最近学了学go语言,想练习一下用go开发web项目,项目结构弄个什么样呢。
去码云上面找了找,找到一个用Go语言搭建的springboot风格的web项目,拿来按自己的习惯改了改,还不错。
文末git地址
先来看一下整体的项目结构
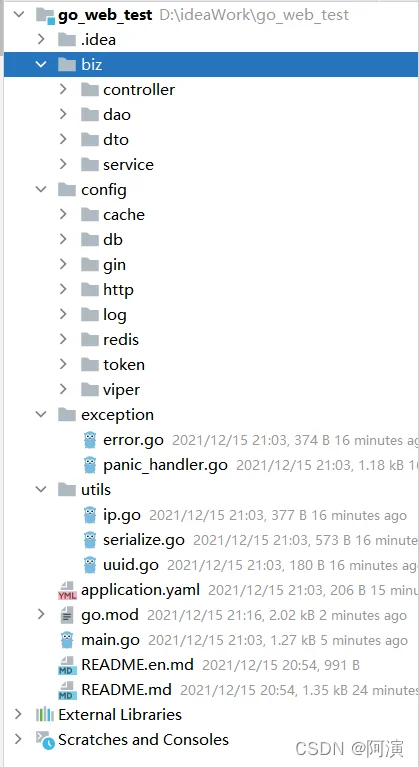
可以看到业务的三层结构和缓存、日志、token、全局异常等。以及一个javaer们最熟悉的application配置文件……
下面说一下整体逻辑
首先肯定是先来搭建一个gomod的go项目,在gomod中引入一些依赖
module go_web_test
go 1.17
require (
github.com/allegro/bigcache v1.2.1
github.com/gin-contrib/cors v1.3.1
github.com/gin-gonic/gin v1.7.7
github.com/satori/go.uuid v1.2.0
github.com/sirupsen/logrus v1.8.1
github.com/spf13/viper v1.9.0
github.com/stretchr/testify v1.7.0
gorm.io/driver/mysql v1.2.1
gorm.io/gorm v1.22.4
)
require (
github.com/davecgh/go-spew v1.1.1 // indirect
github.com/fsnotify/fsnotify v1.5.1 // indirect
github.com/gin-contrib/sse v0.1.0 // indirect
github.com/go-playground/locales v0.13.0 // indirect
github.com/go-playground/universal-translator v0.17.0 // indirect
github.com/go-playground/validator/v10 v10.4.1 // indirect
github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql v1.6.0 // indirect
github.com/golang/protobuf v1.5.2 // indirect
github.com/hashicorp/hcl v1.0.0 // indirect
github.com/jinzhu/inflection v1.0.0 // indirect
github.com/jinzhu/now v1.1.3 // indirect
github.com/json-iterator/go v1.1.11 // indirect
github.com/leodido/go-urn v1.2.0 // indirect
github.com/magiconair/properties v1.8.5 // indirect
github.com/mattn/go-isatty v0.0.12 // indirect
github.com/mitchellh/mapstructure v1.4.2 // indirect
github.com/modern-go/concurrent v0.0.0-20180228061459-e0a39a4cb421 // indirect
github.com/modern-go/reflect2 v1.0.1 // indirect
github.com/pelletier/go-toml v1.9.4 // indirect
github.com/pmezard/go-difflib v1.0.0 // indirect
github.com/spf13/afero v1.6.0 // indirect
github.com/spf13/cast v1.4.1 // indirect
github.com/spf13/jwalterweatherman v1.1.0 // indirect
github.com/spf13/pflag v1.0.5 // indirect
github.com/subosito/gotenv v1.2.0 // indirect
github.com/ugorji/go/codec v1.1.7 // indirect
golang.org/x/crypto v0.0.0-20210817164053-32db794688a5 // indirect
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20210823070655-63515b42dcdf // indirect
golang.org/x/text v0.3.6 // indirect
google.golang.org/protobuf v1.27.1 // indirect
gopkg.in/ini.v1 v1.63.2 // indirect
gopkg.in/yaml.v2 v2.4.0 // indirect
gopkg.in/yaml.v3 v3.0.0-20210107192922-496545a6307b // indirect
)
application配置文件里面自定义一些配置内容
server:
appName: go_web_test
port: 8888
db:
dsn: "root:VHUKZE./start@(192.168.1.8:3306)/vhukze?charset=utf8mb4&parseTime=True&loc=Local"
maxIdleConns: 200
maxOpenConns: 1000
connMaxLifetime: 60然后看启动类,main.go
main方法启动项目,main方法中调用初始化组件的方法,把要用的组件都初始化完成。
下面还有一个自动生成表的方法,可以根据你struct定义的结构来自动生成表结构,就是没每加一个struct就要在这个方法里面加一行生成那个表的代码,在每次启动的时候也是会根据struct的字段来更新表结构的
package main
import (
"fmt"
logger "github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
"go_web_test/biz/controller"
"go_web_test/biz/dao"
"go_web_test/config/cache"
"go_web_test/config/db"
"go_web_test/config/gin"
"go_web_test/config/http"
"go_web_test/config/log"
"go_web_test/config/token"
vc "go_web_test/config/viper"
_ "net/url"
)
func main() {
initComponents()
}
// 初始化服务所有组件
func initComponents() {
// 初始化日志
log.InitLogConfig()
logger.Info("===================================================================================")
logger.Info("Starting Application")
// 读取本地配置文件
vc.InitLocalConfigFile()
// 初始化url配置
//url.InitUrlConfig()
// 初始化Mysql
db.InitDbConfig()
// 自动生成表
autoMigrate()
// 初始化缓存
cache.InitBigCacheConfig()
// 初始化Redis
//redis.InitRedisConfig()
// 初始化HttpClient连接池
//http.InitHttpClientConfig()
// 初始化token
token.InitTokenConfig()
// 初始化Gin
router := gin.InitGinConfig()
// 注册Api
// 用户api
controller.UserApi(router)
// 启动Gin
gin.RunGin(router)
}
// 自动生成表
func autoMigrate() {
err := db.DB.AutoMigrate(dao.User{})
if err != nil {
_ = fmt.Errorf("自动生成user表失败")
panic(err)
}
}
下面来说一下初始化组件中的每个组件内容
初始化日志配置,就是配一下输出日志的格式和输入到文件什么的,下面那个LoggerAccess方法是定义了一个gin的中间件,用来输出请求的日志信息,其实格式跟gin默认的日志输出格式差不多
package log
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
log "github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
"go_web_test/config/log/lumberjack"
"go_web_test/utils"
"io"
"os"
"path"
"time"
)
func InitLogConfig() {
// 设置日志输出路径和名称
logFilePath := path.Join("../log/", "go_web_test.log")
// 日志输出滚动设置
fileOut := &lumberjack.Logger{
Filename: logFilePath, // 日志文件位置
MaxSize: 100, // 单文件最大容量,单位是MB
MaxBackups: 500, // 最大保留过期文件个数
MaxAge: 15, // 保留过期文件的最大时间间隔,单位是天
LocalTime: true, // 启用当地时区计时
}
// 文件和控制台日志输出
writers := []io.Writer{
fileOut,
os.Stdout,
}
fileAndStdoutWriter := io.MultiWriter(writers...)
log.SetOutput(fileAndStdoutWriter)
// 设置日志格式为Text格式
log.SetFormatter(&log.TextFormatter{
DisableColors: false,
FullTimestamp: true,
TimestampFormat: "2006-01-02 15:04:05",
})
// 设置日志级别为Info以上
log.SetLevel(log.InfoLevel)
}
// LoggerAccess 入口日志打印
func LoggerAccess(c *gin.Context) {
// 开始时间
startTime := time.Now()
// 处理请求
c.Next()
// 请求方式
reqMethod := c.Request.Method
// 请求路由
reqUri := c.Request.RequestURI
// 状态码
statusCode := c.Writer.Status()
// 服务器IP
serverIP := utils.GetLocalIP()
// 客户端IP
clientIP := c.ClientIP()
// 结束时间
endTime := time.Now()
// 执行时间
latencyTime := fmt.Sprintf("%6v", endTime.Sub(startTime))
//日志格式
log.WithFields(log.Fields{
"server-ip": serverIP,
"duration": latencyTime,
"status": statusCode,
"method": reqMethod,
"uri": reqUri,
"client-ip": clientIP,
}).Info("Api accessing")
}
读取本地配置文件,就是读取我们的application.yaml配置文件的内容,这里用的是viper这个工具,这里读取完之后,在其他代码里面就可以直接用viper来获取配置文件的内容了
package viper
import (
"fmt"
log "github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
"github.com/spf13/viper"
)
const fileName = "application"
// InitLocalConfigFile 加载本地配置文件
func InitLocalConfigFile() {
log.Info("初始化本地配置文件……")
viper.SetConfigName(fileName)
viper.SetConfigType("yaml")
viper.AddConfigPath("./")
err := viper.ReadInConfig()
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("读取配置文件失败: %s \n", err))
}
log.Info("本地配置文件初始化完成……")
}
初始化mysql,根据配置文件中的URL来连接数据库
package db
import (
"fmt"
log "github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
"github.com/spf13/viper"
"gorm.io/driver/mysql"
"gorm.io/gorm"
"gorm.io/gorm/schema"
"time"
)
var DB *gorm.DB
// InitDbConfig 初始化Db
func InitDbConfig() {
log.Info("初始化数据库 Mysql")
var err error
dsn := viper.GetString("db.dsn")
maxIdleConns := viper.GetInt("db.maxIdleConns")
maxOpenConns := viper.GetInt("db.maxOpenConns")
connMaxLifetime := viper.GetInt("db.connMaxLifetime")
if DB, err = gorm.Open(mysql.Open(dsn), &gorm.Config{
QueryFields: true,
NamingStrategy: schema.NamingStrategy{
TablePrefix: "", // 表名前缀
SingularTable: true, // 使用单数表名
},
}); err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("初始化数据库失败: %s \n", err))
}
sqlDB, err := DB.DB()
if sqlDB != nil {
sqlDB.SetMaxIdleConns(maxIdleConns) // 空闲连接数
sqlDB.SetMaxOpenConns(maxOpenConns) // 最大连接数
sqlDB.SetConnMaxLifetime(time.Second * time.Duration(connMaxLifetime)) // 单位:秒
}
log.Info("Mysql: 数据库初始化完成")
}
初始化缓存,没有redis的时候可以用这个,我这里没有弄redis,先把redis的内容注释了。
package cache
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/allegro/bigcache"
log "github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
"go_web_test/utils"
"math"
"time"
)
var BigCache *Cache
// Cache 缓存
type Cache struct {
BigCache *bigcache.BigCache // 本地缓存
}
// Get 根据key从缓存中获取对象
func (c Cache) Get(key string) (value interface{}, err error) {
valueBytes, err := c.BigCache.Get(key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
value = utils.Deserialize(valueBytes)
return value, nil
}
// Set 根据key,value将目标对象存入缓存中
func (c Cache) Set(key string, value interface{}) {
valueBytes := utils.Serialize(value)
err := c.BigCache.Set(key, valueBytes)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
// InitBigCacheConfig 初始化BigCache
func InitBigCacheConfig() {
log.Info("初始化缓存…… BigCache")
config := bigcache.Config{
Shards: 1024, // 存储的条目数量,值必须是2的幂
LifeWindow: math.MaxInt16 * time.Hour, // 超时后条目被处理
CleanWindow: 2 * time.Minute, // 处理超时条目的时间范围
MaxEntrySize: 500, // 条目最大尺寸,以字节为单位
HardMaxCacheSize: 0, // 设置缓存最大值,以MB为单位,超过了不在分配内存。0表示无限制分配
}
bigCache, err := bigcache.NewBigCache(config)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("初始化BigCache: %s \n", err))
}
BigCache = &Cache{
BigCache: bigCache,
}
log.Info("BigCache: 初始化完成")
}
初始化token配置,就是token验证的配置,可以配置需要忽略的请求路径
package token
var TokenCfg *TokenConfig // token配置
type TokenConfig struct {
IgnorePaths []string
}
// AddIgnorePath 增加token不校验路径
func (config *TokenConfig) AddIgnorePath(ignorePath string) *TokenConfig {
config.IgnorePaths = append(config.IgnorePaths, ignorePath)
return config
}
// TokenIgnorePath token不校验路径集
func (config *TokenConfig) TokenIgnorePath() {
config.AddIgnorePath("/token/*").
AddIgnorePath("/ping").AddIgnorePath("/user/*")
}
// InitTokenConfig 初始化token配置
func InitTokenConfig() {
TokenCfg = &TokenConfig{
IgnorePaths: make([]string, 0),
}
TokenCfg.TokenIgnorePath()
}
初始化gin,拿到router。可以看到这里拿到router之后use了四个中间件,日志中间件、全局异常处理中间件,token验证中间件,跨域处理中间件。跨域中间件是用的gin相关库里面的,token验证中间件在后面。然后在RunGin方法中用指定的端口启动了gin
package gin
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-contrib/cors"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
logger "github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
"github.com/spf13/viper"
"go_web_test/config/log"
"go_web_test/config/token"
err "go_web_test/exception"
)
// InitGinConfig 初始化Gin
func InitGinConfig() *gin.Engine {
logger.Info("初始化 gin……")
gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)
router := gin.Default()
// 入口日志打印
router.Use(log.LoggerAccess)
// 统一异常处理
router.Use(err.ErrHandle)
// 跨域处理
router.Use(cors.Default())
// token校验
router.Use(token.TokenVerify)
// 健康检测
router.GET("/ping", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"message": "pong",
})
})
logger.Info("Gin: 初始化完成……")
return router
}
// RunGin 启动Gin
func RunGin(router *gin.Engine) {
port := viper.GetString("server.port")
logger.Info(fmt.Sprintf("Service started on port(s): %s", port))
_ = router.Run(":" + port)
}
token验证的中间件,先判断一下当前请求路径需不需要验证,验证失败就抛出一个token验证失败的异常,这个时候全局异常处理里面就可以捕获到处理并返回错误信息
package token
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"go_web_test/biz/dto"
"go_web_test/config/cache"
"strings"
)
func TokenVerify(c *gin.Context) {
request := c.Request
// 过滤不用token校验的url
if noTokenVerify(TokenCfg.IgnorePaths, request.RequestURI) {
return
}
// 获取token
tokenStr := request.Header.Get("token")
if len(tokenStr) == 0 {
panic(NewTokenError(dto.Unauthorized, dto.GetResultMsg(dto.Unauthorized)))
}
if _, err := cache.BigCache.Get(tokenStr); err != nil {
panic(NewTokenError(dto.Unauthorized, dto.GetResultMsg(dto.Unauthorized)))
}
c.Next()
}
// noTokenVerify 判断url是否不需要token校验
func noTokenVerify(ignorePaths []string, path string) bool {
// 查询缓存
if noVerify, err := cache.BigCache.Get(path); err == nil {
return noVerify.(bool)
}
// 匹配url
for _, ignorePath := range ignorePaths {
// 路径尾通配符*过滤
if strings.LastIndex(ignorePath, "*") == len(ignorePath)-1 {
ignorePath = strings.Split(ignorePath, "*")[0]
if endIndex := strings.LastIndex(path, "/"); strings.Compare(path[0:endIndex+1], ignorePath) == 0 {
// 添加缓存
cache.BigCache.Set(path, true)
return true
}
// 无通配符*过滤
} else if strings.Compare(path, ignorePath) == 0 {
// 添加缓存
cache.BigCache.Set(path, true)
return true
}
}
return false
}
全局异常
package exception
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
log "github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
"go_web_test/biz/dto"
"go_web_test/config/token"
"net/http"
"runtime/debug"
)
// ErrHandle 统一异常处理
func ErrHandle(c *gin.Context) {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
apiErr, isApiErr := r.(*ApiError)
tokenErr, isTokenErr := r.(*token.TokenError)
if isApiErr {
// 打印错误堆栈信息
log.WithField("ErrMsg", apiErr.Error()).Error("PanicHandler handled apiError: ")
// 封装通用json返回
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, apiErr)
} else if isTokenErr {
// 打印错误堆栈信息
log.WithField("ErrMsg", tokenErr.Error()).Error("PanicHandler handled tokenError: ")
// 封装通用json返回
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, tokenErr)
} else {
// 打印错误堆栈信息
err := r.(error)
log.WithField("ErrMsg", err.Error()).Error("PanicHandler handled ordinaryError: ")
debug.PrintStack()
// 封装通用json返回
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, NewApiError(dto.InternalServerError, dto.GetResultMsg(dto.InternalServerError)))
}
c.Abort()
}
}()
c.Next()
}
最后就是注册api了,每写一个controller就要在这里注册一下,然后启动gin。
说了一堆配置相关的,来看一下业务的三层结构吧
controller层
使用struct定义一个UserHandler,在注册api的方法中给service赋值,这里可以看到service也是有一个接口和实现类的
package controller
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"go_web_test/biz/dto"
"go_web_test/biz/service"
"net/http"
"strconv"
)
type UserHandler struct {
userService service.UserService
}
func UserApi(router *gin.Engine) {
userHandler := UserHandler{
userService: &service.UserServiceImpl{},
}
userGroup := router.Group("user/")
{
userGroup.GET("/:id", userHandler.user)
}
}
// 根据ID查询用户
func (userHandler UserHandler) user(c *gin.Context) {
userIdStr := c.Param("id")
userId, _ := strconv.Atoi(userIdStr)
user := userHandler.userService.User(userId)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, dto.Ok(user))
}
service层
先定义一个接口,然后一个实现,go语言中的实现没有关键字,遵循duck-typeing的原则,只要像,那就是它的实现。在idea中是会有左边的跳转上下箭头的。同样在service里面也有一个dao层的引用
package service
import "go_web_test/biz/dao"
type UserService interface {
User(userId int) *dao.User
}
type UserServiceImpl struct {
}
func (UserServiceImpl) User(userId int) *dao.User {
user := &dao.User{}
user.SelectById(userId)
return user
}
dao层
这个里面有对应数据库表的结构以及这个结构所属的方法
package dao
import "go_web_test/config/db"
type User struct {
Id int `json:"id" gorm:"primary_key"`
Name string `json:"name" gorm:"size:50"`
}
func (user *User) SelectById(userId int) {
db.DB.First(&user, userId)
}
有一点要注意的是,这里在设计的时候要避免循环依赖问题,毕竟没有spring来帮我们解决循环依赖了。其实循环依赖这种问题本来就是要在设计上避免,而不是代码中去解决它吧
