仅做个人备份
使用golang net/http库发送http请求,最后都是调用 transport的 RoundTrip方法中。
type RoundTripper interface {RoundTrip(*Request) (*Response, error)}RoundTrip代表一个http事务,给一个请求返回一个响应。RoundTripper必须是并发安全的。RoundTripper接口的实现Transport结构体在源码包net/http/transport.go 中。
type Transport struct {idleMu sync.MutexwantIdle bool // user has requested to close all idle conns 用户是否已关闭所有的空闲连接idleConn map[connectMethodKey][]*persistConn // most recently used at end,保存从connectMethodKey(代表着不同的协议,不同的host,也就是不同的请求)到persistConn的映射/*idleConnCh 用来在并发http请求的时候在多个 goroutine 里面相互发送持久连接,也就是说,这些持久连接是可以重复利用的, 你的http请求用某个persistConn用完了,通过这个channel发送给其他http请求使用这个persistConn*/idleConnCh map[connectMethodKey]chan *persistConnidleLRU connLRUreqMu sync.MutexreqCanceler map[*Request]func(error) //请求取消器altMu sync.Mutex // guards changing altProto onlyaltProto atomic.Value // of nil or map[string]RoundTripper, key is URI scheme 为空或者map[string]RoundTripper,key为URI 的scheme,用于自定义的协议及对应的处理请求的RoundTripper// Proxy specifies a function to return a proxy for a given// Request. If the function returns a non-nil error, the// request is aborted with the provided error.//// The proxy type is determined by the URL scheme. "http"// and "socks5" are supported. If the scheme is empty,// "http" is assumed.//// If Proxy is nil or returns a nil *URL, no proxy is used.Proxy func(*Request) (*url.URL, error) //根据给定的Request返回一个代理,如果返回一个不为空的error,请求会终止// DialContext specifies the dial function for creating unencrypted TCP connections.// If DialContext is nil (and the deprecated Dial below is also nil),// then the transport dials using package net./*DialContext用于指定创建未加密的TCP连接的dial功能,如果该函数为空,则使用net包下的dial函数*/DialContext func(ctx context.Context, network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)// Dial specifies the dial function for creating unencrypted TCP connections.//// Deprecated: Use DialContext instead, which allows the transport// to cancel dials as soon as they are no longer needed.// If both are set, DialContext takes priority./*Dial获取一个tcp连接,也就是net.Conn结构,然后就可以写入request,从而获取到responseDialContext比Dial函数的优先级高*/Dial func(network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)// DialTLS specifies an optional dial function for creating// TLS connections for non-proxied HTTPS requests.//// If DialTLS is nil, Dial and TLSClientConfig are used.//// If DialTLS is set, the Dial hook is not used for HTTPS// requests and the TLSClientConfig and TLSHandshakeTimeout// are ignored. The returned net.Conn is assumed to already be// past the TLS handshake./*DialTLS 为创建非代理的HTTPS请求的TLS连接提供一个可选的dial功能如果DialTLS为空,则使用Dial和TLSClientConfig如果设置了DialTLS,则HTTPS的请求不使用Dial的钩子,并且TLSClientConfig 和 TLSHandshakeTimeout会被忽略返回的net.Conn假设已经通过了TLS握手*/DialTLS func(network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)// TLSClientConfig specifies the TLS configuration to use with// tls.Client.// If nil, the default configuration is used.// If non-nil, HTTP/2 support may not be enabled by default./*TLSClientConfig指定tls.Client使用的TLS配置信息如果为空,则使用默认配置如果不为空,默认情况下未启动HTTP/2支持*/TLSClientConfig *tls.Config// TLSHandshakeTimeout specifies the maximum amount of time waiting to// wait for a TLS handshake. Zero means no timeout./*指定TLS握手的超时时间*/TLSHandshakeTimeout time.Duration// DisableKeepAlives, if true, prevents re-use of TCP connections// between different HTTP requests.DisableKeepAlives bool //如果为true,则阻止在不同http请求之间重用TCP连接// DisableCompression, if true, prevents the Transport from// requesting compression with an "Accept-Encoding: gzip"// request header when the Request contains no existing// Accept-Encoding value. If the Transport requests gzip on// its own and gets a gzipped response, it's transparently// decoded in the Response.Body. However, if the user// explicitly requested gzip it is not automatically// uncompressed.DisableCompression bool //如果为true,则进制传输使用 Accept-Encoding: gzip// MaxIdleConns controls the maximum number of idle (keep-alive)// connections across all hosts. Zero means no limit.MaxIdleConns int //指定最大的空闲连接数// MaxIdleConnsPerHost, if non-zero, controls the maximum idle// (keep-alive) connections to keep per-host. If zero,// DefaultMaxIdleConnsPerHost is used.MaxIdleConnsPerHost int //用于控制某一个主机的连接的最大空闲数// IdleConnTimeout is the maximum amount of time an idle// (keep-alive) connection will remain idle before closing// itself.// Zero means no limit.IdleConnTimeout time.Duration //指定空闲连接保持的最长时间,如果为0,则不受限制// ResponseHeaderTimeout, if non-zero, specifies the amount of// time to wait for a server's response headers after fully// writing the request (including its body, if any). This// time does not include the time to read the response body./*ResponseHeaderTimeout,如果非零,则指定在完全写入请求(包括其正文,如果有)之后等待服务器响应头的最长时间。此时间不包括读响应体的时间。*/ResponseHeaderTimeout time.Duration// ExpectContinueTimeout, if non-zero, specifies the amount of// time to wait for a server's first response headers after fully// writing the request headers if the request has an// "Expect: 100-continue" header. Zero means no timeout and// causes the body to be sent immediately, without// waiting for the server to approve.// This time does not include the time to send the request header./*如果请求头是"Expect:100-continue",ExpectContinueTimeout 如果不为0,它表示等待服务器第一次响应头的最大时间零表示没有超时并导致正文立即发送,无需等待服务器批准。此时间不包括发送请求标头的时间。*/ExpectContinueTimeout time.Duration// TLSNextProto specifies how the Transport switches to an// alternate protocol (such as HTTP/2) after a TLS NPN/ALPN// protocol negotiation. If Transport dials an TLS connection// with a non-empty protocol name and TLSNextProto contains a// map entry for that key (such as "h2"), then the func is// called with the request's authority (such as "example.com"// or "example.com:1234") and the TLS connection. The function// must return a RoundTripper that then handles the request.// If TLSNextProto is not nil, HTTP/2 support is not enabled// automatically./*TLSNextProto指定在TLS NPN / ALPN协议协商之后传输如何切换到备用协议(例如HTTP / 2)。如果传输使用非空协议名称拨打TLS连接并且TLSNextProto包含该密钥的映射条目(例如“h2”),则使用请求的权限调用func(例如“example.com”或“example” .com:1234“)和TLS连接。该函数必须返回一个RoundTripper,然后处理该请求。 如果TLSNextProto不是nil,则不会自动启用HTTP / 2支持。*/TLSNextProto map[string]func(authority string, c *tls.Conn) RoundTripper// ProxyConnectHeader optionally specifies headers to send to// proxies during CONNECT requests./*ProxyConnectHeader可选地指定在CONNECT请求期间发送给代理的标头。*/ProxyConnectHeader Header// MaxResponseHeaderBytes specifies a limit on how many// response bytes are allowed in the server's response// header.//// Zero means to use a default limit./*指定服务器返回的响应头的最大字节数为0则使用默认的限制*/MaxResponseHeaderBytes int64// nextProtoOnce guards initialization of TLSNextProto and// h2transport (via onceSetNextProtoDefaults)//nextProtoOnce保护 TLSNextProto和 h2transport 的初始化nextProtoOnce sync.Onceh2transport *http2Transport // non-nil if http2 wired up,如果是http2连通,则不为nil// TODO: tunable on max per-host TCP dials in flight (Issue 13957)}以上是Transport结构体及每个字段的主要功能,从中可以看到
idleConn 可以理解成 空闲的连接池,用于存放空闲的连接,从而使连接可以复用。
idleConnCh用来在并发http请求的时候在多个goroutine里相互发送persistConn,可以使persistConn持久化连接得到重复使用。
RoundTrip方法
Transport的核心方法时RoundTrip方法,该方法的工作流程基本如下:
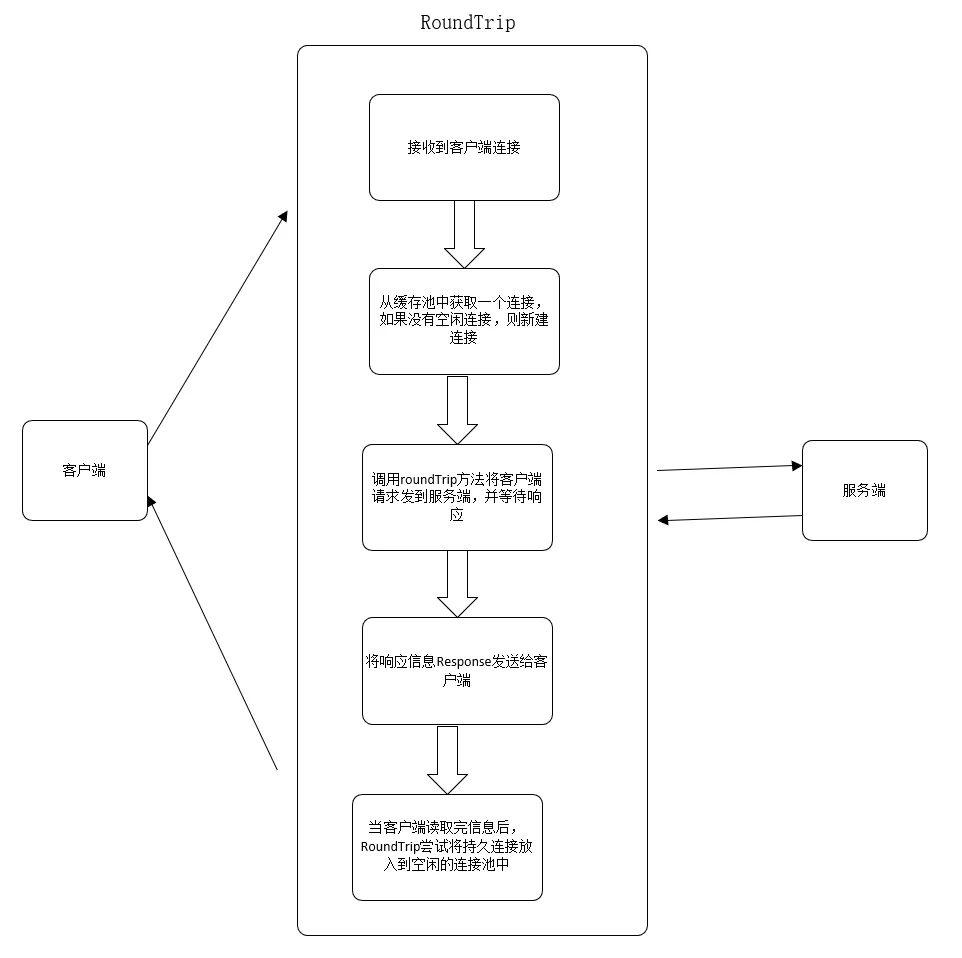
RoundTrip方法源码如下:
//RoundTrip实现了RoundTripper接口func (t *Transport) RoundTrip(req *Request) (*Response, error) {//初始化TLSNextProto http2使用t.nextProtoOnce.Do(t.onceSetNextProtoDefaults)//获取请求的上下文ctx := req.Context()trace := httptrace.ContextClientTrace(ctx)//错误处理if req.URL == nil {req.closeBody()return nil, errors.New("http: nil Request.URL")}if req.Header == nil {req.closeBody()return nil, errors.New("http: nil Request.Header")}scheme := req.URL.SchemeisHTTP := scheme == "http" || scheme == "https"//如果是http或https请求,对Header中的数据进行校验if isHTTP {for k, vv := range req.Header {if !httplex.ValidHeaderFieldName(k) {return nil, fmt.Errorf("net/http: invalid header field name %q", k)}for _, v := range vv {if !httplex.ValidHeaderFieldValue(v) {return nil, fmt.Errorf("net/http: invalid header field value %q for key %v", v, k)}}}}//如果该scheme有自定义的RoundTrip,则使用自定义的RoundTrip处理request,并返回responsealtProto, _ := t.altProto.Load().(map[string]RoundTripper)if altRT := altProto[scheme]; altRT != nil {if resp, err := altRT.RoundTrip(req); err != ErrSkipAltProtocol {return resp, err}}//如果不是http请求,则关闭并退出if !isHTTP {req.closeBody()return nil, &badStringError{"unsupported protocol scheme", scheme}}//对请求的Method进行校验if req.Method != "" && !validMethod(req.Method) {return nil, fmt.Errorf("net/http: invalid method %q", req.Method)}//请求的host为空,则返回if req.URL.Host == "" {req.closeBody()return nil, errors.New("http: no Host in request URL")}for {// treq gets modified by roundTrip, so we need to recreate for each retry.//初始化transportRequest,transportRequest是request的包装器treq := &transportRequest{Request: req, trace: trace}//根据用户的请求信息获取connectMethod cmcm, err := t.connectMethodForRequest(treq)if err != nil {req.closeBody()return nil, err}// Get the cached or newly-created connection to either the// host (for http or https), the http proxy, or the http proxy// pre-CONNECTed to https server. In any case, we'll be ready// to send it requests.//从缓存中获取一个连接,或者新建一个连接pconn, err := t.getConn(treq, cm)if err != nil {t.setReqCanceler(req, nil)req.closeBody()return nil, err}var resp *Responseif pconn.alt != nil {// HTTP/2 path.t.setReqCanceler(req, nil) // not cancelable with CancelRequestresp, err = pconn.alt.RoundTrip(req)} else {resp, err = pconn.roundTrip(treq)}if err == nil {return resp, nil}if !pconn.shouldRetryRequest(req, err) {// Issue 16465: return underlying net.Conn.Read error from peek,// as we've historically done.if e, ok := err.(transportReadFromServerError); ok {err = e.err}return nil, err}testHookRoundTripRetried()// Rewind the body if we're able to. (HTTP/2 does this itself so we only// need to do it for HTTP/1.1 connections.)if req.GetBody != nil && pconn.alt == nil {newReq := *reqvar err errornewReq.Body, err = req.GetBody()if err != nil {return nil, err}req = &newReq}}}该方法首先会进行一些校验,如果客户端请求的scheme有自定的RoundTrip,则使用自定义的RoundTrip处理request,并返回response。
该方法主要的请求处理逻辑在for循环里,首先会根据请求从空闲的连接池中获取一个连接或新建一个连接pconn。忽略HTTP/2请求的处理,其他常用的HTTP请求会调用roundTrip方法将客户端发送给服务器,并等待返回response。
getConn获取或新建连接
func (t *Transport) getConn(treq *transportRequest, cm connectMethod) (*persistConn, error) {req := treq.Requesttrace := treq.tracectx := req.Context()//GetConn是钩子函数在获取连接前调用if trace != nil && trace.GetConn != nil {trace.GetConn(cm.addr())}//如果可以获取到空闲的连接if pc, idleSince := t.getIdleConn(cm); pc != nil {if trace != nil && trace.GotConn != nil { //GotConn是钩子函数,成功获取连接后调用trace.GotConn(pc.gotIdleConnTrace(idleSince))}// set request canceler to some non-nil function so we// can detect whether it was cleared between now and when// we enter roundTrip/*将请求的canceler设置为某些非零函数,以便我们可以检测它是否在现在和我们进入roundTrip之间被清除*/t.setReqCanceler(req, func(error) {})return pc, nil}type dialRes struct {pc *persistConnerr error}dialc := make(chan dialRes)// Copy these hooks so we don't race on the postPendingDial in// the goroutine we launch. Issue 11136.testHookPrePendingDial := testHookPrePendingDialtestHookPostPendingDial := testHookPostPendingDial//该内部函数handlePendingDial的主要作用是,新开启一个协程,当新建连接完成后但没有被使用,将其放到连接池(缓存)中或将其关闭handlePendingDial := func() {testHookPrePendingDial()go func() {if v := <-dialc; v.err == nil {t.putOrCloseIdleConn(v.pc)}testHookPostPendingDial()}()}cancelc := make(chan error, 1)t.setReqCanceler(req, func(err error) { cancelc <- err })go func() {//开启一个协程新建一个连接pc, err := t.dialConn(ctx, cm)dialc <- dialRes{pc, err}}()idleConnCh := t.getIdleConnCh(cm)select {case v := <-dialc: //获取新建的连接// Our dial finished.if v.pc != nil { //如果新建的连接不为nil,则返回新建的连接if trace != nil && trace.GotConn != nil && v.pc.alt == nil {trace.GotConn(httptrace.GotConnInfo{Conn: v.pc.conn})}return v.pc, nil}// Our dial failed. See why to return a nicer error// value.select {case <-req.Cancel:// It was an error due to cancelation, so prioritize that// error value. (Issue 16049)return nil, errRequestCanceledConncase <-req.Context().Done():return nil, req.Context().Err()case err := <-cancelc:if err == errRequestCanceled {err = errRequestCanceledConn}return nil, errdefault:// It wasn't an error due to cancelation, so// return the original error message:return nil, v.err}case pc := <-idleConnCh: //如果在新建连接的过程中,有空闲的连接,则返回该空闲的连接// Another request finished first and its net.Conn// became available before our dial. Or somebody// else's dial that they didn't use.// But our dial is still going, so give it away// when it finishes://如果在dial连接的时候,有空闲的连接,但是这个时候我们仍然正在新建连接,所以当它新建完成后将其放到连接池或丢弃handlePendingDial()if trace != nil && trace.GotConn != nil {trace.GotConn(httptrace.GotConnInfo{Conn: pc.conn, Reused: pc.isReused()})}return pc, nilcase <-req.Cancel:handlePendingDial()return nil, errRequestCanceledConncase <-req.Context().Done():handlePendingDial()return nil, req.Context().Err()case err := <-cancelc:handlePendingDial()if err == errRequestCanceled {err = errRequestCanceledConn}return nil, err}}第一步:尝试从空闲的连接池中获取空闲连接(通过getIdleConn方法)
如果缓存中有空闲的连接,则获取空闲的连接,并从idleConn和idleLRU中删除该连接,getIdleConn方法的源码如下:
func (t *Transport) getIdleConn(cm connectMethod) (pconn *persistConn, idleSince time.Time) {key := cm.key()t.idleMu.Lock()defer t.idleMu.Unlock()for {pconns, ok := t.idleConn[key]if !ok {return nil, time.Time{}}if len(pconns) == 1 {pconn = pconns[0]delete(t.idleConn, key)} else {// 2 or more cached connections; use the most// recently used one at the end.pconn = pconns[len(pconns)-1]t.idleConn[key] = pconns[:len(pconns)-1]}t.idleLRU.remove(pconn)if pconn.isBroken() { //如果该连接被关闭,则继续从缓存中查找// There is a tiny window where this is// possible, between the connecting dying and// the persistConn readLoop calling// Transport.removeIdleConn. Just skip it and// carry on.continue}if pconn.idleTimer != nil && !pconn.idleTimer.Stop() {// We picked this conn at the ~same time it// was expiring and it's trying to close// itself in another goroutine. Don't use it.continue}return pconn, pconn.idleAt}}前面我们提到过空闲的连接存放在idleConn字段中,该字段是map结构,可以通过客户端的请求信息(proxy,scheme,addr)来获取持久连接persistConn。getIdleConn方法尝试从空闲的连接池idleConn中获取空闲连接,如果获取到空闲的连接,则从该idleConn map中删除,并判断该连接是否被关闭,如果该连接已经被关闭则继续获取。如果可以获取到空闲连接则返回该连接,将使用该连接与服务器进行通讯,如果获取不到则新建连接。第二步:如果空闲的连接池中没有可用的连接,则会调用dialConn方法新建连接
当我们无法从空闲的连接池中获取连接,就要新建连接。新建连接的大致过程如下:***首先** *初始化dialc channel, 该channel用于等待新建的连接,如果连接创建成功则将创建的连接放入到dialc中go func() {//开启一个协程新建一个连接pc, err := t.dialConn(ctx, cm)dialc <- dialRes{pc, err}}()handlePendingDial函数,该内部函数的主要作用用于开启一个协程,当新建连接成功但没有被使用,则通过该函数将其放到连接池中或将其关闭。handlePendingDial := func() {testHookPrePendingDial()go func() {if v := <-dialc; v.err == nil {t.putOrCloseIdleConn(v.pc)}testHookPostPendingDial()}()}其次 用select case 监听事件
1.监听连接是否重建成功,如果连接创建成功则返回该新建的连接
2.通过idleConnCh channel监听是否在创建连接的时候有空闲的连接,如果有空闲的连接则返回空闲连接,并调用handlePendingDial函数,处理新建的连接,将新建的连接放入到空闲的连接池中或将其关闭。idleConnCh是为了多个http请求之间复用,当一个客户端的请求处理完成之后,首先会尝试将该连接写入到idleConnCh中,如果有其他http在监听等待该idleConnCh,则会写入成功。从而降低客户端请求的等待时间。如果该连接无法放入到idleConnCh中,则会尝试将该连接放入到idleConn中
3.在等待创建连接的过程中也在监听是否有取消客户端请求的消息,如果有也会调用handlePendingDial函数,并返回错误信息。新建连接的过程
前面我们看到新建连接时,会开启一个协程来执行dialConn方法来创建连接,dialConn方法源码如下:func (t *Transport) dialConn(ctx context.Context, cm connectMethod) (*persistConn, error) {//初始化persistConn结构体pconnpconn := &persistConn{t: t,cacheKey: cm.key(),reqch: make(chan requestAndChan, 1),writech: make(chan writeRequest, 1),closech: make(chan struct{}),writeErrCh: make(chan error, 1),writeLoopDone: make(chan struct{}),}trace := httptrace.ContextClientTrace(ctx)wrapErr := func(err error) error {if cm.proxyURL != nil {// Return a typed error, per Issue 16997return &net.OpError{Op: "proxyconnect", Net: "tcp", Err: err}}return err}//如果scheme为https,并且DialTLS函数不为nilif cm.scheme() == "https" && t.DialTLS != nil {var err errorpconn.conn, err = t.DialTLS("tcp", cm.addr())if err != nil {return nil, wrapErr(err)}if pconn.conn == nil {return nil, wrapErr(errors.New("net/http: Transport.DialTLS returned (nil, nil)"))}if tc, ok := pconn.conn.(*tls.Conn); ok {// Handshake here, in case DialTLS didn't. TLSNextProto below// depends on it for knowing the connection state.if trace != nil && trace.TLSHandshakeStart != nil {trace.TLSHandshakeStart()}if err := tc.Handshake(); err != nil {go pconn.conn.Close()if trace != nil && trace.TLSHandshakeDone != nil {trace.TLSHandshakeDone(tls.ConnectionState{}, err)}return nil, err}cs := tc.ConnectionState()if trace != nil && trace.TLSHandshakeDone != nil {trace.TLSHandshakeDone(cs, nil)}pconn.tlsState = &cs}} else {//创建tcp连接conn, err := t.dial(ctx, "tcp", cm.addr())if err != nil {return nil, wrapErr(err)}pconn.conn = connif cm.scheme() == "https" {var firstTLSHost stringif firstTLSHost, _, err = net.SplitHostPort(cm.addr()); err != nil {return nil, wrapErr(err)}if err = pconn.addTLS(firstTLSHost, trace); err != nil {return nil, wrapErr(err)}}}....... 处理代理等消息省略//初始化br和bwpconn.br = bufio.NewReader(pconn)pconn.bw = bufio.NewWriter(persistConnWriter{pconn})go pconn.readLoop()go pconn.writeLoop()return pconn, nil}新建连接的过程主要在dialConn方法中,新建连接的大致过程如下:
1. 首先初始化persistConn结构体2. 创建连接,创建连接时区分https和http3. 连接创建成功后,会开启两个协程,一个用于处理输入流writeLoop,一个用于处理输出流readLoop从中我们看到当客户端和服务端每建立一个连接,都会开启两个协程,一个处理输入流writeLoop,一个处理输出流readLoop。
readLoop方法
/*从网络连接中读取消息并解析成Response*/func (pc *persistConn) readLoop() {closeErr := errReadLoopExiting // default value, if not changed belowdefer func() {pc.close(closeErr)pc.t.removeIdleConn(pc)}()//函数作用:尝试将pc放入空闲连接池中tryPutIdleConn := func(trace *httptrace.ClientTrace) bool {if err := pc.t.tryPutIdleConn(pc); err != nil {closeErr = errif trace != nil && trace.PutIdleConn != nil && err != errKeepAlivesDisabled {trace.PutIdleConn(err)}return false}if trace != nil && trace.PutIdleConn != nil {trace.PutIdleConn(nil)}return true}// eofc is used to block caller goroutines reading from Response.Body// at EOF until this goroutines has (potentially) added the connection// back to the idle pool.eofc := make(chan struct{})defer close(eofc) // unblock reader on errors// Read this once, before loop starts. (to avoid races in tests)testHookMu.Lock()testHookReadLoopBeforeNextRead := testHookReadLoopBeforeNextReadtestHookMu.Unlock()alive := truefor alive {pc.readLimit = pc.maxHeaderResponseSize()_, err := pc.br.Peek(1)pc.mu.Lock()if pc.numExpectedResponses == 0 {pc.readLoopPeekFailLocked(err)pc.mu.Unlock()return}pc.mu.Unlock()//从reqch通道中获取请求数据和等待返回的response的channelrc := <-pc.reqchtrace := httptrace.ContextClientTrace(rc.req.Context()) //从请求的上下文中获取tracevar resp *Responseif err == nil {resp, err = pc.readResponse(rc, trace) //从网络连接中读取http的响应信息Response} else {err = transportReadFromServerError{err}closeErr = err}if err != nil { //错误处理if pc.readLimit <= 0 {err = fmt.Errorf("net/http: server response headers exceeded %d bytes; aborted", pc.maxHeaderResponseSize())}select {case rc.ch <- responseAndError{err: err}:case <-rc.callerGone:return}return}pc.readLimit = maxInt64 // effictively no limit for response bodiespc.mu.Lock()pc.numExpectedResponses--pc.mu.Unlock()hasBody := rc.req.Method != "HEAD" && resp.ContentLength != 0 //判断是否响应的消息有bodyif resp.Close || rc.req.Close || resp.StatusCode <= 199 {// Don't do keep-alive on error if either party requested a close// or we get an unexpected informational (1xx) response.// StatusCode 100 is already handled above.alive = false}if !hasBody { //如果响应体没有bodypc.t.setReqCanceler(rc.req, nil) //将reqCanceler取消函数中对应的req删除// Put the idle conn back into the pool before we send the response// so if they process it quickly and make another request, they'll// get this same conn. But we use the unbuffered channel 'rc'// to guarantee that persistConn.roundTrip got out of its select// potentially waiting for this persistConn to close.// but after/*在返回response之前,将空闲的conn放到连接池中*/alive = alive &&!pc.sawEOF &&pc.wroteRequest() &&tryPutIdleConn(trace)select {case rc.ch <- responseAndError{res: resp}: //将响应信息返回到roundTrip中case <-rc.callerGone:return}// Now that they've read from the unbuffered channel, they're safely// out of the select that also waits on this goroutine to die, so// we're allowed to exit now if needed (if alive is false)testHookReadLoopBeforeNextRead()continue}waitForBodyRead := make(chan bool, 2)body := &bodyEOFSignal{body: resp.Body,earlyCloseFn: func() error {waitForBodyRead <- false<-eofc // will be closed by deferred call at the end of the functionreturn nil},fn: func(err error) error {isEOF := err == io.EOFwaitForBodyRead <- isEOFif isEOF {<-eofc // see comment above eofc declaration} else if err != nil {if cerr := pc.canceled(); cerr != nil {return cerr}}return err},}resp.Body = bodyif rc.addedGzip && strings.EqualFold(resp.Header.Get("Content-Encoding"), "gzip") {resp.Body = &gzipReader{body: body}resp.Header.Del("Content-Encoding")resp.Header.Del("Content-Length")resp.ContentLength = -1resp.Uncompressed = true}//将response返回到到roundTrip中select {case rc.ch <- responseAndError{res: resp}:case <-rc.callerGone:return}// Before looping back to the top of this function and peeking on// the bufio.Reader, wait for the caller goroutine to finish// reading the response body. (or for cancelation or death)/*等待返回的response中的body被读完后,才会将连接放入到连接池中,等待再次使用该连接*/select {case bodyEOF := <-waitForBodyRead:pc.t.setReqCanceler(rc.req, nil) // before pc might return to idle poolalive = alive &&bodyEOF &&!pc.sawEOF &&pc.wroteRequest() &&tryPutIdleConn(trace)if bodyEOF {eofc <- struct{}{}}case <-rc.req.Cancel:alive = falsepc.t.CancelRequest(rc.req)case <-rc.req.Context().Done():alive = falsepc.t.cancelRequest(rc.req, rc.req.Context().Err())case <-pc.closech:alive = false}testHookReadLoopBeforeNextRead()}}readLoop方法的主要作用是从网络中读取消息并解析成Response返回定义内部函数tryPutIdleConn,该函数的主要作用是将持久化连接persistConn放入到空闲连接池中persistConn持久化连接中的reqch chan requestAndChan该channel是用于获取客户端的请求信息并等待返回的response。requestAndChan结构体如下:type requestAndChan struct {req *Request ch chan responseAndError // unbuffered; always send in select on callerGone// whether the Transport (as opposed to the user client code)// added the Accept-Encoding gzip header. If the Transport// set it, only then do we transparently decode the gzip.addedGzip bool// Optional blocking chan for Expect: 100-continue (for send).// If the request has an "Expect: 100-continue" header and// the server responds 100 Continue, readLoop send a value// to writeLoop via this chan.continueCh chan<- struct{}callerGone <-chan struct{} // closed when roundTrip caller has returned}其中req是用户请求信息。ch是response和error相关信息,用于等待从服务端读取响应信息。continueCh用于判断100-continue的情况。其中req是用户请求信息。ch是response和error相关信息,用于等待从服务端读取响应信息。continueCh用于判断100-continue的情况。
readLoop的大致流程如下:
1.如果连接正常则轮询读取要发送到服务端的客户端请求信息rc
2.调用readResponse方法从网络连接中读取http的响应信息并封装成Response
3.如果读取时有错误信息,则将error信息发送通过rc中的ch字段将错误信息返回
4.如果读取到的响应信息没有响应体(即Body),如果连接正常则尝试将连接放入到连接池中。并将响应信息通过rc中的ch channel发送到roundTrip中,从而响应给http客户端请求。5.如果读取到的响应信息有响应体(即Body),则会将响应体进行封装,封装成bodyEOFSignal结构体,目的是为了当客户端读取响应体之后,才会将该连接放入到连接池中,等待再次被使用。tryPutIdleConn将连接放入到空闲连接池中
func (t *Transport) tryPutIdleConn(pconn *persistConn) error {........waitingDialer := t.idleConnCh[key]select {case waitingDialer <- pconn:// We're done with this pconn and somebody else is// currently waiting for a conn of this type (they're// actively dialing, but this conn is ready// first). Chrome calls this socket late binding. See// https://insouciant.org/tech/connection-management-in-chromium/return nildefault:if waitingDialer != nil {// They had populated this, but their dial won// first, so we can clean up this map entry.delete(t.idleConnCh, key)}}if t.wantIdle {return errWantIdle}if t.idleConn == nil {t.idleConn = make(map[connectMethodKey][]*persistConn)}idles := t.idleConn[key]if len(idles) >= t.maxIdleConnsPerHost() {return errTooManyIdleHost}for _, exist := range idles {if exist == pconn {log.Fatalf("dup idle pconn %p in freelist", pconn)}}t.idleConn[key] = append(idles, pconn)t.idleLRU.add(pconn)if t.MaxIdleConns != 0 && t.idleLRU.len() > t.MaxIdleConns {oldest := t.idleLRU.removeOldest()oldest.close(errTooManyIdle)t.removeIdleConnLocked(oldest)}if t.IdleConnTimeout > 0 {if pconn.idleTimer != nil {pconn.idleTimer.Reset(t.IdleConnTimeout)} else {pconn.idleTimer = time.AfterFunc(t.IdleConnTimeout, pconn.closeConnIfStillIdle)}}pconn.idleAt = time.Now()return nil}tryPutIdleConn将持久化连接放入到空闲连接池的过程大致如下:
1.如果有其他http请求正在等待该连接,则将该连接写入到waitingDialer,从而使其他http请求复用
2.尝试将该连接放入到空闲的连接池中idleConn
writeLoop方法
func (pc *persistConn) writeLoop() {defer close(pc.writeLoopDone)for {select {case wr := <-pc.writech: //获取到要写入到输入流中的request相关数据startBytesWritten := pc.nwriteerr := wr.req.Request.write(pc.bw, pc.isProxy, wr.req.extra, pc.waitForContinue(wr.continueCh)) //向网络连接中写入数据if bre, ok := err.(requestBodyReadError); ok { //错误处理err = bre.error// Errors reading from the user's// Request.Body are high priority.// Set it here before sending on the// channels below or calling// pc.close() which tears town// connections and causes other// errors.wr.req.setError(err)}if err == nil { //写入时没有错误,则刷新缓存err = pc.bw.Flush()}if err != nil { //错误处理wr.req.Request.closeBody()if pc.nwrite == startBytesWritten {err = nothingWrittenError{err}}}pc.writeErrCh <- err // to the body reader, which might recycle uswr.ch <- err // to the roundTrip function,将err发送到roundTrip,roundTrip根据是否为nil,来判断是否请求发送成功if err != nil {pc.close(err)return}case <-pc.closech:return}}}writeLoop相对比较简单,主要是向输入流中写入数据,监听pc.writech获取要写入到输入流的request相关数据,并写入到网络连接中。到此新建连接的大致过程已经讲解完成。
RoundTrip方法源码中的通过getConn方法获取或新建连接我们已经了解,建立连接之后就可以数据的读写了,后面http事务主要在roundTrip方法中完成
roundTrip方法处理请求并等待响应
从上面新建连接我们知道每一个持久连接persistConn,都会有两个协程,一个处理输入流,一个处理输出流。输出流readLoop主要读取 reqch chan requestAndChan中的数据,读取到数据后会等待从网络连接中读取响应数据。输入流writeLoop主要处理writech chan writeRequest中的消息,并将该消息写入到网络连接中。func (pc *persistConn) roundTrip(req *transportRequest) (resp *Response, err error) {testHookEnterRoundTrip()....../*将请求消息写入到输入流*/startBytesWritten := pc.nwritewriteErrCh := make(chan error, 1)pc.writech <- writeRequest{req, writeErrCh, continueCh}//将请求消息发送到输出流,并等待返回resc := make(chan responseAndError)pc.reqch <- requestAndChan{req: req.Request,ch: resc,addedGzip: requestedGzip,continueCh: continueCh,callerGone: gone,}var respHeaderTimer <-chan time.TimecancelChan := req.Request.CancelctxDoneChan := req.Context().Done()for {testHookWaitResLoop()select {case err := <-writeErrCh:if debugRoundTrip {req.logf("writeErrCh resv: %T/%#v", err, err)}if err != nil {pc.close(fmt.Errorf("write error: %v", err))return nil, pc.mapRoundTripError(req, startBytesWritten, err)}if d := pc.t.ResponseHeaderTimeout; d > 0 {if debugRoundTrip {req.logf("starting timer for %v", d)}timer := time.NewTimer(d)defer timer.Stop() // prevent leaksrespHeaderTimer = timer.C}case <-pc.closech:if debugRoundTrip {req.logf("closech recv: %T %#v", pc.closed, pc.closed)}return nil, pc.mapRoundTripError(req, startBytesWritten, pc.closed)case <-respHeaderTimer:if debugRoundTrip {req.logf("timeout waiting for response headers.")}pc.close(errTimeout)return nil, errTimeoutcase re := <-resc: //等待获取response信息if (re.res == nil) == (re.err == nil) {panic(fmt.Sprintf("internal error: exactly one of res or err should be set; nil=%v", re.res == nil))}if debugRoundTrip {req.logf("resc recv: %p, %T/%#v", re.res, re.err, re.err)}if re.err != nil {return nil, pc.mapRoundTripError(req, startBytesWritten, re.err)}return re.res, nilcase <-cancelChan:pc.t.CancelRequest(req.Request)cancelChan = nilcase <-ctxDoneChan:pc.t.cancelRequest(req.Request, req.Context().Err())cancelChan = nilctxDoneChan = nil}}}roundTrip方法的大致流程:
1.将请求消息写入到writech,将请求信息发送给输入流
2.将请求消息写入到reqch,等待服务端响应的消息
3.resc chan就是为了等待从服务端响应的消息。
4.返回从服务端响应的消息或错误信息
以上就是RoundTrip方法的主要流程,如果有理解不足或错误的地方还请指正。
