pprof和trace 是golang程序性能分析中经常用到的两个工具。
本文简单介绍其使用方法。
1.程序中引入pprof packagenet/http/pprof使用方法非常简单,只要import package的地方加上:
import _ "net/http/pprof"
就可以使用提供的接口包括:
"/debug/pprof/"
"/debug/pprof/cmdline"
"/debug/pprof/profile"
"/debug/pprof/symbol"
"/debug/pprof/trace"
"/debug/pprof/goroutine"
"/debug/pprof/heap"
...
例子如下所示:
/*simple.go*/
package main
import (
"log"
_ "net/http/pprof"
"net/http"
"time"
)
func main() {
go func() {
log.Println(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:6060", nil))
}()
go worker()
select{}
}
// simple worker
func worker(){
strSlice := []string{}
for {
str := "hello world "
strSlice = append(strSlice, str)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}
http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof可以看到如下的界面:
/debug/pprof/
Types of profiles available:
Count Profile
2 allocs
0 block
0 cmdline
5 goroutine
2 heap
0 mutex
0 profile
9 threadcreate
0 trace
full goroutine stack dump
Profile Descriptions:
allocs:
A sampling of all past memory allocations
block:
Stack traces that led to blocking on synchronization primitives
cmdline:
The command line invocation of the current program
goroutine:
Stack traces of all current goroutines
heap:
A sampling of memory allocations of live objects. You can specify the gc GET parameter to run GC before taking the heap sample.
mutex:
Stack traces of holders of contended mutexes
profile:
CPU profile. You can specify the duration in the seconds GET parameter. After you get the profile file, use the go tool pprof command to investigate the profile.
threadcreate:
Stack traces that led to the creation of new OS threads
trace:
A trace of execution of the current program. You can specify the duration in the seconds GET parameter. After you get the trace file, use the go tool trace command to investigate the trace.
2.1 查看当前正在执行的goroutine
127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/goroutine下载后,在命令行下执行:
go tool pprof -http=":8081" goroutine
会自动打开浏览器页面如下图所示。
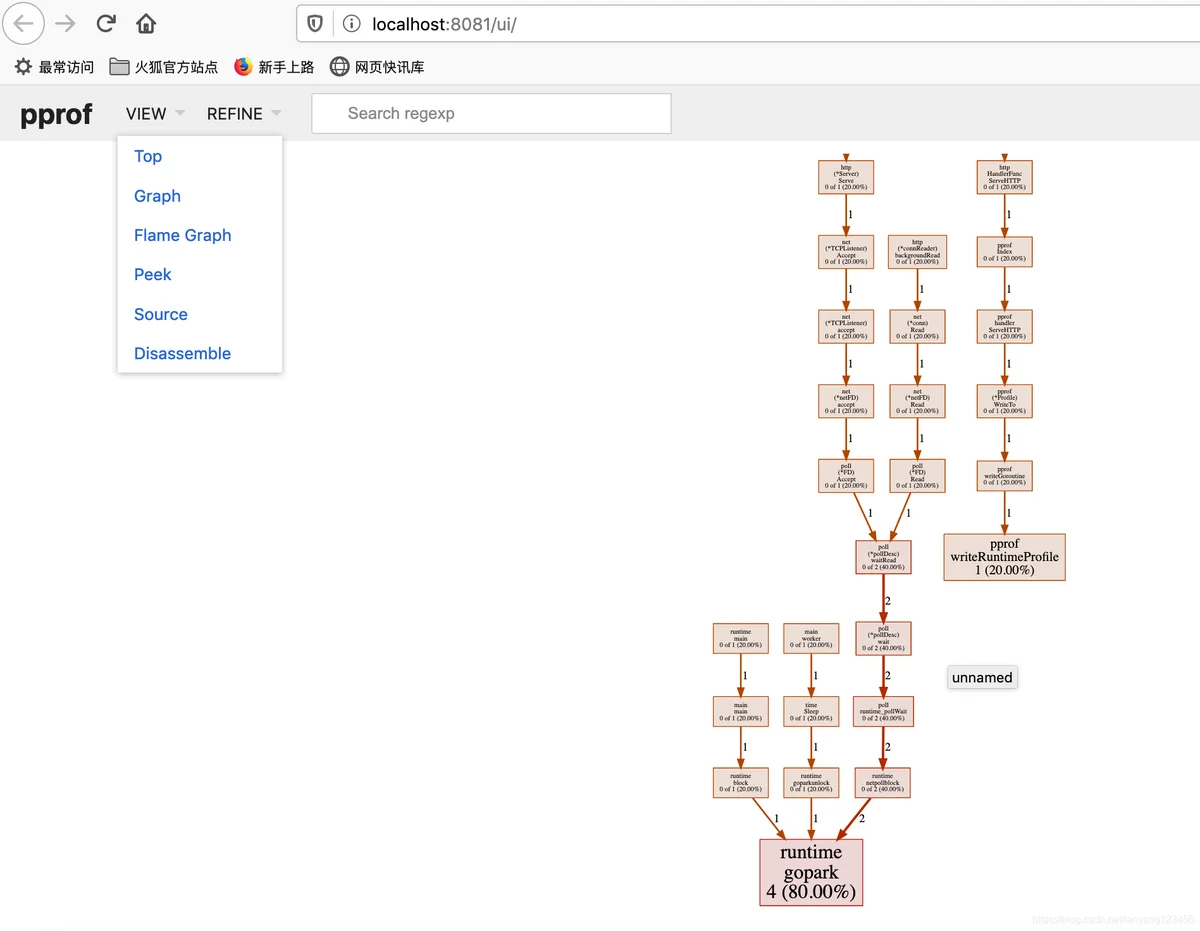
在图中可以清晰的看到goroutine的数量以及调用关系。
Top、Graph、Flame Graph2.2 查看内存占用
127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/heap下载后,在命令行下执行:
go tool pprof -http=":8081" heap
会自动打开浏览器页面如下图所示。
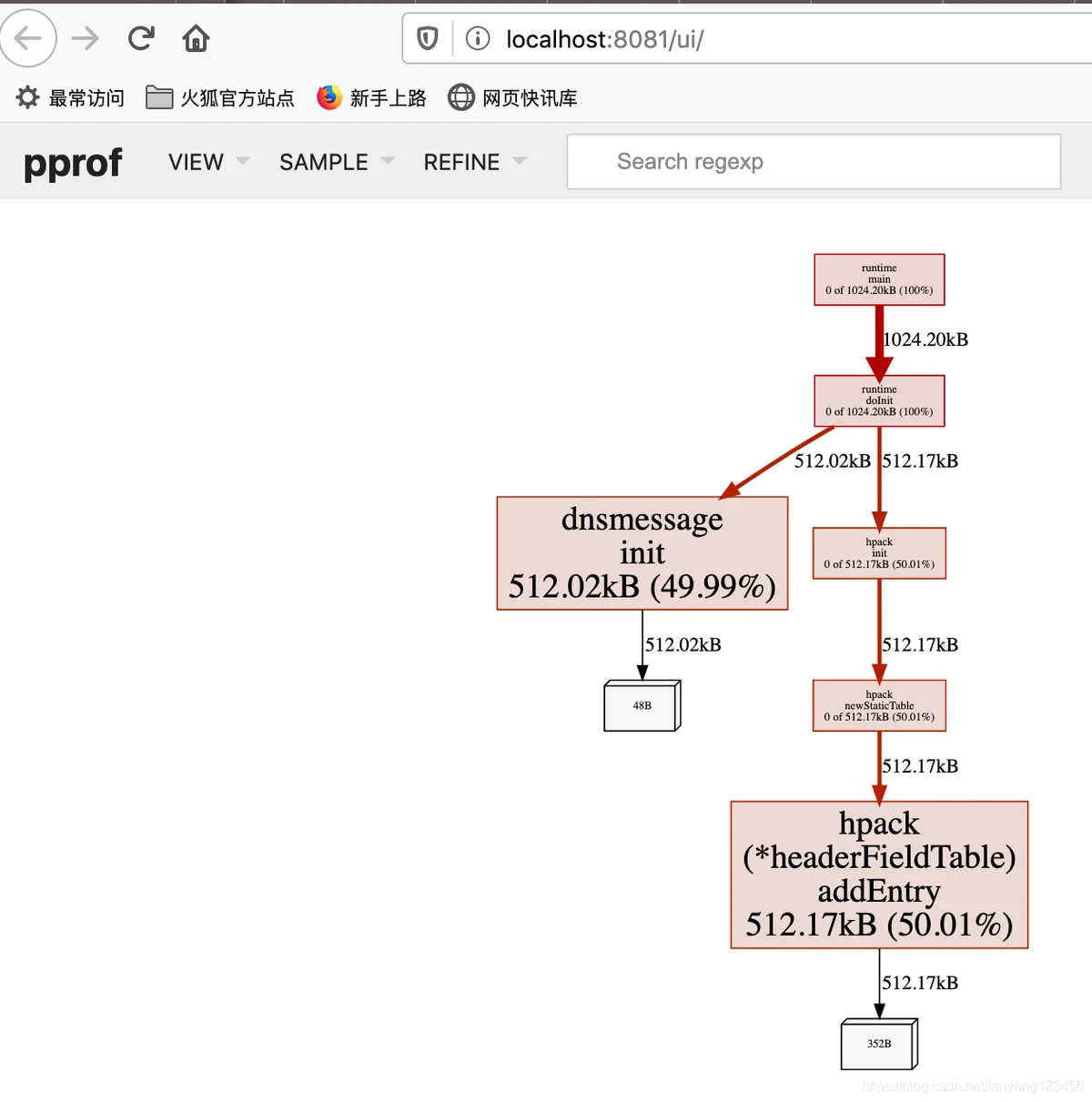
从图中可以直观的发现内存占用最多的都是哪些部分。
2.3 查看CPU使用情况
http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/profile?seconds=5会下载profile文件。
seconds下载后,在命令行下执行:
go tool pprof -http=":8081" profile
会自动打开浏览器页面如下图所示。
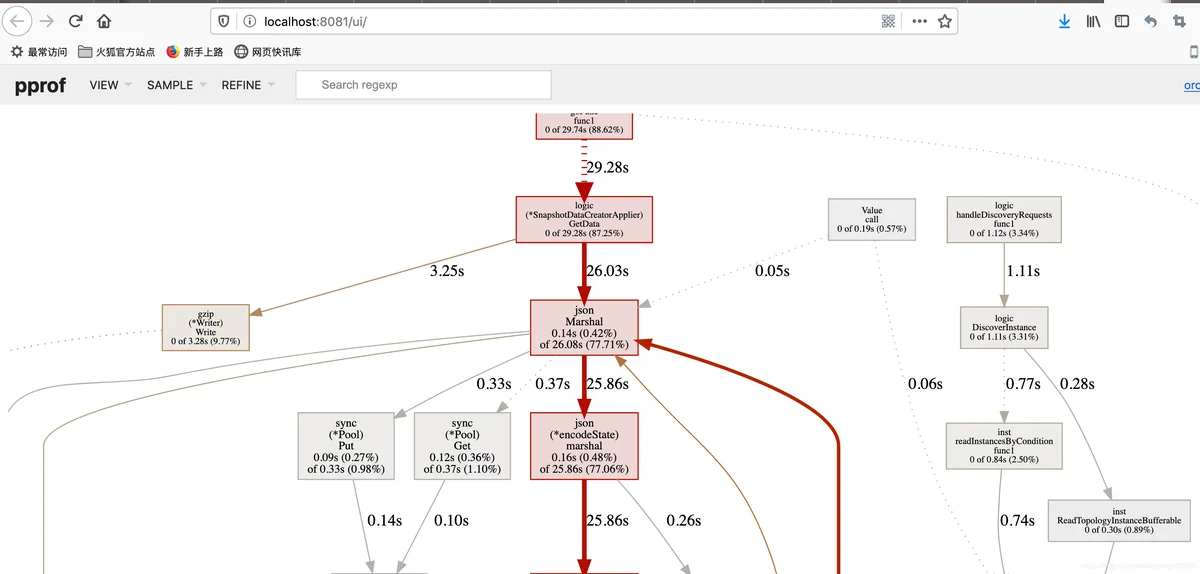
从图中可以直观的发现内存占用最多的都是哪些部分。
由于例子程序一直空闲,此处的图借用其他程序的图。:)
2.4 跟踪当前程序的执行
http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/trace?seconds=5会下载trace文件。
通过trace文件,可以查看各个goroutine执行耗时情况,包括网络等待耗时、同步耗时、GC耗时等。
go tool trace -http=":8081" trace会自动打开浏览器页面如下图所示。

点击“Goroutine analysis” 打开页面如下所示。
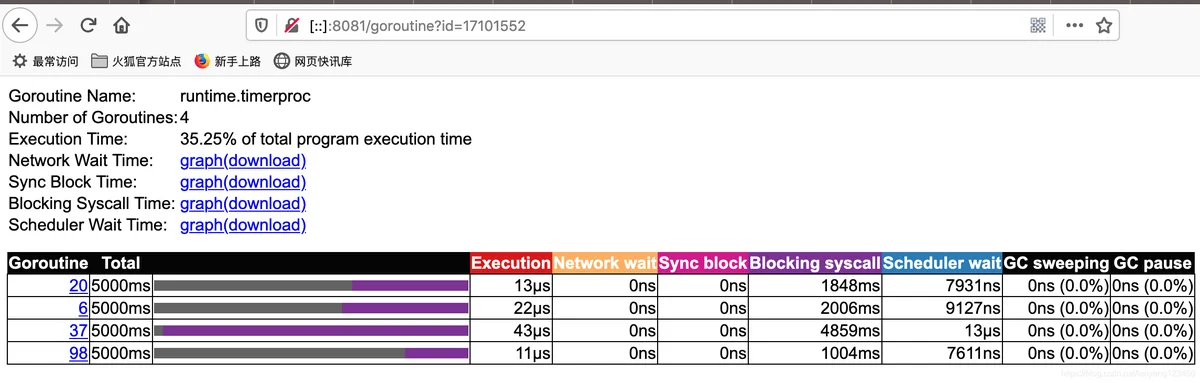
图中列出所有goroutine。

打开第一个,可以看到各阶段耗时情况表。
graph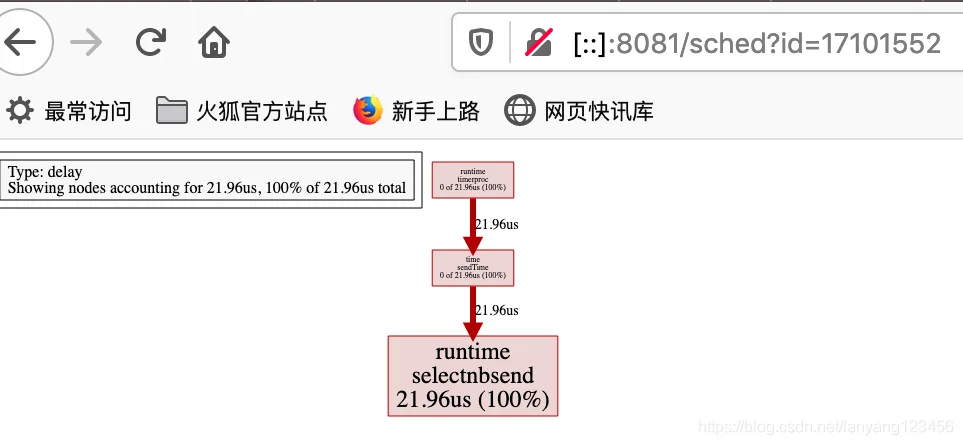
go tool trace延迟问题,是指程序执行过程被意外阻塞住。例如,被系统调用阻塞,被channel、muext阻塞, 或者调度器问题, 或者GC问题等。
并发问题,是指程序没有充分利用CPU。可能的原因包括,串行化、资源竞争等。
3.总结本文介绍了pprof和trace的使用,更多详情见链接:
golang 性能剖析pprof
