


具体的题目如下:(就是将多维数组的行列互换)
A multi-dimensional array is an array of arrays. 2-dimensional arrays are the most commonly used. They are used to store data in a tabular manner.

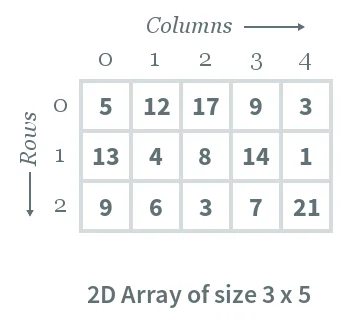
Consider following 2D array, which is of the size 3×53×5. For an array of size N×MN×M, the rows and columns are numbered from 00 to N−1N−1 and columns are numbered from 00 to M−1M−1, respectively. Any element of the array can be accessed by arr[i][j]arr[i][j] where 0≤i<N0≤i<N and 0≤j<M0≤j<M. For example, in the following array, the value stored at arr[1][3]arr[1][3] is 1414.
golang 代码如下:
其中定义二维数组没有什么复杂的,在赋值的过程中我们需要先定义一个一维数组 carray := make([]int, column, column),然后在赋值给外面的数组 array[i] =carray
下来就是字符串拼接和其他的语言不太一样,先定义一个var buffer bytes.Buffer, 然后写数据buffer.WriteString("ddd"),最后就是输出 buffer.String()
还有就是一些数值和字符的互相转换用到了包strconv
package main
import "fmt"
import "strconv"
import "bytes"
func main() {
var row,column int
fmt.Scanln(&row,&column)
var array = make([][]int,row,row)
for i:=0;i<row;i++{
carray := make([]int, column, column)
for j:=0;j<column;j++{
var columnValue string
fmt.Scan(&columnValue)
//fmt.Println(columnValue)
intv,_:= strconv.Atoi(columnValue)
carray[j] = intv
}
array[i] =carray
}
//fmt.Println(array)
var buffer bytes.Buffer
for i:=0;i<column;i++{
buffer.Reset()
for j:=0;j<row;j++{
buffer.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(array[j][i])+" ")
}
fmt.Println(buffer.String())
}
}
- 还没有人评论,欢迎说说您的想法!
