main()在文件头部有一段对 的介绍,我们先了解一下。
goroutinesGMmachineP Go code MP Go code再往下会发现一段注释说明
// src/runtime/proc.go // The bootstrap sequence is: // // call osinit // call schedinit // make & queue new G // call runtime·mstart // // The new G calls runtime·main.
m0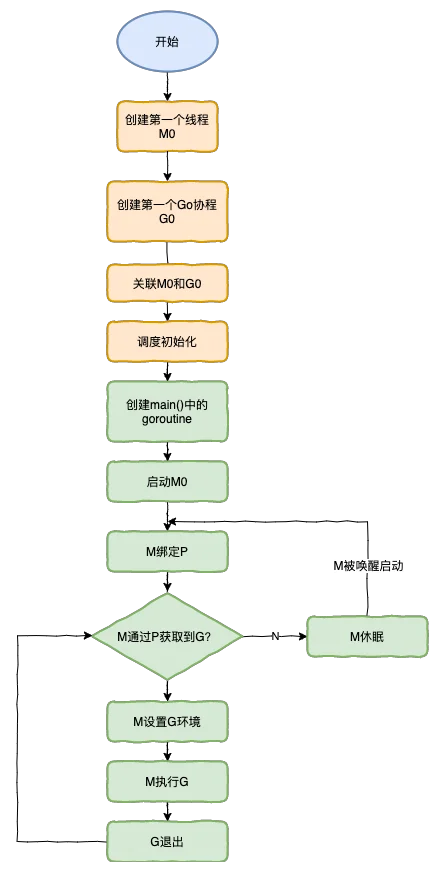
M00Mosinit
runtime.osinit() os_linux.goosinitfunc osinit() {
ncpu = getproccount()
physHugePageSize = getHugePageSize()
osArchInit()
}
CPU数量页大小操作系统初始化schedinit
调度器初始化, 调用的函数为。
func schedinit() {
lockInit(&sched.lock, lockRankSched)
lockInit(&sched.sysmonlock, lockRankSysmon)
lockInit(&sched.deferlock, lockRankDefer)
lockInit(&sched.sudoglock, lockRankSudog)
lockInit(&deadlock, lockRankDeadlock)
lockInit(&paniclk, lockRankPanic)
lockInit(&allglock, lockRankAllg)
lockInit(&allpLock, lockRankAllp)
lockInit(&reflectOffs.lock, lockRankReflectOffs)
lockInit(&finlock, lockRankFin)
lockInit(&trace.bufLock, lockRankTraceBuf)
lockInit(&trace.stringsLock, lockRankTraceStrings)
lockInit(&trace.lock, lockRankTrace)
lockInit(&cpuprof.lock, lockRankCpuprof)
lockInit(&trace.stackTab.lock, lockRankTraceStackTab)
...
}
全是与锁有关的函数,前四个是和调度器相关,接着两个与panic和deadlock相关。
lockInit(&allglock, lockRankAllg) lockInit(&allpLock, lockRankAllp) lockInit(&cpuprof.lock, lockRankCpuprof) func schedinit() {
...
// raceinit must be the first call to race detector.
// In particular, it must be done before mallocinit below calls racemapshadow.
_g_ := getg()
if raceenabled {
_g_.racectx, raceprocctx0 = raceinit()
}
sched.maxmcount = 10000
...
}
raceinit()m10000func schedinit() {
...
tracebackinit()
moduledataverify()
stackinit()
mallocinit()
fastrandinit() // must run before mcommoninit
mcommoninit(_g_.m, -1)
cpuinit() // must run before alginit
alginit() // maps must not be used before this call
modulesinit() // provides activeModules
typelinksinit() // uses maps, activeModules
itabsinit() // uses activeModules
...
}
stackinit() mallocinit()mcommoninit()cpuinit()alginit()typelinksinit()modulesinit()itabsinit()func schedinit() {
...
sigsave(&_g_.m.sigmask)
initSigmask = _g_.m.sigmask
goargs()
goenvs()
parsedebugvars()
gcinit()
...
}
gcinit()func schedinit() {
...
sched.lastpoll = uint64(nanotime())
procs := ncpu
if n, ok := atoi32(gogetenv("GOMAXPROCS")); ok && n > 0 {
procs = n
}
if procresize(procs) != nil {
throw("unknown runnable goroutine during bootstrap")
}
...
}
sched.lastpollprocsosinit()func schedinit() {
...
// For cgocheck > 1, we turn on the write barrier at all times
// and check all pointer writes. We can't do this until after
// procresize because the write barrier needs a P.
if debug.cgocheck > 1 {
writeBarrier.cgo = true
writeBarrier.enabled = true
for _, p := range allp {
p.wbBuf.reset()
}
}
if buildVersion == "" {
// Condition should never trigger. This code just serves
// to ensure runtime·buildVersion is kept in the resulting binary.
buildVersion = "unknown"
}
if len(modinfo) == 1 {
// Condition should never trigger. This code just serves
// to ensure runtime·modinfo is kept in the resulting binary.
modinfo = ""
}
}
cgocheck 与cgo 相关,可能会与 writeBarrier 相关,建议了解一下 writeBarrier
总结
这个函数是首个调用的函数,大部分与基本配置有关,如锁、M的最大数量为10000,CPU 个数,GC等等。
make && queue new G
newprocG// Create a new g running fn with siz bytes of arguments.
// Put it on the queue of g's waiting to run.
// The compiler turns a go statement into a call to this.
// 使用一个 siz 字节的参数创建一个 fn 的新 g,将它放在g队列里等待运行
// 编译器将 go 语句转换为对这个函数的调用
//
// The stack layout of this call is unusual: it assumes that the
// arguments to pass to fn are on the stack sequentially immediately
// after &fn. Hence, they are logically part of newproc's argument
// frame, even though they don't appear in its signature (and can't
// because their types differ between call sites).
//
// This must be nosplit because this stack layout means there are
// untyped arguments in newproc's argument frame. Stack copies won't
// be able to adjust them and stack splits won't be able to copy them.
//
//go:nosplit
func newproc(siz int32, fn *funcval) {}
mstart
调用 函数。这个函数是M的入口。函数原型:
// mstart is the entry-point for new Ms.
//
// This must not split the stack because we may not even have stack
// bounds set up yet.
//
// May run during STW (because it doesn't have a P yet), so write
// barriers are not allowed.
//
//go:nosplit
//go:nowritebarrierrec
func mstart() {}
mstartSTW写屏障//go:nosplit
//go:nowritebarrierrec
func mstart() {
// 获取一个G(当前为g0)
_g_ := getg()
// 检查当前G的边界lo是否等于0,如果等于则初始化系统栈
osStack := _g_.stack.lo == 0
if osStack {
// Initialize stack bounds from system stack.
// Cgo may have left stack size in stack.hi.
// minit may update the stack bounds.
// 从 system statck 中初始化 _g_.stack 边界
size := _g_.stack.hi
// Cgo
if size == 0 {
size = 8192 * sys.StackGuardMultiplier
}
// 初始化_g_.stack
_g_.stack.hi = uintptr(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&size)))
_g_.stack.lo = _g_.stack.hi - size + 1024
}
// Initialize stack guard so that we can start calling regular
// Go code.
// 初始化 _g_.stackguard0,以便可以运行 go code
_g_.stackguard0 = _g_.stack.lo + _StackGuard
// This is the g0, so we can also call go:systemstack
// functions, which check stackguard1.
// 这是g0,所以我们也可以调用go:systemstack 函数检查 stackguard1
_g_.stackguard1 = _g_.stackguard0
// 启动m
mstart1()
// Exit this thread.
// 退出当前线程
switch GOOS {
case "windows", "solaris", "illumos", "plan9", "darwin", "aix":
// Windows, Solaris, illumos, Darwin, AIX and Plan 9 always system-allocate
// the stack, but put it in _g_.stack before mstart,
// so the logic above hasn't set osStack yet.
osStack = true
}
// 重要函数
mexit(osStack)
}
mstart()Gfunc mstart1() {
_g_ := getg()
// 判断当前g是否为g0, 在 mstart() 函数里获取的就是g0,这里再判断一次
// g0 是m创建的第一个goroutine,与后面创建的普通goroutine不同,g0主要用来实现对普通goroutine的调度
if _g_ != _g_.m.g0 {
throw("bad runtime·mstart")
}
// Record the caller for use as the top of stack in mcall and
// for terminating the thread.
// We're never coming back to mstart1 after we call schedule,
// so other calls can reuse the current frame.
// 记录caller用在mcall中栈顶和终止线程
// 在调用 schedule 后,将不会再返回到 mstart1,所以其它调用可以复用当前 frame
// 需要关注下 minit() 函数
save(getcallerpc(), getcallersp())
asminit()
minit()
// Install signal handlers; after minit so that minit can
// prepare the thread to be able to handle the signals.
// 安装信息处理器,以便 minit 后,线程可以处理信息
// 当前g0 是 m0 ,则直接启用 m0, m0是一个全局变量
if _g_.m == &m0 {
mstartm0()
}
// 当前m0注册有初始化函数
if fn := _g_.m.mstartfn; fn != nil {
fn()
}
// 当前g0 不是 m0(上面是相等的判断),则从当前绑定的m 里获取一个准备好的P (_g_.m.nextp.ptr())并关联到当前 m 上
if _g_.m != &m0 {
acquirep(_g_.m.nextp.ptr())
_g_.m.nextp = 0
}
// 调度 重点!重点!重点!
schedule()
}
minit()执行顺序从上到下依次为:
minit()mstartm0()m0mstart1acquirep() schedule()runnable