如何在Go代码中调用C语言代码?
Go语言是通过自带的一个叫CGO的工具来支持C语言函数调用,同时我们可以用Go语言导出C动态库接口给其它语言使用。
方式一、直接在 Go 代码中写入 C 代码
检查是否开启cgo工具
go env | findstr CGOset CGO_ENABLED=1编写main.go文件
import "C"注意 C 代码和 i m p o r t " c " 语句之间不能有空行 ! \color{red}{注意C 代码和import "c" 语句之间不能有空行 !} 注意C代码和import"c"语句之间不能有空行!
package main
// #include <stdio.h>
// #include <stdlib.h>
/*
void print_fun(char *s) {
printf("print used by C language: %s\n", s);
}
*/
import "C"
func main() {
cStr := C.CString("hello world !") // golang 操作c 标准库中的CString函数
C.print_fun(cStr) // 调用C函数:print_fun 打印输出
}
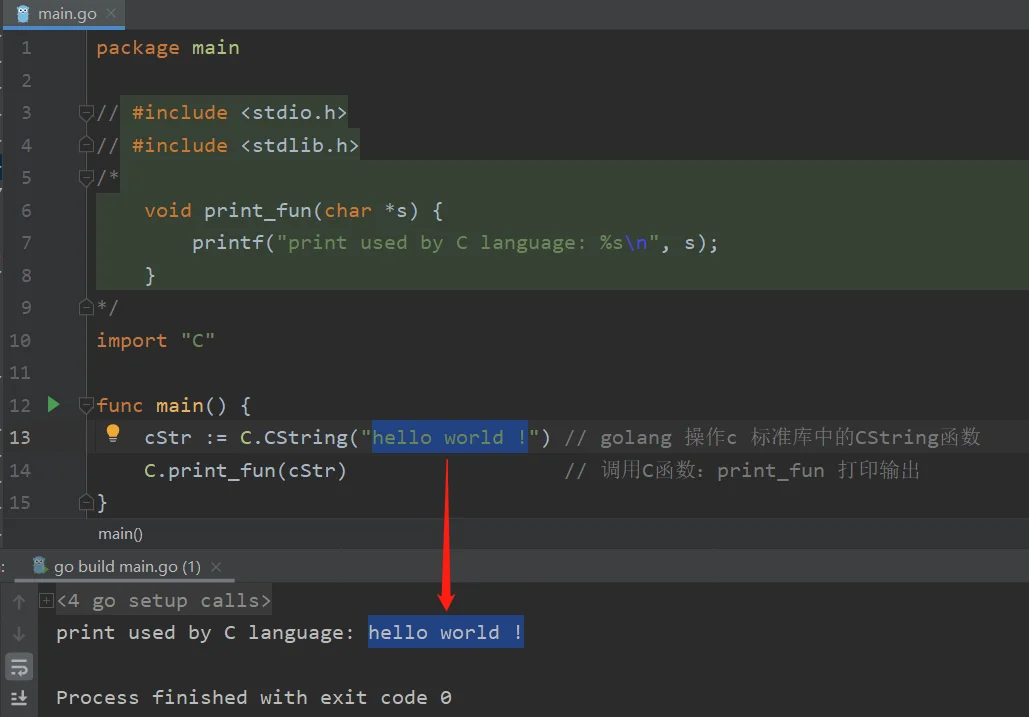
这种方式的 C 代码和 Go 代码在同一个文件中,所以大家能明显发现这种方式的代码耦合度太高,仅适用于项目简单单一的情形。
一个更合理的方式应该是 C 代码单独在一个文件。
方式二、Go 直接调用 C 文件
那么,如果已经写好一个封装好的 C 文件代码,Go 语言该如何调用呢?
此时我们需要直接写好 C 相关代码,因为 Go 代码是无法对 C 代码文件进行重写或者修改的。
以如下文件目录结构,创建相关 .h、.c、.go文件:
C语言 .h 头文件
- 编写 hello.h 头文件,示例代码如下:
#ifndef HELLO_H
#define HELLO_H
void print_fun1(char *s);
#endif
C语言 .c 源文件
编写 hello.c 源文件,示例代码如下:
#include "hello.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void print_fun1(char *s) {
printf("print used by C language: %s\n", s);
}
Go语言 .go 文件
最后编写 main.go 文件:
#cgo CFLAGS: -I xxx#cgo LDFLAGS: xxx/hello.a注意 C 代码和 i m p o r t " c " 语句之间不能有空行 ! \color{red}{注意C 代码和import "c" 语句之间不能有空行 !} 注意C代码和import"c"语句之间不能有空行!
具体示例如下:
package main
/*
#cgo CFLAGS: -I .
#cgo LDFLAGS: ./hello.a
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <hello.h>
*/
import "C"
import (
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
cStr := C.CString("hello world !") // golang 操作c 标准库中的CString函数
C.print_fun1(cStr) // 调用C函数:print_fun 打印输出
defer C.free(unsafe.Pointer(cStr)) // 因为 CSstring 这个函数没有对变量申请的空间进行内存释放
}
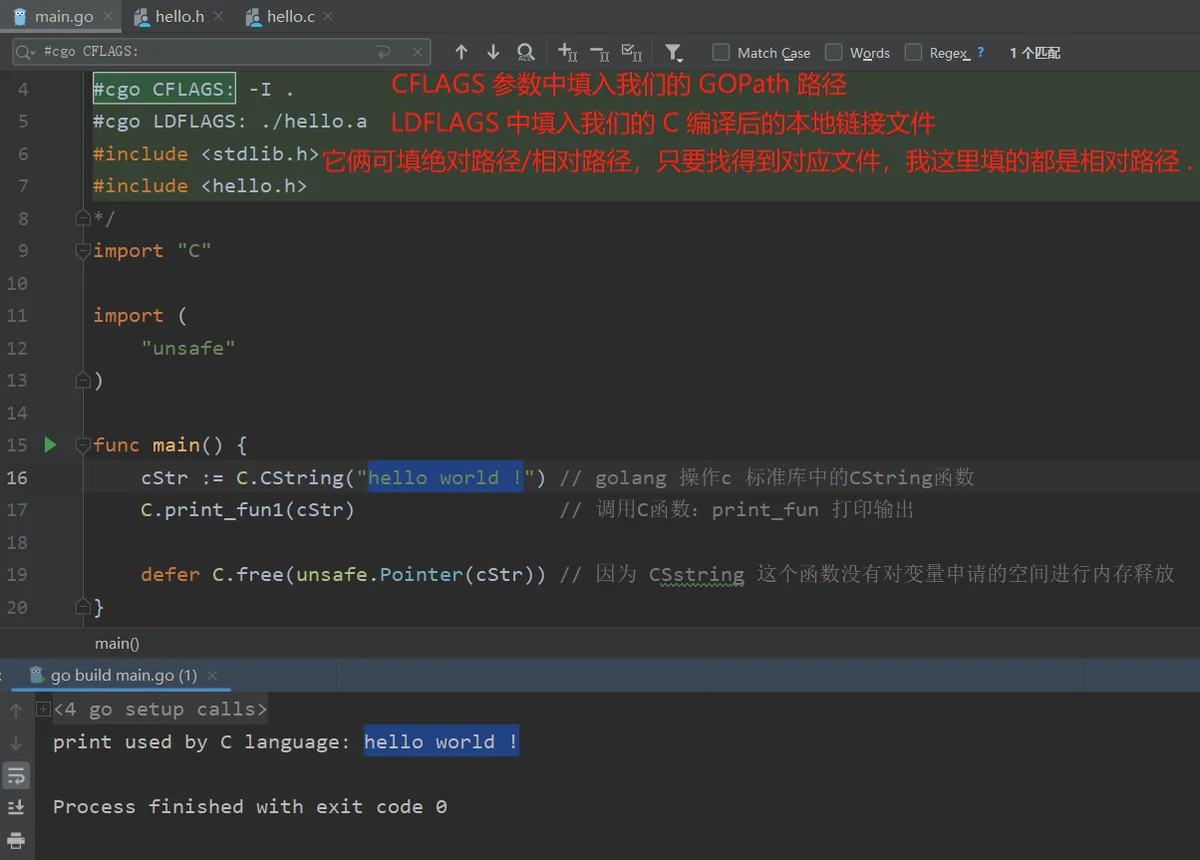
编写完以上文件后,距离可运行的程序只有一步之遥了。
编译 c 代码
$ gcc -c *.c # 生成.o文件
$ ar rs hello.a *.o # 生成.a文件
ar: creating archive hello.a
$ rm ./hello.o # 删除已不需要的.o文件,linux下为rm命令,windows下为del命令
生成.a文件需要用到 ar 命令建立或修改备存文件,可参考:Linux ar命令
执行 go 代码
go run main.go
补充
cStr := C.CString("hello world !")C.free(unsafe.Pointer(cStr))可参考:golang 操作c 标准库中的CString函数注意事项
