Flask-RESTful(venv) D:\python-code\flask-vuejs-madblog\back-end> pip install flask-restful (venv) D:\python-code\flask-vuejs-madblog\back-end> pip freeze > requirements.txt2. 初始化插件
back-end/app/api_v2back-end/app/api_v2/__init__.pyback-end/app/api_v2/app.pyfrom flask import Blueprint
from flask_restful import Api
# Blueprint
bp = Blueprint('api_v2', __name__)
# Init Flask-RESTful
api = Api(bp)
蓝图(Blubprint)flask_restful.Api()bpback-end/app/__init__.py...
from app.api_v2.app import bp as api_v2_bp
...
def configure_blueprints(app):
# 注册 blueprint
app.register_blueprint(api_bp, url_prefix='/api')
app.register_blueprint(api_v2_bp, url_prefix='/api/v2')
...
Flask-RESTful/api/v2http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/v2/pingFlask-RESTful资源(Resources)Flask MethodViewflask_restful.Resourceclass Resource(MethodView):
"""
Represents an abstract RESTful resource. Concrete resources should
extend from this class and expose methods for each supported HTTP
method. If a resource is invoked with an unsupported HTTP method,
the API will return a response with status 405 Method Not Allowed.
Otherwise the appropriate method is called and passed all arguments
from the url rule used when adding the resource to an Api instance. See
:meth:`~flask_restful.Api.add_resource` for details.
"""
representations = None
method_decorators = []
def dispatch_request(self, *args, **kwargs):
# Taken from flask
#noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
meth = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), None)
if meth is None and request.method == 'HEAD':
meth = getattr(self, 'get', None)
assert meth is not None, 'Unimplemented method %r' % request.method
if isinstance(self.method_decorators, Mapping):
decorators = self.method_decorators.get(request.method.lower(), [])
else:
decorators = self.method_decorators
for decorator in decorators:
meth = decorator(meth)
resp = meth(*args, **kwargs)
if isinstance(resp, ResponseBase): # There may be a better way to test
return resp
representations = self.representations or OrderedDict()
#noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
mediatype = request.accept_mimetypes.best_match(representations, default=None)
if mediatype in representations:
data, code, headers = unpack(resp)
resp = representations[mediatype](data, code, headers)
resp.headers['Content-Type'] = mediatype
return resp
return resp
资源back-end/app/api_v2/resources/back-end/app/api_v2/resources/ping.pyfrom flask_restful import Resource
class Ping(Resource):
def get(self):
return {'message': 'Pong!'}
back-end/app/api_v2/resources/back-end/app/api_v2/resources/__init__.pyback-end/app/api_v2/urls.pyfrom app.api_v2.app import api from app.api_v2.resources.ping import Ping # 统一注册路由 api.add_resource(Ping, '/', '/ping')
Endpoints:
add_resource()endpointflask.url_for()1. 单个 URL api.add_resource(Foo, '/foo') 2. 多个 URL api.add_resource(Foo, '/foo1', '/foo2') 3. 同时指定 endpoint,默认是资源名的小写,比如 Foo 资源的 endpoint=foo api.add_resource(Foo, '/foo1', '/foo2', endpoint='foo_ep')
back-end/app/api_v2/app.pyurls.pyfrom flask import Blueprint
from flask_restful import Api
# Blueprint
bp = Blueprint('api_v2', __name__)
# Init Flask-RESTful
api = Api(bp)
# 统一注册路由
from app.api_v2 import urls
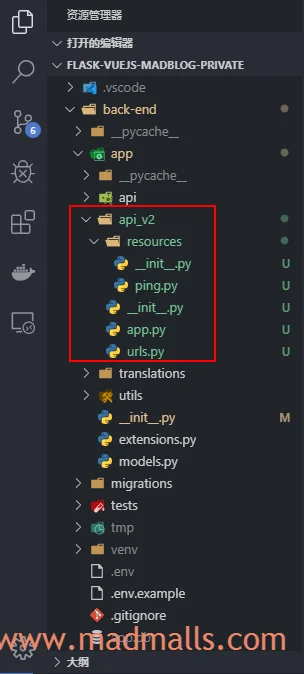
最终的目录结构如下:
此时,启动 Flask 应用:
(venv) D:\python-code\flask-vuejs-madblog\back-end> flask run * Serving Flask app "madblog.py" (lazy loading) * Environment: production WARNING: Do not use the development server in a production environment. Use a production WSGI server instead. * Debug mode: on * Restarting with stat * Debugger is active! * Debugger PIN: 968-712-707 * Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Postmanhttp://127.0.0.1:5000/api/v2http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/v2/pingPong!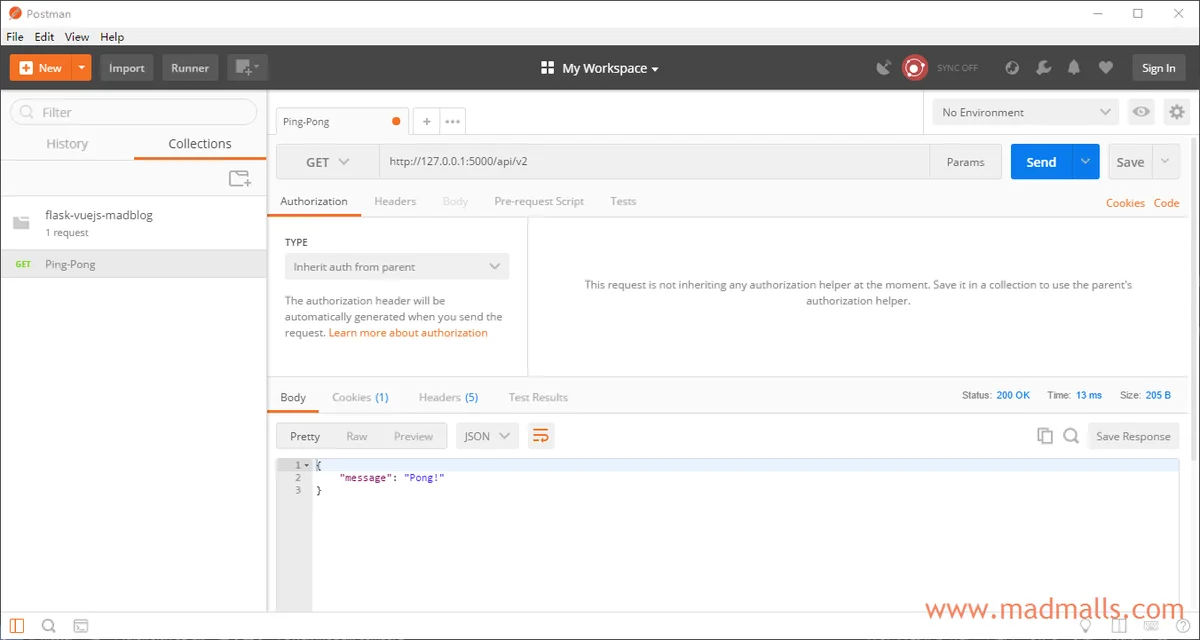

POST405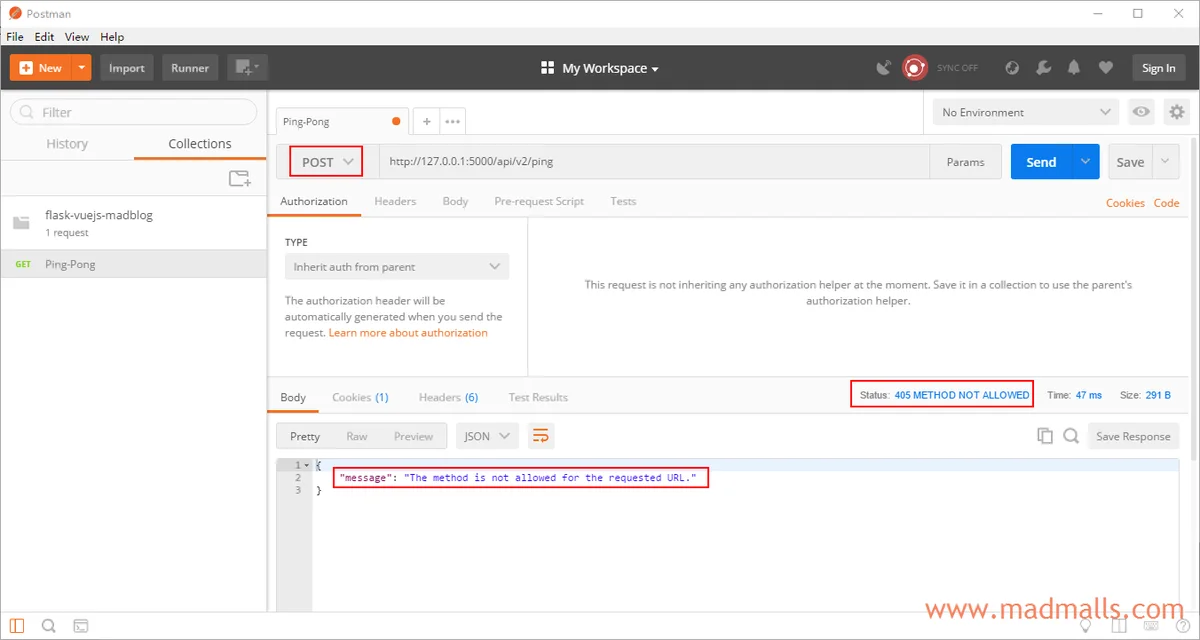
GET/api/v2/usersPOST/api/v2/usersGET/api/v2/users/PUT/api/v2/users/DELETE/api/v2/users/ URLhttp://127.0.0.1:5000/api/v2/usershttp://127.0.0.1:5000/api/v2/users/Flask-RESTfulResourceback-end/app/api_v2/resources/users.py from flask_restful import Resource
# User: shows a single user item and lets you delete a user item
class UserAPI(Resource):
def get(self, id):
pass
def delete(self, id):
pass
def put(self, id):
pass
# UserList: shows a list of all users, and lets you POST to add new user
class UserListAPI(Resource):
def get(self):
pass
def post(self):
pass
back-end/app/api_v2/urls.py... from app.api_v2.resources.users import User, UserList ... api.add_resource(UserListAPI, '/users', endpoint='users') api.add_resource(UserAPI, '/users/<int:id>', endpoint='user')
现在只需要考虑各 HTTP 操作方法的具体实现即可
4.1 注册新用户
from flask import url_for
from flask_restful import Resource, reqparse, inputs
from app.extensions import db
from app.models import User
# UserList: shows a list of all users, and lets you POST to add new user
class UserListAPI(Resource):
def __init__(self):
self.parser = reqparse.RequestParser(bundle_errors=True)
self.parser.add_argument('username', type=str, required=True, help='Please provide a valid username.', location='json')
self.parser.add_argument('email', type=inputs.regex('^(([^<>()\[\]\\.,;:\s@"]+(\.[^<>()\[\]\\.,;:\s@"]+)*)|(".+"))@((\[[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\])|(([a-zA-Z\-0-9]+\.)+[a-zA-Z]{2,}))$'), required=True, help='Please provide a valid email address.', location='json')
self.parser.add_argument('password', type=str, required=True, help='Please provide a valid password.', location='json')
super(UserListAPI,
