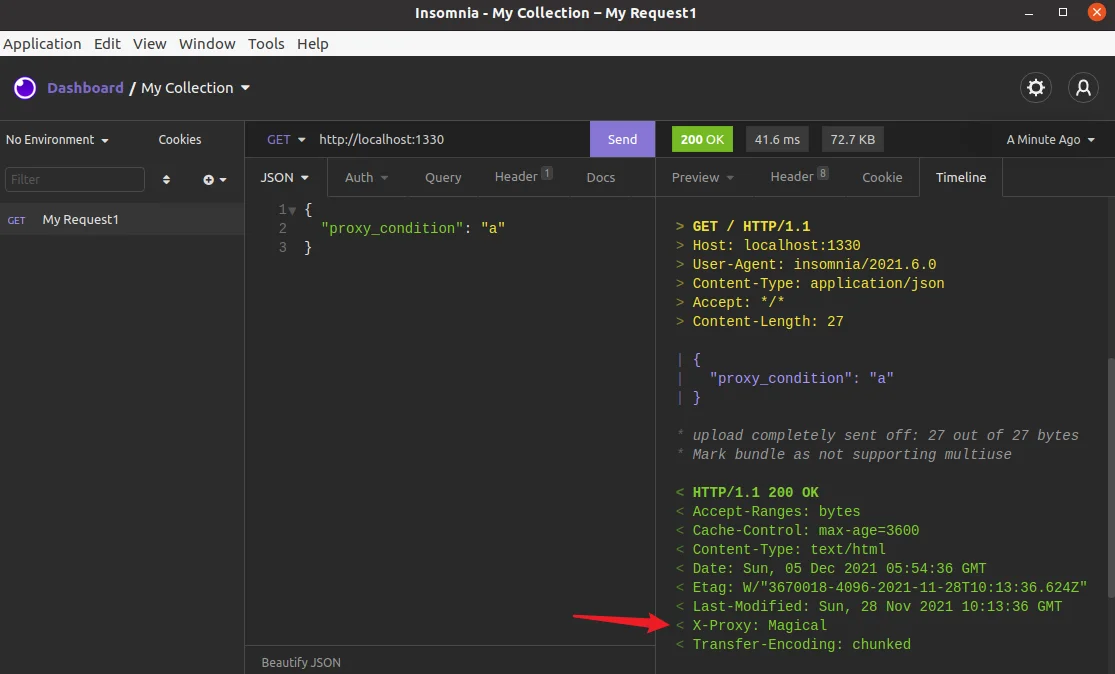
现在我们来测试一下,下图是还未添加 modifyResponse 时的输出结果,可以看到此时的响应头中没有 X-Proxy 的信息。
X-Proxy: Magical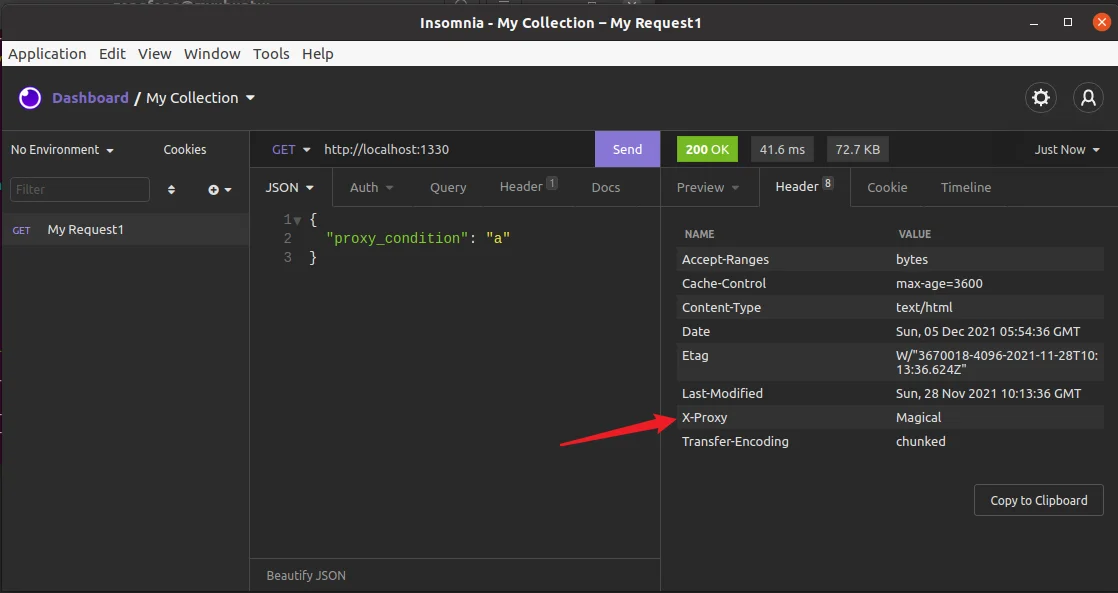
也可以在右侧的 Timeline 窗口看到请求和响应信息,如下图所示:
modifyResponse 中的错误处理
在 modifyResponse 中,可以返回一个错误(如果你在处理响应发生了错误),如果你设置了 proxy.ErrorHandler, modifyResponse 返回错误时会自动调用 ErrorHandler 进行错误处理。
// Serve a reverse proxy for a given url
func serveReverseProxy(target string, res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// parse the url
url, _ := url.Parse(target)
// create the reverse proxy
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(url)
// modify the response
proxy.ModifyResponse = modifyResponse
proxy.ErrorHandler = errorHandler
// Note that ServeHttp is non blocking and uses a go routine under the hood
proxy.ServeHTTP(res, req)
}
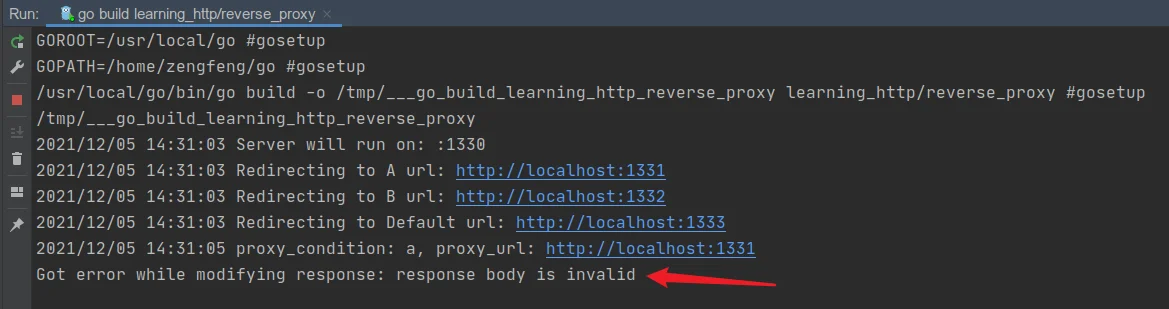
func modifyResponse(*http.Response) error {
return errors.New("response body is invalid")
}
func errorHandler(resp http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request, err error) {
fmt.Printf("Got error while modifying response: %v \n", err)
return
}
测试结果:
修改 Request 信息
你也可以在将请求发送到服务器之前对其进行修改。在下面的例子中,我们将会在请求发送到服务器之前添加了一个 Header 头。同样的,你可以在请求发送之前对其进行任何更改。
// Serve a reverse proxy for a given url
func serveReverseProxy(target string, res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// parse the url
url, _ := url.Parse(target)
// create the reverse proxy
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(url)
// modify the request
originalDirector := proxy.Director
proxy.Director = func(req *http.Request) {
originalDirector(req)
modifyRequest(req)
}
// Note that ServeHttp is non blocking and uses a go routine under the hood
proxy.ServeHTTP(res, req)
}
func modifyRequest(req *http.Request) {
req.Header.Set("X-Proxy", "Simple-Reverse-Proxy")
}
修改请求头之后,在测试的时候看不到修改成功后的请求头信息,这个问题暂时放着,以后真正遇到后再来这里补充。
反向代理非常强大,如文章之前所说,它有很多应用场景。你可以根据你的情况对其进行自定义。
推荐阅读
参考文章
Go 简单而强大的反向代理(Reverse Proxy) | 东隅已逝/桑榆非晚 (h1z3y3.me)
Go 代码实现反向代理 - Go语言中文网 - Golang中文社区 (studygolang.com)
http-server (github.com)
Insomnia (github.com)
