正当有这个需求的时候,就看到了这个实现姿势。源自coreos的一篇博客,转载到了grpc官方博客gRPC with REST and Open APIs。
etcd3改用grpc后为了兼容原来的api,同时要提供http/json方式的API,为了满足这个需求,要么开发两套API,要么实现一种转换机制,他们选择了后者,而我们选择跟随他们的脚步。
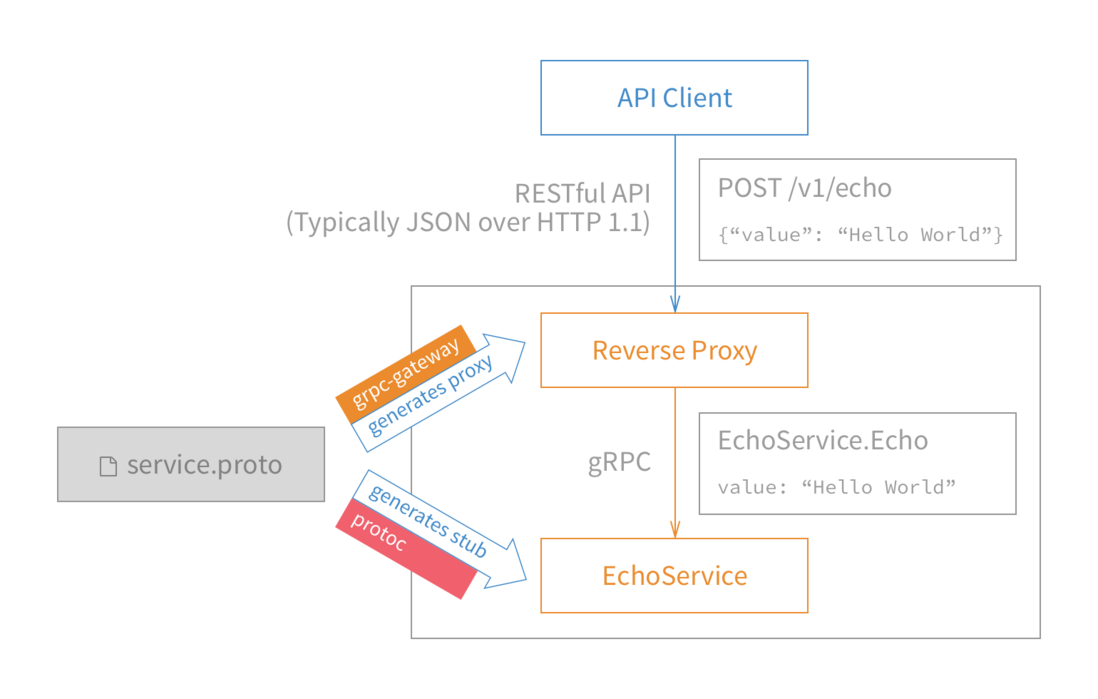
他们实现了一个协议转换的网关,对应github上的项目grpc-gateway,这个网关负责接收客户端请求,然后决定直接转发给grpc服务还是转给http服务,当然,http服务也需要请求grpc服务获取响应,然后转为json响应给客户端。结构如图:
下面我们就直接实战吧。基于hello-tls项目扩展,客户端改动不大,服务端和proto改动较大。
安装grpc-gateway
go get -u github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway
项目结构:
$GOPATH/src/grpc-go-practice/
example/
|—— hello-http-2/
|—— client/
|—— main.go // 客户端
|—— server/
|—— main.go // 服务端
|—— keys/ // 证书目录
|—— server.key
|—— server.pem
|—— proto/
|—— google // googleApi http-proto定义
|—— api
|—— annotations.proto
|—— annotations.pb.go
|—— http.proto
|—— http.pb.go
|—— hello_http.proto // proto描述文件
|—— hello_http.pb.go // proto编译后文件
|—— hello_http_pb.gw.go // gateway编译后文件这里用到了google官方Api中的两个proto描述文件,直接拷贝不要做修改,里面定义了protocol buffer扩展的HTTP option,为grpc的http转换提供支持。
示例代码
proto/hello_http.proto
syntax = "proto3"; // 指定proto版本
package proto; // 指定包名
import "google/api/annotations.proto";
// 定义Hello服务
service HelloHttp {
// 定义SayHello方法
rpc SayHello(HelloHttpRequest) returns (HelloHttpReply) {
// http option
option (google.api.http) = {
post: "/example/echo"
body: "*"
};
}
}
// HelloRequest 请求结构
message HelloHttpRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// HelloReply 响应结构
message HelloHttpReply {
string message = 1;
}SayHello编译proto
cd $GOPATH/src/grpc-go-practice/example/hello-http-2/proto
# 编译google.api
protoc -I . --go_out=plugins=grpc,Mgoogle/protobuf/descriptor.proto=github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go/descriptor:. google/api/*.proto
# 编译hello_http.proto
protoc -I . --go_out=plugins=grpc,Mgoogle/api/annotations.proto=git.vodjk.com/go-grpc/example/proto/google/api:. ./*.proto
# 编译hello_http.proto gateway
protoc --grpc-gateway_out=logtostderr=true:. ./hello_http.protohello_http_pb.gw.goserver/main.go
package main
import (
"crypto/tls"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"strings"
"github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/runtime"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
pb "git.vodjk.com/go-grpc/example/proto"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials"
"google.golang.org/grpc/grpclog"
)
// 定义helloHttpService并实现约定的接口
type helloHttpService struct{}
// HelloHttpService ...
var HelloHttpService = helloHttpService{}
func (h helloHttpService) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *pb.HelloHttpRequest) (*pb.HelloHttpReply, error) {
resp := new(pb.HelloHttpReply)
resp.Message = "Hello " + in.Name + "."
return resp, nil
}
// grpcHandlerFunc 检查请求协议并返回http handler
func grpcHandlerFunc(grpcServer *grpc.Server, otherHandler http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// TODO(tamird): point to merged gRPC code rather than a PR.
// This is a partial recreation of gRPC's internal checks https://github.com/grpc/grpc-go/pull/514/files#diff-95e9a25b738459a2d3030e1e6fa2a718R61
if r.ProtoMajor == 2 && strings.Contains(r.Header.Get("Content-Type"), "application/grpc") {
grpcServer.ServeHTTP(w, r)
} else {
otherHandler.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
})
}
func main() {
endpoint := "127.0.0.1:50052"
// 实例化标准grpc server
creds, err := credentials.NewServerTLSFromFile("../../keys/server.pem", "../../keys/server.key")
if err != nil {
grpclog.Fatalf("Failed to generate credentials %v", err)
}
conn, _ := net.Listen("tcp", endpoint)
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer(grpc.Creds(creds))
pb.RegisterHelloHttpServer(grpcServer, HelloHttpService)
// http-grpc gateway
ctx := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
dcreds, err := credentials.NewClientTLSFromFile("../../keys/server.pem", "server name")
if err != nil {
grpclog.Fatalf("Failed to create TLS credentials %v", err)
}
dopts := []grpc.DialOption{grpc.WithTransportCredentials(dcreds)}
gwmux := runtime.NewServeMux()
err = pb.RegisterHelloHttpHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, gwmux, endpoint, dopts)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("serve: %v\n", err)
return
}
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.Handle("/", gwmux)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 开启HTTP服务
cert, _ := ioutil.ReadFile("../../keys/server.pem")
key, _ := ioutil.ReadFile("../../keys/server.key")
var demoKeyPair *tls.Certificate
pair, err := tls.X509KeyPair(cert, key)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
demoKeyPair = &pair
srv := &http.Server{
Addr: endpoint,
Handler: grpcHandlerFunc(grpcServer, mux),
TLSConfig: &tls.Config{
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{*demoKeyPair},
},
}
fmt.Printf("grpc and https on port: %d\n", 50052)
err = srv.Serve(tls.NewListener(conn, srv.TLSConfig))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("ListenAndServe: ", err)
}
return
}
grpcHandlerFunc基本流程:
-
实例化标准grpc server
-
将grpc server注册给gateway
-
开启http服务,handler指定给grpcHandlerFunc方法
注意:必须开启HTTPS
运行结果
开启服务:
# hello-http-2/server
go run main.go
> grpc and https on port: 50052 调用grpc客户端:
# hello-http-2/client
go run main.go
> Hello gRPC.请求https:
curl -X POST -k https://localhost:50052/example/echo -d '{"name": "gRPC-HTTP is working!"}'
> {"message":"Hello gRPC-HTTP is working!."}为什么是hello-http-2,因为1是个不完整的实现姿势,可以不用https,但是需要分别开启grpc服务和http服务,这里不做说明了。